in vitro PHARMACOLOGY 2011 CATALOG - Cerep
in vitro PHARMACOLOGY 2011 CATALOG - Cerep
in vitro PHARMACOLOGY 2011 CATALOG - Cerep
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
voltage-gated channels [K + channels] ❚<br />
95<br />
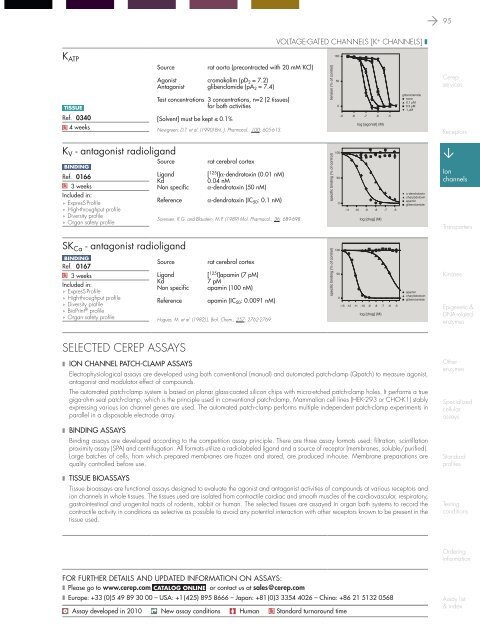
K ATP<br />
tissue<br />
Source<br />
rat aorta (precontracted with 20 mM KCl)<br />
Agonist cromakalim (pD 2 = 7.2)<br />
Antagonist glibenclamide (pA 2 = 7.4)<br />
Test concentrations 3 concentrations, n=2 (2 tissues)<br />
for both activities<br />
tension (% of control)<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
glibenclamide<br />
none<br />
0.1 µM<br />
0.3 µM<br />
1 µM<br />
<strong>Cerep</strong><br />
services<br />
Ref. 0340<br />
Q 4 weeks<br />
[Solvent] must be kept ≤ 0.1%<br />
Newgreen, D.T. et al. (1990) Brit. J. Pharmacol., 100: 605-613.<br />
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5<br />
log [agonist] (M)<br />
Receptors<br />
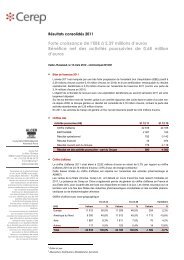
K V - antagonist radioligand<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Ref. 0166<br />
Q 3 weeks<br />
Included <strong>in</strong>:<br />
ExpresS Profile<br />
High-throughput profile<br />
Diversity profile<br />
Organ safety profile<br />
Source<br />
Ligand<br />
Kd<br />
Non specific<br />
Reference<br />
rat cerebral cortex<br />
[ 125 I]α-dendrotox<strong>in</strong> (0.01 nM)<br />
0.04 nM<br />
α-dendrotox<strong>in</strong> (50 nM)<br />
α-dendrotox<strong>in</strong> (IC 50 : 0.1 nM)<br />
Sorensen, R.G. and Blauste<strong>in</strong>, M.P. (1989) Mol. Pharmacol., 36: 689-698.<br />
specific b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g (% of control)<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
-11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6<br />
log [drug] (M)<br />
α-dendrotox<strong>in</strong><br />
charybdotox<strong>in</strong><br />
apam<strong>in</strong><br />
glibenclamide<br />
<br />
Ion<br />
channels<br />
Transporters<br />
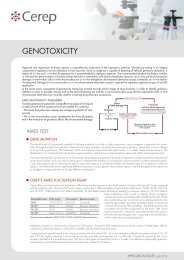
SK Ca - antagonist radioligand<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Ref. 0167<br />
Q 3 weeks<br />
Included <strong>in</strong>:<br />
ExpresS Profile<br />
High-throughput profile<br />
Diversity profile<br />
BioPr<strong>in</strong>t ® profile<br />
Organ safety profile<br />
Source<br />
Ligand<br />
Kd<br />
Non specific<br />
Reference<br />
rat cerebral cortex<br />
[ 125 I]apam<strong>in</strong> (7 pM)<br />
7 pM<br />
apam<strong>in</strong> (100 nM)<br />
apam<strong>in</strong> (IC 50 : 0.0091 nM)<br />
Hugues, M. et al. (1982) J. Biol. Chem., 257: 2762-2769.<br />
specific b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g (% of control)<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
-13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5<br />
log [drug] (M)<br />
apam<strong>in</strong><br />
charybdotox<strong>in</strong><br />
glibenclamide<br />
K<strong>in</strong>ases<br />
Epigenetic &<br />
DNA-related<br />
enzymes<br />
selected cerep assays<br />
❚ ion channel patch-clamp assays<br />
Electrophysiological assays are developed us<strong>in</strong>g both conventional (manual) and automated patch-clamp (Qpatch) to measure agonist,<br />
antagonist and modulator effect of compounds.<br />
The automated patch-clamp system is based on planar glass-coated silicon chips with micro-etched patch-clamp holes. It performs a true<br />
giga-ohm seal patch-clamp, which is the pr<strong>in</strong>ciple used <strong>in</strong> conventional patch-clamp. Mammalian cell l<strong>in</strong>es (HEK-293 or CHO-K1) stably<br />
express<strong>in</strong>g various ion channel genes are used. The automated patch-clamp performs multiple <strong>in</strong>dependent patch-clamp experiments <strong>in</strong><br />
parallel <strong>in</strong> a disposable electrode array.<br />
❚ b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g assays<br />
B<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g assays are developed accord<strong>in</strong>g to the competition assay pr<strong>in</strong>ciple. There are three assay formats used: filtration, sc<strong>in</strong>tillation<br />
proximity assay (SPA) and centrifugation. All formats utilize a radiolabeled ligand and a source of receptor (membranes, soluble/purified).<br />
Large batches of cells, from which prepared membranes are frozen and stored, are produced <strong>in</strong>-house. Membrane preparations are<br />
quality controlled before use.<br />
❚ tissue bioassays<br />
Tissue bioassays are functional assays designed to evaluate the agonist and antagonist activities of compounds at various receptors and<br />
ion channels <strong>in</strong> whole tissues. The tissues used are isolated from contractile cardiac and smooth muscles of the cardiovascular, respiratory,<br />
gastro<strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>al and urogenital tracts of rodents, rabbit or human. The selected tissues are assayed <strong>in</strong> organ bath systems to record the<br />
contractile activity <strong>in</strong> conditions as selective as possible to avoid any potential <strong>in</strong>teraction with other receptors known to be present <strong>in</strong> the<br />
tissue used.<br />
Other<br />
enzymes<br />
Specialized<br />
cellular<br />
assays<br />
Standard<br />
profiles<br />
Test<strong>in</strong>g<br />
conditions<br />
Order<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation<br />
For further details and updated <strong>in</strong>formation on assays:<br />
❚ Please go to www.cerep.com catalog onl<strong>in</strong>e or contact us at sales@cerep.com<br />
❚ Europe: +33 (0)5 49 89 30 00 – USA: +1 (425) 895 8666 – Japan: +81 (0)3 3354 4026 – Ch<strong>in</strong>a: +86 21 5132 0568<br />
Assay developed <strong>in</strong> 2010 New assay conditions Human Q Standard turnaround time<br />
Assay list<br />
& <strong>in</strong>dex