IJUP08 - Universidade do Porto
IJUP08 - Universidade do Porto
IJUP08 - Universidade do Porto
- TAGS
- universidade
- porto
- ijup.up.pt
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Prenylated and bromoalkylated xanthones as potential antitumor<br />
agents: synthesis and biological activities<br />
A. Paiva 1,3 , E. Sousa 1,3 , M. Pinto 1,3 , A. Camões 2,3 , N. Nazareth 2,3 and M. S. J.<br />
Nascimento 2,3<br />
1 Department of Organic Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of <strong>Porto</strong>, Portugal.<br />
2 Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of <strong>Porto</strong>, Portugal.<br />
3 Research Centre of Organic Chemistry, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of the University of<br />
<strong>Porto</strong> (CEQOFFUP), Faculty of Pharmacy, University of <strong>Porto</strong>, Portugal.<br />
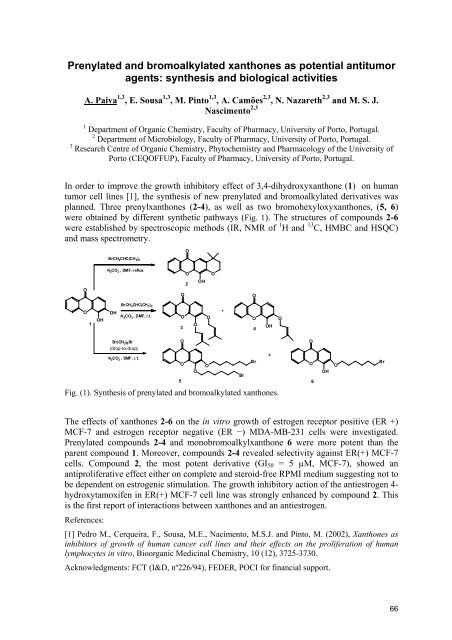
In order to improve the growth inhibitory effect of 3,4-dihydroxyxanthone (1) on human<br />
tumor cell lines [1], the synthesis of new prenylated and bromoalkylated derivatives was<br />
planned. Three prenylxanthones (2-4), as well as two bromohexyloxyxanthones, (5, 6)<br />
were obtained by different synthetic pathways (Fig. 1). The structures of compounds 2-6<br />
were established by spectroscopic methods (IR, NMR of 1 H and 13 C, HMBC and HSQC)<br />
and mass spectrometry.<br />
O<br />
O<br />
1<br />
OH<br />
BrCH 2 CHC(CH 3 ) 2<br />
K 2CO 3 ,DMF,reflux<br />
OH<br />
Br CH 2 CHC(CH 3 ) 2<br />
K 2 CO 3 ,DMF,r.t.<br />
Br(CH 2) 6Br<br />
(drop-to-drop)<br />
K 2 CO 3 ,DMF,r.t.<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
2<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
+<br />
O O<br />
O<br />
3<br />
O<br />
4<br />
Fig. (1). Synthesis of prenylated and bromoalkylated xanthones.<br />
5<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
The effects of xanthones 2-6 on the in vitro growth of estrogen receptor positive (ER +)<br />
MCF-7 and estrogen receptor negative (ER −) MDA-MB-231 cells were investigated.<br />
Prenylated compounds 2-4 and monobromoalkylxanthone 6 were more potent than the<br />
parent compound 1. Moreover, compounds 2-4 revealed selectivity against ER(+) MCF-7<br />
cells. Compound 2, the most potent derivative (GI50 = 5 µM, MCF-7), showed an<br />
antiproliferative effect either on complete and steroid-free RPMI medium suggesting not to<br />
be dependent on estrogenic stimulation. The growth inhibitory action of the antiestrogen 4hydroxytamoxifen<br />
in ER(+) MCF-7 cell line was strongly enhanced by compound 2. This<br />
is the first report of interactions between xanthones and an antiestrogen.<br />
References:<br />
[1] Pedro M., Cerqueira, F., Sousa, M.E., Nacimento, M.S.J. and Pinto, M. (2002), Xanthones as<br />
inhibitors of growth of human cancer cell lines and their effects on the proliferation of human<br />
lymphocytes in vitro, Bioorganic Medicinal Chemistry, 10 (12), 3725-3730.<br />
Acknowledgments: FCT (I&D, nº226/94), FEDER, POCI for financial support.<br />
Br<br />
O<br />
Br<br />
OH<br />
+<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
6<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
Br<br />
66