Transformada de Fourier
Transformada de Fourier
Transformada de Fourier
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
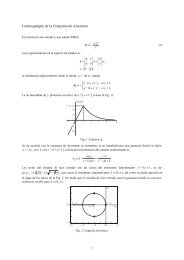
2.3. La transformada <strong>de</strong> <strong>Fourier</strong> 95Fig. 2.18. <strong>Transformada</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>Fourier</strong> <strong>de</strong> un pulso.CONDICIÓN 1. Si x (t) es absolutamente integrable,Z ∞−∞|x (t)| dt < ∞ (2.43)existe la transformada <strong>de</strong> <strong>Fourier</strong> X ( f ) existe, y está dada por la ecuación (2.36). Demanera similar, si X( f ) es absolutamente integrable,Z ∞−∞|x ( f )| d f < ∞,existe la transformada <strong>de</strong> <strong>Fourier</strong> inversa dada por la ecuación (2.37).Esta condición ya fue comentada en la Sección 2.3.2, ecuación (2.36).EJEMPLO 2.10. <strong>Transformada</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>Fourier</strong> <strong>de</strong> un pulsoEl pulso <strong>de</strong> la Fig. 2.18 <strong>de</strong>finido como8A, |t| < τ/2,>:0, |t| > τ/2.verifica la Condición 1 [ecuación (2.43)]. Por lo tanto, su transformada <strong>de</strong> <strong>Fourier</strong> existe y estádada porX ( f ) == AZ τ/2−τ/2Z τ/2−τ/2Ae −j2π f t dtZ τ/2cos (2π f t) dt − jALa segunda integral es cero porque el integrando es impar. Entonces,X ( f ) =A τ/22π f sen (2π f t)−τ/2sen (2π f t) dt.−τ/2| {z }=0sen (πτ f )= Aτ = Aτ sinc (τ f ) . (2.44)πτ fNuevamente, como en el Ejemplo 2.5, los términos que pue<strong>de</strong>n cancelarse se mantienen para enfatizarla característica sen(ax)/ax <strong>de</strong> la transformada <strong>de</strong> <strong>Fourier</strong> <strong>de</strong> un pulso (Fig. 2.18).Procesamiento Digital <strong>de</strong> Señales U.N.S. 2011