Program - Brookhaven National Laboratory
Program - Brookhaven National Laboratory
Program - Brookhaven National Laboratory
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
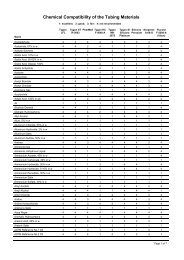
safety cases from the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project, ranging from lowenriched<br />
uranium, compound fuel, thermal spectrum ones (LEU-COMP-THERM), to mixed uraniumplutonium,<br />
metallic fuel, fast spectrum ones (MIX-MET-FAST). For fusion shielding many benchmarks<br />
were based on IAEA specifications for the Oktavian experiments (for Al, Co, Cr, Cu, LiF, Mn, Mo, Si,<br />
Ti, W, Zr), Fusion Neutronics Source in Japan (for Be, C, N, O, Fe, Pb), and Pulsed Sphere experiments<br />
at Lawrence Livermore <strong>National</strong> <strong>Laboratory</strong> (for 6 Li, 7 Li, Be, C, N, O, Mg, Al, Ti, Fe, Pb, D2O, H2O,<br />
concrete, polyethylene and teflon). The new functionality in MCNP to calculate the effective delayed<br />
neutron fraction was tested by comparison with more than thirty measurements in widely varying systems.<br />
Among these were measurements in the Tank Critical Assembly (TCA in Japan) and IPEN/MB-01 (Brazil),<br />
both with a thermal spectrum, and two cores in Masurca (France) and three cores in the Fast Critical<br />
Assembly (FCA, Japan), all with fast spectra.<br />
RE 3 11:20 AM<br />
Bayesian Statistical Analysis Applied to NAA Data for Neutron Flux Spectrum<br />
Determination<br />
Davide Chiesa, Massimiliano Clemenza, Monica Sisti<br />
Milano Bicocca University, Italy<br />
Luca Pattavina, Ezio Previtali<br />
Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN), Milano Bicocca, Italy<br />
Andrea Borio di Tigliole, Andrea Salvini<br />
Laboratorio di Energia Nucleare Applicata (LENA), Pavia University, Italy<br />
Antonio Cammi<br />
Polytechnic University of Milan, Italy<br />
In this paper, we present a statistical methodology to analyze the neutron activation data and to evaluate<br />
the neutron flux and its energetic distribution. The neutron activation analysis (NAA) technique was used<br />
to perform an absolute measurement of the neutron flux. Many samples containing a known amount of<br />
parent nuclei were irradiated at the TRIGA Mark II reactor of Pavia University (Italy) and the activation<br />
rate of a large number of isotopes was measured through gamma-ray spectroscopy with very low background<br />
HPGe detectors. In order to have a precise determination of the activation rate, the measurements were<br />
repeated on different HPGe detectors and Monte Carlo codes based on GEANT4 were developed to evaluate<br />
the gamma detection efficiency for every radioisotope of interest. Then the activation data of the different<br />
isotopes were combined to evaluate the energy spectrum of the neutron flux. For this purpose a system<br />
of linear equations, containing the group cross section data and the experimental results of the activation<br />
rate, should be solved. Since the coefficients and the parameters of this system are affected by experimental<br />
uncertainties, a rigorous statistical approach is fundamental to get the correct physics results. The Bayesian<br />
statistical approach allows to solve this kind of problems by including the uncertainties of the coefficients<br />
and the a priori information about the flux. A program for the analysis of Bayesian hierarchical models,<br />
based on Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulations, was used to describe a statistical model of the<br />
problem and to determine the flux energy group distributions. This methodology has been tested using<br />
the activation data acquired in three different irradiation facilities of the TRIGA reactor. The results<br />
presented in this paper show that this technique of analysis is promising, since it allows the evaluation of<br />
the flux energy groups and their uncertainties with great precision. The dependence of the results on the<br />
prior distribution choice and on the group cross section data was investigated, confirming the reliability of<br />
the analysis. Finally, the correlations between the different energy groups were evaluated, underlining the<br />
degree of information added by the experiment.<br />
257