Geologic Studies in Alaska by the U.S. Geological Survey, 1992
Geologic Studies in Alaska by the U.S. Geological Survey, 1992
Geologic Studies in Alaska by the U.S. Geological Survey, 1992
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
RUBIDIUM-STRONTIUM ISOTOPIC SYSTEMATICS OF VEIN MINERALS, JUNEAU GOLD BELT<br />
6I3c of -10.6 per mil (table 1) is similar to carbon isoto-<br />
pic compositions of C02 measured <strong>in</strong> hot spr<strong>in</strong>gs at<br />
Steamboat Spr<strong>in</strong>gs, Colorado, and at The Geysers and<br />
Lassen Peak, California.<br />
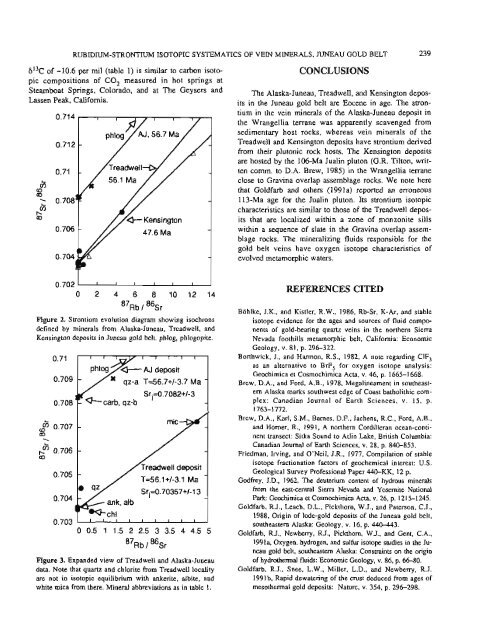
Figure 2. Strontium evolution diagram show<strong>in</strong>g isochrons<br />
def<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>by</strong> m<strong>in</strong>erals from <strong>Alaska</strong>-Juneau, Treadwell, and<br />
Kens<strong>in</strong>gton deposits <strong>in</strong> Juneau gold belt. phlog, phlogopite.<br />
Figure 3. Expanded view of Treadwell and <strong>Alaska</strong>-Juneau<br />
data. Note that quartz and chlorite from Treadwell locality<br />
are not <strong>in</strong> isotopic equilibrium with ankerite, albite, and<br />
white mica from <strong>the</strong>re. M<strong>in</strong>eral abbreviations as <strong>in</strong> table 1.<br />
CONCLUSIONS<br />
239<br />
The <strong>Alaska</strong>-Juneau, Treadwell, and Kens<strong>in</strong>gton depos-<br />
its <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Juneau gold belt are Eocene <strong>in</strong> age. The stron-<br />
tium <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> ve<strong>in</strong> m<strong>in</strong>erals of <strong>the</strong> <strong>Alaska</strong>-Juneau deposit <strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> Wrangellia terrane was apparently scavenged from<br />
sedimentary host rocks, whereas ve<strong>in</strong> m<strong>in</strong>erals of <strong>the</strong><br />
Treadwell and Kens<strong>in</strong>gton deposits have strontium derived<br />
from <strong>the</strong>ir plutonic rock hosts. The Kens<strong>in</strong>gton deposits<br />
are hosted <strong>by</strong> <strong>the</strong> 106-Ma Jual<strong>in</strong> pluton (G.R. Tilton, writ-<br />
ten comm. to D.A. Brew, 1985) <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Wrangellia terrane<br />
close to Grav<strong>in</strong>a overlap assemblage rocks. We note here<br />
that Goldfarb and o<strong>the</strong>rs (1991a) reported an erroneous<br />
113-Ma age for <strong>the</strong> Jual<strong>in</strong> pluton. Its strontium isotopic<br />
characteristics are similar to those of <strong>the</strong> Treadwell depos-<br />
its that are localized with<strong>in</strong> a zone of monzonite sills<br />
with<strong>in</strong> a sequence of slate <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Grav<strong>in</strong>a overlap assem-<br />
blage rocks. The m<strong>in</strong>eraliz<strong>in</strong>g fluids responsible for <strong>the</strong><br />
gold belt ve<strong>in</strong>s have oxygen isotope characteristics of<br />
evolved metamorphic waters.<br />
REFERENCES CITED<br />
Bohlke, J.K., and Kistler, R.W., 1986, Rb-Sr, K-Ar, and stable<br />
isotope evidence for <strong>the</strong> ages and sources of fluid compo-<br />
nents of gold-bear<strong>in</strong>g quartz ve<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> nor<strong>the</strong>rn Sierra<br />
Nevada foothills metamorphic belt, California: Economic<br />
Geology, v. 81, p. 296-322.<br />
Borthwick, J., and Harmon, R.S., 1982, A note regard<strong>in</strong>g CIF,<br />
as an alternative to BrF5 for oxygen isotope analysis:<br />
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 46, p. 1665-1668.<br />
Brew, D.A., and Ford, A.B., 1978, Megal<strong>in</strong>eament <strong>in</strong> sou<strong>the</strong>ast-<br />
ern <strong>Alaska</strong> marks southwest edge of Coast batholithic com-<br />
plex: Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, v. 15, p.<br />
1763-1772.<br />
Brew, D.A., Karl, S.M., Barnes, D.F., Jachens, R.C., Ford, A.B.,<br />
and Horner, R., 199 1, A nor<strong>the</strong>rn Cordilleran ocean-conti-<br />
nent transect: Sitka Sound to Atl<strong>in</strong> Lake, British Columbia:<br />
Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, v. 28, p. 840-853.<br />
Friedman, Irv<strong>in</strong>g, and O'Neil, J.R., 1977, Compilation of stable<br />
isotope fractionation factors of geochemical <strong>in</strong>terest: U.S.<br />
<strong>Geologic</strong>al <strong>Survey</strong> Professional Paper 440-KK, 12 p.<br />
Godfrey, J.D., 1962, The deuterium content of hydrous m<strong>in</strong>erals<br />
from <strong>the</strong> east-central Sierra Nevada and Yosemite National<br />
Park: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 26, p. 1215-1245.<br />
Goldfarb, R.J., Leach, D.L., Pickthorn, W.J., and Paterson, C.J.,<br />
1988, Orig<strong>in</strong> of lode-gold deposits of <strong>the</strong> Juneau gold belt,<br />
sou<strong>the</strong>astern <strong>Alaska</strong>: Geology, v. 16, p. 440443.<br />
Goldfarb, R.J., Newbeny, R.J., Pickthorn, W.J., and Gent, C.A.,<br />
1991a, Oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur isotope studies <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Ju-<br />
neau gold belt, sou<strong>the</strong>astern <strong>Alaska</strong>: Constra<strong>in</strong>ts on <strong>the</strong> orig<strong>in</strong><br />
of hydro<strong>the</strong>rmal fluids: Economic Geology, v. 86, p. 66-80.<br />
Goldfarb, R.J., Snee, L.W., Miller, L.D., and Newberry, R.J.<br />
1991b, Rapid dewater<strong>in</strong>g of <strong>the</strong> crust deduced from ages of<br />
meso<strong>the</strong>rmal gold deposits: Nature, v. 354, p. 296-298.