the challenges facing landlocked developing countries: a case study ...
the challenges facing landlocked developing countries: a case study ...
the challenges facing landlocked developing countries: a case study ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ARMENIA<br />
While Armenia’s central geographic position in <strong>the</strong> Caucasus<br />
potentially allows it to serve as a regional crossroad like it did<br />
prior to independence in 1991, this has not been possible over<br />
<strong>the</strong> last decade due to conflicts with neighbors Turkey and<br />
Azerbaijan and severely deteriorated infrastructure. Such<br />
<strong>challenges</strong> have contributed to Armenia’s high transport costs,<br />
which are significantly greater than those of most former<br />
Soviet Union republics. One estimate of <strong>the</strong>se costs,<br />
calculated by <strong>the</strong> World Bank, suggests that if Armenia’s<br />
average freight factor was that of <strong>the</strong> EU - 8 times less than<br />
Armenia’s - it could save approximately US$100 million per<br />
year. 34<br />
The trade costs of conflict have been severe. Armenia’s<br />
traditional trade route through Azerbaijan, which accounted<br />
for over 85% of Armenian trade flows, was blockaded in 1991<br />
as a result of <strong>the</strong> conflict over Nagoro-Karabakh. Shortly<br />
<strong>the</strong>reafter <strong>the</strong> Turkish border was also closed to transport.<br />
With transit corridors undeveloped to <strong>the</strong> south, Armenia was<br />
forced to reroute nearly all of its trade through Georgia. This<br />
too presented problems for Armenia when a ravaging civil war<br />
broke out in Georgia. A recently developed corridor to Iran<br />
has been witnessing an increased trade flow.<br />
TRANSPORTATION INFRASTRUCTURE<br />
Road<br />
With <strong>the</strong> closure of <strong>the</strong> Azerbaijan rail corridor, most of<br />
Armenia’s freight transit traffic has been rerouted to <strong>the</strong> road<br />
corridor from Yerevan to Georgia. This increasing<br />
dependence on <strong>the</strong> road network has been accompanied by<br />
significant deterioration in <strong>the</strong> infrastructure, resulting from<br />
years of neglect following independence. A 1998 European<br />
Bank for Reconstruction and Development <strong>study</strong> estimated<br />
that nearly 40% of Armenian roads were in need of immediate<br />
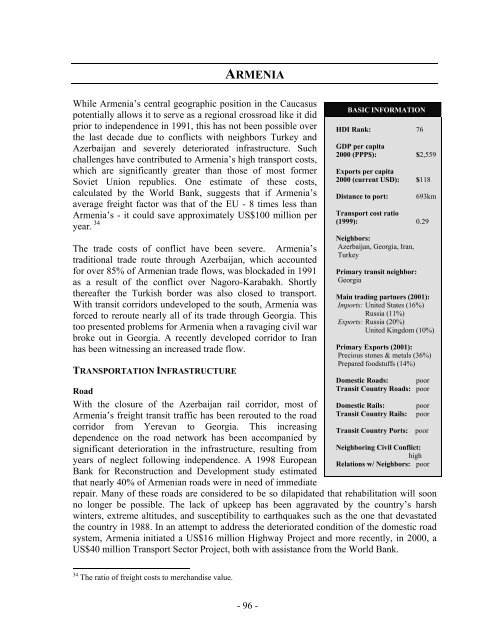
BASIC INFORMATION<br />
HDI Rank: 76<br />
GDP per capita<br />
2000 (PPP$): $2,559<br />
Exports per capita<br />
2000 (current USD): $118<br />
Distance to port:<br />
693km<br />
Transport cost ratio<br />
(1999): 0.29<br />
Neighbors:<br />
Azerbaijan, Georgia, Iran,<br />
Turkey<br />
Primary transit neighbor:<br />
Georgia<br />
Main trading partners (2001):<br />
Imports: United States (16%)<br />
Russia (11%)<br />
Exports: Russia (20%)<br />
United Kingdom (10%)<br />
Primary Exports (2001):<br />
Precious stones & metals (36%)<br />
Prepared foodstuffs (14%)<br />
Domestic Roads: poor<br />
Transit Country Roads: poor<br />
Domestic Rails:<br />
Transit Country Rails:<br />
repair. Many of <strong>the</strong>se roads are considered to be so dilapidated that rehabilitation will soon<br />
no longer be possible. The lack of upkeep has been aggravated by <strong>the</strong> country’s harsh<br />
winters, extreme altitudes, and susceptibility to earthquakes such as <strong>the</strong> one that devastated<br />
<strong>the</strong> country in 1988. In an attempt to address <strong>the</strong> deteriorated condition of <strong>the</strong> domestic road<br />
system, Armenia initiated a US$16 million Highway Project and more recently, in 2000, a<br />
US$40 million Transport Sector Project, both with assistance from <strong>the</strong> World Bank.<br />
poor<br />
poor<br />
Transit Country Ports: poor<br />
Neighboring Civil Conflict:<br />
high<br />
Relations w/ Neighbors: poor<br />
34 The ratio of freight costs to merchandise value.<br />
- 96 -