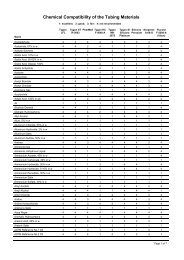
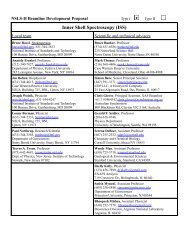
- Page 1 and 2: ND2013 2013 International Nuclear D
- Page 3 and 4: Session BF Evaluated Nuclear Data L
- Page 5 and 6: Session DD Nuclear Structure and De
- Page 7 and 8: Hale, G. n+ 12 C Cross Sections fro
- Page 9 and 10: Domula, A. New Nuclear Structure an
- Page 11 and 12: Session KC Evaluated Nuclear Data L
- Page 13 and 14: MacCormick, M. Survey and Evaluatio
- Page 15 and 16: ments. Ivanova, T. Uncertainty Asse
- Page 17 and 18: Arnold, C. Precision Velocity Measu
- Page 19 and 20: 19 Abridged Agenda Sunday March 4,
- Page 21 and 22: 21 Tuesday March 5, 2013 Time Met E
- Page 23 and 24: 23 Thursday March 7, 2013 Time Met
- Page 26 and 27: Book of Abstracts Session AA ND2013
- Page 28 and 29: multi-foil Parallel Plate Avalanche
- Page 30 and 31: A Regional Coupled-channel Dispersi
- Page 32 and 33: show the versatility of the code in
- Page 34 and 35: [h] Table 1: Comparison of all the
- Page 36 and 37: step was to determine which detecto
- Page 38 and 39: In an effort to maintain the qualit
- Page 40 and 41: Advances in Reactor Physics Linking
- Page 44 and 45: A revolutionary nuclear data system
- Page 46 and 47: done in Ref. [1]. We demonstrate th
- Page 48 and 49: CD 4 2:40 PM Development of a Syste
- Page 50 and 51: with a central cavity where small s
- Page 52 and 53: C. Arnold, E. Bond, T. Bredeweg, M.
- Page 54 and 55: DA 3 4:20 PM Characterization and P
- Page 56 and 57: detectors at the newly constructed
- Page 58 and 59: Lead and lead-based alloys are - am
- Page 60 and 61: of the setup. One option explored i
- Page 62 and 63: DC 2 4:00 PM Improved Capture Gamma
- Page 64 and 65: DC 5 5:00 PM Thermal Neutron Cross
- Page 66 and 67: M.R. Gilbert, L.W. Packer, S. Lille
- Page 68 and 69: Correlations Between Nuclear Charge
- Page 70 and 71: Community’s 7th Framework Program
- Page 72 and 73: we achieve very good separation of
- Page 74 and 75: analysis of neutron leakage spectru
- Page 76 and 77: a lower nuclear temperature than th
- Page 78 and 79: Tungsten occurs naturally in five i
- Page 80 and 81: for the combined use of integral ex
- Page 82 and 83: in XUNDL and bibliographic informat
- Page 84 and 85: former case, more realistic covaria
- Page 86 and 87: WInfried Zwermann, Kiril Velkov, An
- Page 88 and 89: LA-UR-12-23712 The ENDF/B-VII.1 [1,
- Page 90 and 91: comparison of results C/E of fissio
- Page 92 and 93:
Session GA Evaluated Nuclear Data L
- Page 94 and 95:
Session GC accelerator applications
- Page 96 and 97:
Session GD Antineutrinos Tuesday Ma
- Page 98 and 99:
M. Fallot, S. Cormon, M.Estienne, V
- Page 100 and 101:
for extraction of very rare isotope
- Page 102 and 103:
and neutron multiplicity, informati
- Page 104 and 105:
as Monte Carlo simulations, and inc
- Page 106 and 107:
on its surface. The amplification t
- Page 108 and 109:
direction was recently used at n TO
- Page 110 and 111:
were chemically separated and the 2
- Page 112 and 113:
Strontium-82 Production at ARRONAX
- Page 114 and 115:
A. Guertin, C. Duchemin, F. Haddad,
- Page 116 and 117:
expected via an (n,γ) reaction. Pr
- Page 118 and 119:
Shinsuke Nakayama, Shouhei Araki, Y
- Page 120 and 121:
specific feature of the procedure e
- Page 122 and 123:
good timing characteristics.Example
- Page 124 and 125:
Materials and Measurements, Retiese
- Page 126 and 127:
derive reliable covariances from ta
- Page 128 and 129:
Concerns about the limits of worldw
- Page 130 and 131:
Accurate and reliable nuclear data
- Page 132 and 133:
Facility (HRIBF) at Oak Ridge Natio
- Page 134 and 135:
CALIFA, a Calorimeter for the R3B/F
- Page 136 and 137:
a modified Lorentzian model (MLO) o
- Page 138 and 139:
enchmark for existing atomic mass p
- Page 140 and 141:
A significant breakthrough in our t
- Page 142 and 143:
and the neutron and proton emission
- Page 144 and 145:
horizontal plane, the measured posi
- Page 146 and 147:
The high precision of recent measur
- Page 148 and 149:
Session JF Neutron Cross Section Me
- Page 150 and 151:
Alamos National Laboratory, Los Ala
- Page 152 and 153:
During more than four decades since
- Page 154 and 155:
KC 2 2:00 PM R-matrix Analysis for
- Page 156 and 157:
new covariance contributions to the
- Page 158 and 159:
importance in nuclear technology, a
- Page 160 and 161:
source SINQ (Swiss Spallation Neutr
- Page 162 and 163:
KF 2 2:00 PM MANTRA: An Integral Re
- Page 164 and 165:
J. P. Lestone, E. F. Shores Los Ala
- Page 166 and 167:
LA 5 5:00 PM Measurements relevant
- Page 168 and 169:
elow the neutron separation energy
- Page 170 and 171:
The A = 130 Solar-System r-process
- Page 172 and 173:
espectively, and identified approxi
- Page 174 and 175:
W. Zwermann Gesellschaft fuer Anlag
- Page 176 and 177:
LC 5 5:00 PM Uncertainty Study of N
- Page 178 and 179:
solving the quantum three-body prob
- Page 180 and 181:
Session LE Evaluated Nuclear Data L
- Page 182 and 183:
LE 5 5:00 PM Method of Best Represe
- Page 184 and 185:
for 89 fission products (representi
- Page 186 and 187:
Impact of the Energy Dependent DDXS
- Page 188 and 189:
from non 1/v behavior of nuclei. Mo
- Page 190 and 191:
evaluation (including covariances)
- Page 192 and 193:
system without isotope separation.
- Page 194 and 195:
NC 3 11:20 AM Propagation of Nuclea
- Page 196 and 197:
Results of the first complete compi
- Page 198 and 199:
Arjan Koning and Dimitri Rochman Nu
- Page 200 and 201:
calculating their mathematical mome
- Page 202 and 203:
The 33 S(n,α) cross section is of
- Page 204 and 205:
OA 2 2:00 PM Event-by-Event Fission
- Page 206 and 207:
available for ENDF/B-VII. The obser
- Page 208 and 209:
egions: the resolved resonances ran
- Page 210 and 211:
y the screening potential predicted
- Page 212 and 213:
[1] Y. Kojima et al., Nucl. Instr.
- Page 214 and 215:
y the emitted neutron. The Versatil
- Page 216 and 217:
enchmarking, the excitation functio
- Page 218 and 219:
PA 1 3:30 PM Investigation of Neutr
- Page 220 and 221:
as well as for a variety of Minor A
- Page 222 and 223:
Society, Vol. 59, No. 2, August 201
- Page 224 and 225:
A. Hermanne, R. Adam-Rebeles Cyclot
- Page 226 and 227:
We measured the isomeric yield rati
- Page 228 and 229:
the trends in the experimental data
- Page 230 and 231:
However, experiments often measure
- Page 232 and 233:
Statistical description of the gamm
- Page 234 and 235:
fragments formed are highly neutron
- Page 236 and 237:
F. Farget, J. Pancin GANIL, Caen, F
- Page 238 and 239:
ZPR-6/10 cores were applied as comp
- Page 240 and 241:
each nucleus in agreement with unce
- Page 242 and 243:
atios) is performed. In relation to
- Page 244 and 245:
school in science or engineering. I
- Page 246 and 247:
programs demanding only one compuls
- Page 248 and 249:
gamma-ray spectra will be theoretic
- Page 250 and 251:
RA 3 11:20 AM A Microscopic Theory
- Page 252 and 253:
Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tenn., Novem
- Page 254 and 255:
Session RD Safeguards and Security
- Page 256 and 257:
Seeking Reproducibility in Fast Cri
- Page 258 and 259:
RE 4 11:40 AM Verification of Curre
- Page 260 and 261:
that a lot of them generally descri
- Page 262 and 263:
R. Hirschi, A. Hungerford, G. Magko
- Page 264 and 265:
- a density of levels too low for w
- Page 266 and 267:
the MONTEBURNS(1.0)-MCNP5-ORIGEN(2.
- Page 268 and 269:
The Nuclear Science References (NSR
- Page 270 and 271:
and applications using statistical
- Page 272 and 273:
Shielding objects are assembled fro
- Page 274 and 275:
The knowledge of neutron-induced re
- Page 276 and 277:
thus for the second time after the
- Page 278 and 279:
the global children health and cons
- Page 280 and 281:
Lawrence Livermore National Laborat
- Page 282 and 283:
The Russian Nuclear Data Library fo
- Page 284 and 285:
OECD Nuclear Energy Agency consider
- Page 286 and 287:
For experimental determination of t
- Page 288 and 289:
The European Activation SYstem has
- Page 290 and 291:
Neutron capture measurements of dys
- Page 292 and 293:
[1] H. Penttilä, P. Karvonen, T. E
- Page 294 and 295:
Measurement of Activation Cross Sec
- Page 296 and 297:
PR 66 Processing and Validation of
- Page 298 and 299:
law of the temperature ratio (RT =
- Page 300 and 301:
PR 74 Resonance Analysis of the 233
- Page 302 and 303:
Study of Various Potentials in Heav
- Page 304 and 305:
experimental data and for the produ
- Page 306 and 307:
fuel cycle impose tight requirement
- Page 308 and 309:
they do not satisfy (for example, b
- Page 310 and 311:
Differential Cross Sections for the
- Page 312 and 313:
extends the previous evaluation and
- Page 314 and 315:
various benchmark tests. The mainly
- Page 316 and 317:
PR 104 Evaluations for n+ 54,56,57,
- Page 318 and 319:
PR 109 Recent LAQGSM Developments a
- Page 320 and 321:
PR 113 Modelling of Spallation Sour
- Page 322 and 323:
Jagiellonian University, Reymonta 4
- Page 324 and 325:
PR 120 Coupled-Channel Models of Di
- Page 326 and 327:
PR 124 Nuclear Data Evaluation and
- Page 328 and 329:
physicist. - There is no perfect se
- Page 330 and 331:
Manturov, M.N. Nikolaev, A.M. Tsibo
- Page 332 and 333:
Vasiliev, W. Wieselquist and H. Fer
- Page 334 and 335:
Author Index 1, Vojtěch Rypar, PR
- Page 336 and 337:
HF 5, KD 4, LA 3, LA 6, LA 7, LA 8,
- Page 338 and 339:
Dunn, M. E., BF 4, RC 3 Dupont, Emm
- Page 340 and 341:
Gulliford, Jim, CE 1 Gunsing, Frank
- Page 342 and 343:
Kahl, David, HD 7 Kahler, A. C., CA
- Page 344 and 345:
Lehaut, G., PD 6 Leinweber, Greg, L
- Page 346 and 347:
Munkhsaikhan, J., HC 7 Mura, Luis F
- Page 348 and 349:
Prael, Richard E., PE 5 Praena, Jav
- Page 350 and 351:
Sheets, S., CF 2 Shen, Qingbiao, PC
- Page 352 and 353:
Typel, S., JA 3 Tyutyunnikov, S., L