in vitro PHARMACOLOGY 2011 CATALOG - Cerep
in vitro PHARMACOLOGY 2011 CATALOG - Cerep
in vitro PHARMACOLOGY 2011 CATALOG - Cerep
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
101<br />
❚ pur<strong>in</strong>ergic channels<br />
<strong>Cerep</strong><br />
services<br />
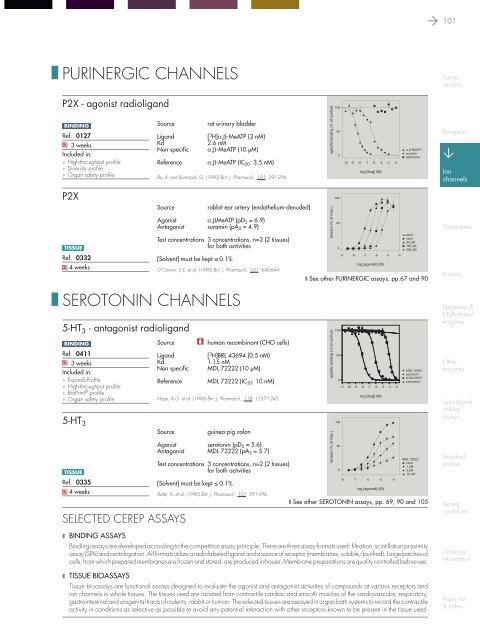
P2X - agonist radioligand<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Ref. 0127<br />
Q 3 weeks<br />
Included <strong>in</strong>:<br />
High-throughput profile<br />
Diversity profile<br />
Organ safety profile<br />
Source<br />
Ligand<br />
Kd<br />
Non specific<br />
Reference<br />
rat ur<strong>in</strong>ary bladder<br />
[ 3 H]α,β-MeATP (3 nM)<br />
2.6 nM<br />
α,β-MeATP (10 µM)<br />
α,β-MeATP (IC 50 : 3.5 nM)<br />
Bo, X. and Burnstock, G. (1990) Brit. J. Pharmacol., 101: 291-296.<br />
specific b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g (% of control)<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
-10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3<br />
log [drug] (M)<br />
α,β-MeATP<br />
suram<strong>in</strong><br />
adenos<strong>in</strong>e<br />
Receptors<br />
<br />
Ion<br />
channels<br />
P2X<br />
tissue<br />
Ref. 0332<br />
Q 4 weeks<br />
Source<br />
rabbit ear artery (endothelium-denuded)<br />
Agonist α,βMeATP (pD 2 = 6.9)<br />
Antagonist suram<strong>in</strong> (pA 2 = 4.9)<br />
Test concentrations 3 concentrations, n=2 (2 tissues)<br />
for both activities<br />
[Solvent] must be kept ≤ 0.1%<br />
O’Connor, S.E. et al. (1990) Brit. J. Pharmacol., 101: 640-644.<br />
❚ seroton<strong>in</strong> channels<br />
5-HT 3 - antagonist radioligand<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Ref. 0411<br />
Q 3 weeks<br />
Included <strong>in</strong>:<br />
ExpresS Profile<br />
High-throughput profile<br />
BioPr<strong>in</strong>t ® profile<br />
Organ safety profile<br />
5-HT 3<br />
tissue<br />
Ref. 0335<br />
Q 4 weeks<br />
Source<br />
Ligand<br />
Kd<br />
Non specific<br />
Reference<br />
human recomb<strong>in</strong>ant (CHO cells)<br />
[ 3 H]BRL 43694 (0.5 nM)<br />
1.15 nM<br />
MDL 72222 (10 µM)<br />
MDL 72222 (IC 50 : 10 nM)<br />
Hope, A.G. et al. (1996) Brit. J. Pharmacol., 118: 1237-1245.<br />
Source<br />
selected cerep assays<br />
gu<strong>in</strong>ea-pig colon<br />
Agonist seroton<strong>in</strong> (pD 2 = 5.6)<br />
Antagonist MDL 72222 (pA 2 = 5.7)<br />
Test concentrations 3 concentrations, n=2 (2 tissues)<br />
for both activities<br />
[Solvent] must be kept ≤ 0.1%<br />
Butler, A. et al. (1990) Brit. J. Pharmacol., 101: 591-598.<br />
tension (% of max.)<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4<br />
log [agonist] (M)<br />
suram<strong>in</strong><br />
none<br />
30 µM<br />
100 µM<br />
300 µM<br />
❚ See other Pur<strong>in</strong>ergic assays, pp.67 and 90<br />
specific b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g (% of control)<br />
tension (% of max.)<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
-11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3<br />
log [drug] (M)<br />
-8 -7 -6 -5 -4<br />
log [agonist] (M)<br />
MDL 72222<br />
seroton<strong>in</strong><br />
8-OH-DPAT<br />
ketanser<strong>in</strong><br />
MDL 72222<br />
none<br />
1 µM<br />
3 µM<br />
10 µM<br />
❚ See other Seroton<strong>in</strong> assays, pp. 69, 90 and 105<br />
❚ b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g assays<br />
B<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g assays are developed accord<strong>in</strong>g to the competition assay pr<strong>in</strong>ciple. There are three assay formats used: filtration, sc<strong>in</strong>tillation proximity<br />
assay (SPA) and centrifugation. All formats utilize a radiolabeled ligand and a source of receptor (membranes, soluble/purified). Large batches of<br />
cells, from which prepared membranes are frozen and stored, are produced <strong>in</strong>-house. Membrane preparations are quality controlled before use.<br />
❚ tissue bioassays<br />
Tissue bioassays are functional assays designed to evaluate the agonist and antagonist activities of compounds at various receptors and<br />
ion channels <strong>in</strong> whole tissues. The tissues used are isolated from contractile cardiac and smooth muscles of the cardiovascular, respiratory,<br />
gastro<strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>al and urogenital tracts of rodents, rabbit or human. The selected tissues are assayed <strong>in</strong> organ bath systems to record the contractile<br />
activity <strong>in</strong> conditions as selective as possible to avoid any potential <strong>in</strong>teraction with other receptors known to be present <strong>in</strong> the tissue used.<br />
Transporters<br />
K<strong>in</strong>ases<br />
Epigenetic &<br />
DNA-related<br />
enzymes<br />
Other<br />
enzymes<br />
Specialized<br />
cellular<br />
assays<br />
Standard<br />
profiles<br />
Test<strong>in</strong>g<br />
conditions<br />
Order<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Assay list<br />
& <strong>in</strong>dex