IJUP08 - Universidade do Porto
IJUP08 - Universidade do Porto
IJUP08 - Universidade do Porto
- TAGS
- universidade
- porto
- ijup.up.pt
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Fiber optic pH sensors based on CdTe quantum <strong>do</strong>ts<br />
Helena Gonçalves 1 , Conceição Men<strong>do</strong>nça 1 , Joaquim C.G. Esteves da Silva 1 ,<br />
César Maule 2 and Pedro Jorge 2<br />
1 Department of Chemistry, CIQ-UP, Faculty of Sciences, University of <strong>Porto</strong>, Portugal.<br />
2 Optoelectronics Unit of INESC <strong>Porto</strong>, Department of Physics, University of <strong>Porto</strong>, Portugal.<br />
Quantum <strong>do</strong>ts (QDs) are gaining a great scientific interest due to their tunable optical<br />
(absorption and emission of radiation) properties. Also, by modifying the surface of QDs<br />
with hydrophilic capping ligands provides stability in water. One end of these hydrophilic<br />
capping ligands contains a thio group that binds with the QDs surface, and the other, polar<br />
end contains a carboxylic group that makes them water soluble. Because the carboxylic<br />
acid group has acid-base properties the optical properties of QDs may be used as pH<br />
sensing molecular devices.<br />
In this communication the synthesis of thiglycolate capped CdTe QDs is described and<br />
their luminescence properties (excitation and emission wavelength and lifetimes) obtained<br />
as function of the reaction time, concentration and pH are presented. Moreover, the<br />
immobilization of QDs in fiber optics using sol-gel techniques is described and their use as<br />
fiber optic pH sensors assessed.<br />
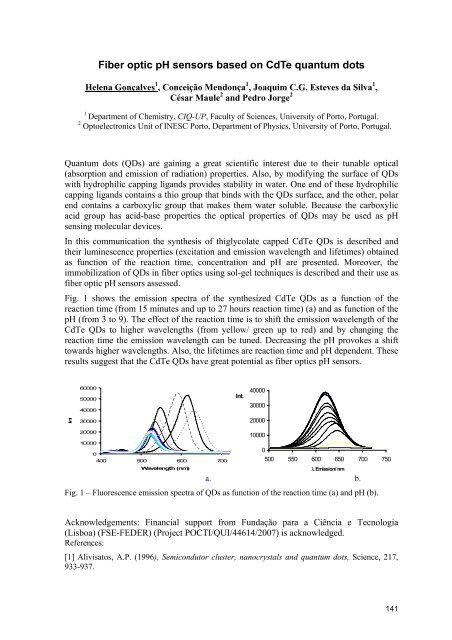
Fig. 1 shows the emission spectra of the synthesized CdTe QDs as a function of the<br />
reaction time (from 15 minutes and up to 27 hours reaction time) (a) and as function of the<br />
pH (from 3 to 9). The effect of the reaction time is to shift the emission wavelength of the<br />
CdTe QDs to higher wavelengths (from yellow/ green up to red) and by changing the<br />
reaction time the emission wavelength can be tuned. Decreasing the pH provokes a shift<br />
towards higher wavelengths. Also, the lifetimes are reaction time and pH dependent. These<br />
results suggest that the CdTe QDs have great potential as fiber optics pH sensors.<br />
Int.<br />
60000<br />
50000<br />
40000<br />
30000<br />
20000<br />
10000<br />
0<br />
400 500 600 700<br />
Wavelength (nm)<br />
a. b.<br />
Fig. 1 – Fluorescence emission spectra of QDs as function of the reaction time (a) and pH (b).<br />
Acknowledgements: Financial support from Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia<br />
(Lisboa) (FSE-FEDER) (Project POCTI/QUI/44614/2007) is acknowledged.<br />
References:<br />
[1] Alivisatos, A.P. (1996), Semicondutor cluster, nanocrystals and quantum <strong>do</strong>ts, Science, 217,<br />
933-937.<br />
Int.<br />
40000<br />
30000<br />
20000<br />
10000<br />
0<br />
500 550 600 650 700 750<br />
λ Emission/ nm<br />
141