Eble JN, Sauter G., Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA - iarc
Eble JN, Sauter G., Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA - iarc
Eble JN, Sauter G., Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA - iarc
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Miscellaneous tumours<br />
P.H. Tan<br />
L. Cheng<br />
M. Furusato<br />
C.C. Pan<br />
ICD-O codes<br />
Cystadenoma 8440/0<br />
Wilms tumour (nephroblastoma) 8960/3<br />
Malignant rhabdoid tumour 8963/3<br />
Clear cell adenocarcinoma 8310/3<br />
Melanoma of the prostate 8720/3<br />
Paraganglioma 8680/1<br />
Neuroblastoma 9500/3<br />
Cystadenoma<br />
Also known as multilocular cyst or giant<br />
multilocular prostatic cystadenoma, it is<br />
a rare entity characterized by benign<br />
multilocular prostatic cysts that can<br />
enlarge massively. Affected men are<br />
aged 20-80 years, presenting with<br />
obstructive urinary symptoms, with or<br />
without a palpable abdominal mass<br />
{1324}. Postulated causes include<br />
obstruction, involutional atrophy {1594},<br />
or retrovesical ectopic prostatic tissue<br />
with cystic change {2872}.<br />
It occurs between the bladder and the<br />
rectum {62,1501,1611,2872}, either separate<br />
from the prostate or attached to it<br />
by a pedicle. Similar lesions can be<br />
found within the prostate gland.<br />
Cystadenomas weigh up to 6,500 grams,<br />
ranging from 7.5 cm to 20 cm in size.<br />
They are well-circumscribed, resembling<br />
nodular hyperplasia with multiple cysts<br />
macroscopically. Atrophic prostatic<br />
epithelium lines the cysts, reacting with<br />
antibodies to PSA and PSAP, with high<br />
grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia<br />
reported in one case {62}. When cystadenomas<br />
occur within the prostate,<br />
distinction from cystic nodular hyperplasia<br />
may be difficult. Intraprostatic cystadenoma<br />
should be diagnosed only<br />
when half the prostate appears normal,<br />
while the remaining gland is enlarged by<br />
a solitary encapsulated cystic nodule<br />
{1323,1704}.<br />
Prostatic cystadenomas are not biologically<br />
aggressive {1611}, but can recur if<br />
incompletely excised. Extensive surgery<br />
may be necessary because of their large<br />
size and impingement on surrounding<br />
structures.<br />
Wilms tumour (nephroblastoma)<br />
Wilms tumour rarely occurs in the<br />
prostate {386}.<br />
Malignant rhabdoid tumour<br />
Malignant rhabdoid tumour may be<br />
found in the prostate {673}.<br />
Germ cell tumours<br />
Primary germ cell tumours of the prostate<br />
have been rarely described {1046,1725,<br />
2586}. It is critical to exclude a metastasis<br />
from a testicular primary.<br />
Clear cell adenocarcinoma<br />
Clear cell adenocarcinoma resembling<br />
those seen in the Müllerian system may<br />
affect the prostate. It can develop from<br />
the prostatic urethra {636}, Müllerian<br />
derivatives such as Müllerian duct cyst<br />
{874}, or exceptionally, from the peripheral<br />
parenchyma {2004}. Histologically, it is<br />
composed of tubulocystic or papillary<br />
structures lined by cuboidal or hobnail<br />
cells with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm.<br />
The tumour cells immunohistochemically<br />
do not express prostate specific<br />
antigen and prostate acid phosphatase,<br />
but may express CA-125. The<br />
patient may have elevated serum level of<br />
CA-125.<br />
Melanoma of the prostate<br />
Primary malignant melanomas of the<br />
prostate are extremely rare {2493}.<br />
Malignant melanoma of the prostate<br />
should be distinguished from melanosis<br />
and cellular blue nevus of the prostate<br />
{2208}.<br />
Paraganglioma<br />
Several case reports of paragangliomas<br />
originating in the prostate have been<br />
reported, including one in a child {599,<br />
2747}. Although extra-adrenal paragan-<br />
A<br />
B<br />
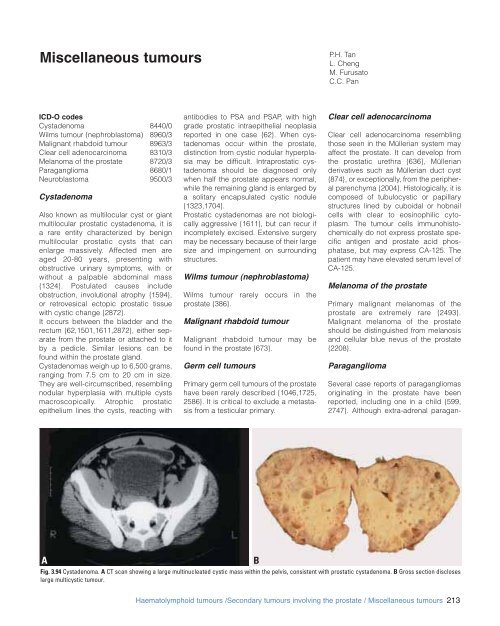
Fig. 3.94 Cystadenoma. A CT scan showing a large multinucleated cystic mass within the pelvis, consistent with prostatic cystadenoma. B Gross section discloses<br />
large multicystic tumour.<br />
Haematolymphoid tumours /Secondary tumours involving the prostate / Miscellaneous tumours 213