Workshopband als PDF - Mpc.belwue.de
Workshopband als PDF - Mpc.belwue.de
Workshopband als PDF - Mpc.belwue.de
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
MPC-WORKSHOP FEBRUAR 2013<br />
Headless Android Systems for<br />
Industrial Automation and Control<br />
Aneeque Hassan, Axel Sikora, Dominique-Stephan Kunz, David Eberlein<br />
Abstract—Android is an operating system which<br />
was <strong>de</strong>veloped for use in smart mobile phones and<br />
is the current lea<strong>de</strong>r in this market. A lot of efforts<br />
are being spent to make Android available to the<br />
embed<strong>de</strong>d world, as well. Many embed<strong>de</strong>d systems<br />
do not have a local GUI and are therefore called<br />
headless <strong>de</strong>vices. This paper presents the results of<br />
an analysis of the general suitability of Android in<br />
headless embed<strong>de</strong>d systems and pon<strong>de</strong>rs the advantages<br />
and disadvantages. It focuses on the<br />
hardware related issues, i.e. to what extent Android<br />
supports hardware peripher<strong>als</strong> normally<br />
used in embed<strong>de</strong>d systems.<br />
In<strong>de</strong>x Terms—Android, Accessory Development<br />
Kit (ADK), Android Open Source Project (AOSP),<br />
Asynchronous Shared Memory (Ashmem), Microcontrollers<br />
(MCUs).<br />
I. INTRODUCTION<br />
Android is an operating system for mobile <strong>de</strong>vices<br />
<strong>de</strong>veloped by the Open Handset Alliance (OHA).<br />
Android enjoys being the market lea<strong>de</strong>r in the field of<br />
smart phones with a market share of more than 70 %<br />
[1]. Android is based on the Linux kernel. So the<br />
question arises if there are any additional benefits in<br />
using Android instead of Linux for applications outsi<strong>de</strong><br />
the smart phone or tablet world, i.e. for applications<br />
from industrial, process, or building automation.<br />
The objective of this project was to discuss the suitability,<br />
i.e. the advantages and disadvantages of Android<br />
for headless systems in industrial automation. In<br />
the projected case, the anticipated end product was a<br />
system without a local user interface, but with the<br />
option to add a GUI for a certain percentage of the<br />
applications. This paper will only cover the use case<br />
that all applications are Android based and there are<br />
no Linux applications. A heterogeneous system (Android<br />
and Linux applications) would need further<br />
investigations.<br />
Aneeque Hassan, ahassan@stud.hs-offenburg.<strong>de</strong>, and Axel Sikora,<br />
axel.sikora@hs-offenburg.<strong>de</strong>, are with Hochschule Offenburg,<br />
Badstraße 24, D77652 Offenburg.<br />
Dominique-Stephan Kunz, dominique.kunz@ch.sauter-bc.com,<br />
and David Eberlein, david.eberlein@ch.sauter-bc.com, are with Fr.<br />
Sauter AG, Im Surinam 55, CH4058 Basel.<br />
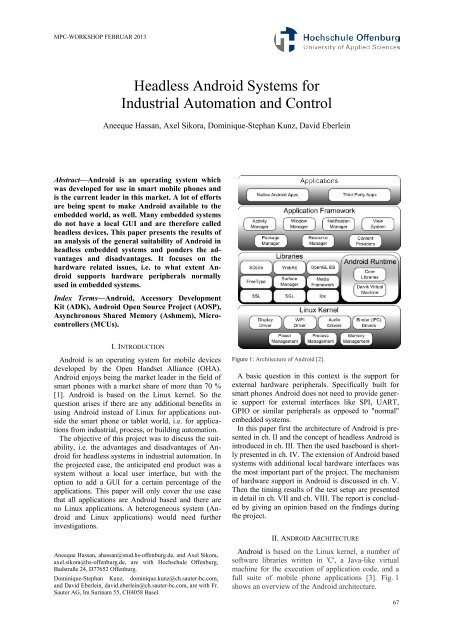
Figure 1: Architecture of Android [2].<br />
A basic question in this context is the support for<br />
external hardware peripher<strong>als</strong>. Specifically built for<br />
smart phones Android does not need to provi<strong>de</strong> generic<br />
support for external interfaces like SPI, UART,<br />
GPIO or similar peripher<strong>als</strong> as opposed to "normal"<br />
embed<strong>de</strong>d systems.<br />
In this paper first the architecture of Android is presented<br />
in ch. II and the concept of headless Android is<br />
introduced in ch. III. Then the used baseboard is shortly<br />
presented in ch. IV. The extension of Android based<br />
systems with additional local hardware interfaces was<br />
the most important part of the project. The mechanism<br />
of hardware support in Android is discussed in ch. V.<br />
Then the timing results of the test setup are presented<br />
in <strong>de</strong>tail in ch. VII and ch. VIII. The report is conclu<strong>de</strong>d<br />
by giving an opinion based on the findings during<br />
the project.<br />
II. ANDROID ARCHITECTURE<br />
Android is based on the Linux kernel, a number of<br />
software libraries written in 'C', a Java-like virtual<br />
machine for the execution of application co<strong>de</strong>, and a<br />
full suite of mobile phone applications [3]. Fig. 1<br />
shows an overview of the Android architecture.<br />
67




![[Geben Sie hier die Überschrift ein] - MPC](https://img.yumpu.com/8654082/1/188x260/geben-sie-hier-die-uberschrift-ein-mpc.jpg?quality=85)




