- Page 1:
Food plants of Papua New Guinea A c
- Page 4 and 5:
4 Dedication This book is dedicated
- Page 8 and 9:
Root and tuber crops and starchy st
- Page 10 and 11:
10 Insects: Achaea janata (Linnaeus
- Page 12 and 13:
12 Names English: Taro Scientific n
- Page 14 and 15:
14 Names English: Chinese taro Scie
- Page 16 and 17:
16 Names English: Swamp taro Scient
- Page 18 and 19:
18 Insects: Aspidiella sacchari (Co
- Page 20 and 21:
20 Use: The corm is cooked and eate
- Page 22 and 23:
22 Food Value: Per 100 g edible por
- Page 24 and 25:
Insects: Abgrallaspis cyanophylli (
- Page 26 and 27:
26 Names English: Lesser yam Scient
- Page 28 and 29:
28 Names English: Potato yam Scient
- Page 30 and 31:
30 Names English: Five leaflet yam
- Page 32 and 33:
32 Names English: White yam, White
- Page 34 and 35:
34 Food Value: Per 100 g edible por
- Page 36 and 37:
36 Henosepilachna haemorrhoea (Biel
- Page 38 and 39:
38 Names English: Yam bean Scientif
- Page 40 and 41:
40 Names English: Jerusalem articho
- Page 42 and 43:
42 Names English: Anu, Peruvian nas
- Page 44 and 45:
44 Names English: Banana, Plantain
- Page 46 and 47:
46 Names English: Sago Scientific n
- Page 48:
48 Names English: Solomon’s sago
- Page 51 and 52:
51 Names English: Peanut Scientific
- Page 53 and 54:
53 Names English: Winged bean Scien
- Page 55 and 56:
55 Spodoptera litura Fab. Noctuidae
- Page 57 and 58:
57 Names English: Yard long bean, S
- Page 59 and 60:
59 Names English: Cowpea Scientific
- Page 61 and 62:
61 Names English: Pigeon pea, Dhal
- Page 63 and 64:
63 Names English: Soybean Scientifi
- Page 65 and 66:
65 Names English: Lima bean Scienti
- Page 67 and 68:
67 Cassena intermedia Jac. Chrysome
- Page 69 and 70:
69 Lamprosema indica F. Pyralidae (
- Page 71 and 72:
71 Names English: Sword bean Scient
- Page 73 and 74:
73 Aulacophora similis Olivier Chry
- Page 75 and 76:
75 Names English: Rice bean Scienti
- Page 77 and 78:
77 Names English: Velvet bean Scien
- Page 79 and 80:
79 Names English: D'Albertis creepe
- Page 81 and 82:
81 Names English: Guar bean Scienti
- Page 84 and 85:
Green leafy vegetables or Kumus 84
- Page 86 and 87:
86 Insects: Cletus sp. Colobathrist
- Page 88 and 89:
88 Names English: Grain Amaranth, Q
- Page 90 and 91:
90 Names English: Spleen amaranth S
- Page 92 and 93:
92 Names English: Native Amaranth S
- Page 94 and 95:
94 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 96 and 97:
96 Names English: Spinach Joint fir
- Page 98 and 99:
Names English: Water drop wort Scie
- Page 100 and 101:
100 Names English: Blackberried nig
- Page 102 and 103:
102 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 104 and 105:
104 Names English: Highlands kapiak
- Page 106 and 107:
106 Names English: Dye fig Scientif
- Page 108 and 109:
108 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 110 and 111:
110 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 112 and 113:
112 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 114 and 115:
114 Names English: Watercress Scien
- Page 116 and 117:
116 Names English: Waterleaf Scient
- Page 118 and 119:
118 Names English: Sweet leaf Scien
- Page 120 and 121:
120 Names English: Leucaena Scienti
- Page 122 and 123:
122 Names English: Hibiscus Scienti
- Page 124 and 125:
124 Names English: Wandering Jew Sc
- Page 126 and 127:
126 Names English: Indian coral tre
- Page 128 and 129:
128 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 130 and 131:
130 Names English: Purslane, Pigwee
- Page 132 and 133:
132 Names English: Striped cucumber
- Page 134 and 135:
Edible ferns 134 English name Tok P
- Page 136 and 137:
136 Names English: Fern Scientific
- Page 138 and 139:
138 Names English: Tree fern Scient
- Page 140 and 141:
140 Names English: Tree fern Scient
- Page 142 and 143:
142 Names English: Tree fern Scient
- Page 144 and 145:
144 Names English: Climbing swamp f
- Page 146 and 147:
146 Names English: Giant Creek Fern
- Page 148 and 149:
148 Names English: Ladder fern Scie
- Page 150 and 151:
150 Names English: Hairy Sword Fern
- Page 152 and 153:
152 Names English: King fern, Giant
- Page 154 and 155:
154 Names English: Bird’s Nest Fe
- Page 156 and 157:
156 Names English: Adder’s Tongue
- Page 158 and 159:
158 Names English: Parsley fern, Au
- Page 160 and 161:
160 Names English: Swamp fern, Wate
- Page 162 and 163:
162 Names English: Fern Scientific
- Page 164 and 165:
164 Names English: Climbing maidenh
- Page 166 and 167:
166
- Page 168 and 169:
168 English name Tok Pisin Scientif
- Page 170 and 171:
170 Insects: Agapophyta bipunctata
- Page 172 and 173:
172 Names English: Betel nut Scient
- Page 174 and 175:
174 Names English: Highland Betel n
- Page 176 and 177:
176 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 178 and 179:
178 Names English: Pejibaye, Peach
- Page 180 and 181:
180 Names English: Wine palm, Palmy
- Page 182 and 183:
182 Names English: Papuan white rat
- Page 184 and 185:
184 Names English: Corypha palm Sci
- Page 186 and 187:
186 Food Value: Per 100 g edible po
- Page 188 and 189:
188 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 190 and 191:
190 Names English: Fan palm Scienti
- Page 192 and 193:
192 Names English: Black Palm Scien
- Page 194 and 195:
194 Names English: Solitaire palm,
- Page 196 and 197:
196 Names English: Traveller's palm
- Page 198 and 199:
198 Names English: Claudie River La
- Page 200 and 201:
Vegetables 200 English name Tok Pis
- Page 202 and 203:
202 Parastasia guttulata Fairmaire
- Page 204 and 205:
Food Value: Per 100 g edible portio
- Page 206 and 207:
206 Food Value: Per 100 g edible po
- Page 208 and 209:
208 Names English: Snake gourd Scie
- Page 210 and 211:
210 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 212 and 213:
212 Insects: Amblypelta lutescens p
- Page 214 and 215:
214 Names English: Pumpkin, Winter
- Page 216 and 217:
216 Names English: Cucumber Scienti
- Page 218 and 219:
218 Names English: Marrow, Pumpkin
- Page 220 and 221:
220 Names English: Bottle gourd Sci
- Page 222 and 223:
222 Names English: Smooth loofah Sc
- Page 224 and 225:
224 Names English: Bitter cucumber
- Page 226 and 227:
226 Names English: Spiny bitter cuc
- Page 228 and 229:
228 Names English: Bok-choy Celery
- Page 230 and 231:
230 Names English: Kohl rabi Scient
- Page 232 and 233:
232 Names English: Broccoli Scienti
- Page 234 and 235:
234 Names English: Chinese kale Sci
- Page 236 and 237:
236 Names English: Bai cai, Petsai
- Page 238 and 239:
238 Names English: Chinese radish S
- Page 240 and 241:
240 Names English: Bulb onion Scien
- Page 242 and 243:
242 Names English: Chives Scientifi
- Page 244 and 245:
244 Names English: Leek Scientific
- Page 246 and 247:
246 Names English: Celery Scientifi
- Page 248 and 249:
248 Names English: Asparagus Scient
- Page 250 and 251:
250 Diseases: Leaf spot Fungus Alte
- Page 252 and 253:
252 Names English: Pea eggplant Sci
- Page 254 and 255:
254 And Thanatephorus cucumeris Bro
- Page 256 and 257:
256 Names English: Lettuce Scientif
- Page 258 and 259:
Minor and less common vegetables 25
- Page 260 and 261:
260 Names English: Parsley Scientif
- Page 262 and 263:
262 Names English: New Guinea Edibl
- Page 264 and 265:
264 Names English: Giant bamboo Sci
- Page 266 and 267:
266 Names English: Endive Scientifi
- Page 268 and 269:
268 Names English: Common bamboo Sc
- Page 270 and 271:
270 Names English: Buckwheat Scient
- Page 272 and 273:
272 Names English: Sunflower Scient
- Page 274 and 275:
Grains and cereals 274 English name
- Page 276 and 277:
276 Chilo suppressalis (Walker) Pyr
- Page 278 and 279:
278 Names English: Wild rice Scient
- Page 280 and 281:
280 Names English: Wheat Scientific
- Page 282 and 283:
282 Names English: Job’s tears Sc
- Page 284 and 285:
Waterlilies 284 English name Tok Pi
- Page 286 and 287:
286 Names English: Giant waterlily,
- Page 288 and 289:
288 Names English: Waterlily Scient
- Page 290 and 291:
290 Names English: Blue Water lily
- Page 292 and 293:
292 Nuts English name Tok Pisin Sci
- Page 294 and 295:
294 stored in sealed containers for
- Page 296 and 297:
296 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 298 and 299:
298 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 300 and 301:
300 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 302 and 303:
302 Names English: Melville Island
- Page 304 and 305:
304 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 306 and 307:
306 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 308 and 309:
308 Names English: Breadfruit Scien
- Page 310 and 311:
310 Parasaissetia nigra (Nietner) C
- Page 312 and 313:
312 Production: Jackfruit is a fast
- Page 314 and 315:
314
- Page 316 and 317:
316 cooked and eaten and the two ha
- Page 318 and 319:
318 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 320 and 321:
320 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 322 and 323:
322 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 324 and 325:
324 Names English: Java almond, Tro
- Page 326 and 327:
326 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 328 and 329:
328 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 330 and 331:
330 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 332 and 333:
332 Names English: Macadamia nut Sc
- Page 334 and 335:
334 Names English: Polynesian chest
- Page 336 and 337:
336 Names English: Nypa palm Scient
- Page 338 and 339:
338 Names English: Cape nutmeg Scie
- Page 340 and 341:
340 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 342 and 343:
342 Names English: Queensland almon
- Page 344 and 345:
344 Names English: Arnhem Land quan
- Page 346 and 347:
346 Names English: Castanopsis ches
- Page 348 and 349:
348 Dysmicoccus nesophilus Williams
- Page 350 and 351:
Minor and introduced nuts 350 Engli
- Page 352 and 353:
The apple is used to make alcoholic
- Page 354 and 355:
354 Names English: Fragrant screwpi
- Page 356 and 357:
356 Names English: Pecan Scientific
- Page 358 and 359:
358 Names English: Walnut Scientifi
- Page 360 and 361:
360 Names English: Pistachio nut Sc
- Page 362 and 363:
362 Names English: Java olive Scien
- Page 364 and 365:
364 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 366 and 367:
366
- Page 368 and 369:
368 Fruit and other often sweet foo
- Page 370 and 371:
370 Leaf eating insects Anomala com
- Page 372 and 373:
372 Food Value: Per 100 g edible po
- Page 374 and 375:
374 Names English: Pineapple Scient
- Page 376 and 377: 376 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 378 and 379: 378 Diseases: Leaf spot Fungus Cerc
- Page 380 and 381: Food Value: Per 100 g edible portio
- Page 382 and 383: 382 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 384 and 385: 384 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 386 and 387: 386 Names English: Cherimoya Scient
- Page 388 and 389: 388 Names English: Atemoya, Custard
- Page 390 and 391: 390 Graphium agamemnon L. Papilioni
- Page 392 and 393: 392 Names English: Sweetsop Scienti
- Page 394 and 395: 394 Names English: Pacific lychee S
- Page 396 and 397: 396 Ceroplastes destructor Newstead
- Page 398 and 399: 398 Food Value: Per 100 g edible po
- Page 400 and 401: 400 Names English: Golden apple, Sc
- Page 402 and 403: 402 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 404 and 405: 404 Food Value: Per 100 g edible po
- Page 406 and 407: West Indian lime Citrus aurantifoli
- Page 408 and 409: 408 Names English: Lime, West India
- Page 410 and 411: 410 Names English: Orange, Sweet or
- Page 412 and 413: 412 Names English: Citron Scientifi
- Page 414 and 415: 414 Names English: Wild lime Scient
- Page 416 and 417: 416 Names English: Clymenia Scienti
- Page 418 and 419: 418 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 420 and 421: 420 Names English: Tree tomato, Tam
- Page 422 and 423: 422 Names English: Naranjilla Scien
- Page 424 and 425: 424 Names English: Surinam cherry S
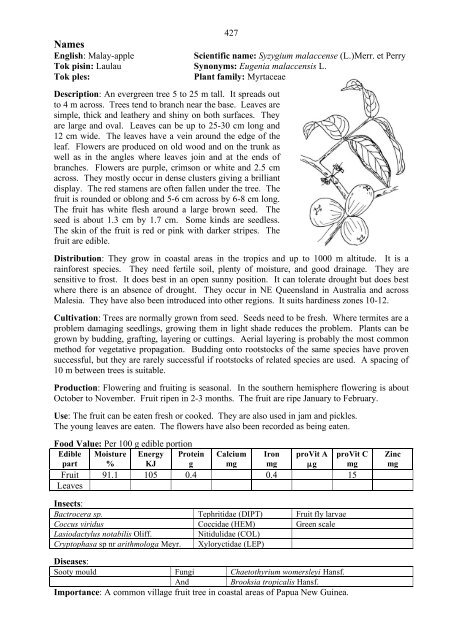
- Page 428 and 429: 428 Names English: Java apple Scien
- Page 430 and 431: 430 Names English: Pink satinash Sc
- Page 432 and 433: 432 Fruit (Continued) English name
- Page 434 and 435: 434 Names English: White apple Scie
- Page 436 and 437: 436 Names English: Lady apple, Red
- Page 438 and 439: 438 Names English: Governor’s plu
- Page 440 and 441: 440 Names English: Coffee plum Scie
- Page 442 and 443: 442 Names English: Red raspberry Sc
- Page 444 and 445: 444 Names English: Molucca bramble
- Page 446 and 447: 446 Names English: Rose-leaf brambl
- Page 448 and 449: 448 Names English: Alpine strawberr
- Page 450 and 451: 450 Names English: Purple passionfr
- Page 452 and 453: 452 Names English: Banana passionfr
- Page 454 and 455: 454 Names English: Sweet granadilla
- Page 456 and 457: 456 Names English: Granadilla Scien
- Page 458 and 459: 458 Names English: Toothed-leaved w
- Page 460 and 461: 460 Names English: Canistel, Yellow
- Page 462 and 463: 462 Names English: Peach Scientific
- Page 464 and 465: 464 Names English: Durian Scientifi
- Page 466 and 467: 466 Names English: Mangosteen Scien
- Page 468 and 469: 468 Names English: Warren’s mango
- Page 470 and 471: 470 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 472 and 473: 472 Names English: Loquat Scientifi
- Page 474 and 475: 474 Production: Seeds germinate aft
- Page 476 and 477:
476 Names English: Horse mango Scie
- Page 478 and 479:
478 Names English: Scientific name:
- Page 480 and 481:
480 Names English: European grape S
- Page 482 and 483:
482 Names English: Salak, Snake fru
- Page 484 and 485:
484 Names English: Santol Scientifi
- Page 486 and 487:
486 Names English: Rambutan Scienti
- Page 488 and 489:
488 Names English: Panama berry Sci
- Page 490 and 491:
490 Names English: Mulberry Scienti
- Page 492 and 493:
492 Names English: Indian mulberry
- Page 494 and 495:
494 Names English: Garraway lime Sc
- Page 496 and 497:
496 Names English: Fei banana Scien
- Page 498 and 499:
498 Names English: Sapodilla Scient
- Page 500 and 501:
500 Names English: Litchi, Lychee S
- Page 502 and 503:
502 Names English: Langsat Scientif
- Page 504 and 505:
504 Names English: Garuga Scientifi
- Page 506 and 507:
506 Names English: Fig Scientific n
- Page 508 and 509:
508 Names English: Velvet apple Sci
- Page 510 and 511:
510 Names English: Longan Scientifi
- Page 512 and 513:
512 Names English: Red beach, Golde
- Page 514 and 515:
514 Names English: Black currant tr
- Page 516 and 517:
516 Names English: Chinese laurel S
- Page 518 and 519:
518 Names English: Broad leafed lil
- Page 520 and 521:
520 Names English: Pineapple guava,
- Page 522 and 523:
522 English name Tok Pisin Scientif
- Page 524 and 525:
524 Names English: Oregano Scientif
- Page 526 and 527:
526 Names English: Spearmint Scient
- Page 528 and 529:
528 Names English: Dill Scientific
- Page 530 and 531:
530 Names English: Chilli, Bird's e
- Page 532 and 533:
532 Names English: Perilla Scientif
- Page 534 and 535:
534 Names English: Native cardamon
- Page 536 and 537:
536 Names English: Coriander Scient
- Page 538 and 539:
538 Names English: Lemon balm Scien
- Page 540 and 541:
540 Names English: Queensland Nutme
- Page 542 and 543:
542 Names English: Tamarind Scienti
- Page 544 and 545:
544 Names English: Betel pepper Sci
- Page 546 and 547:
546 Names English: Thyme Scientific
- Page 548 and 549:
548 Names English: Ginger Scientifi
- Page 550 and 551:
550 Names English: Wild ginger Scie
- Page 552 and 553:
552 Scientific name Page Asplenium
- Page 554 and 555:
554 Scientific name Page Deeringia
- Page 556 and 557:
556 Scientific name Page Manihot es
- Page 558 and 559:
558 Scientific name Page Psidium gu
- Page 560 and 561:
560 English name Page Adder’s ton
- Page 562 and 563:
562 European chestnut 353 European
- Page 564 and 565:
564 Oca 41 Oil palm 185 Okra 247 Ol
- Page 566 and 567:
566 Sweetsop 392 Sword bean 71 Tama
- Page 568:
Pao 307 Pao 305 Paragum 17 Peteta 3