Sustainable Construction A Life Cycle Approach in Engineering
Sustainable Construction A Life Cycle Approach in Engineering
Sustainable Construction A Life Cycle Approach in Engineering
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
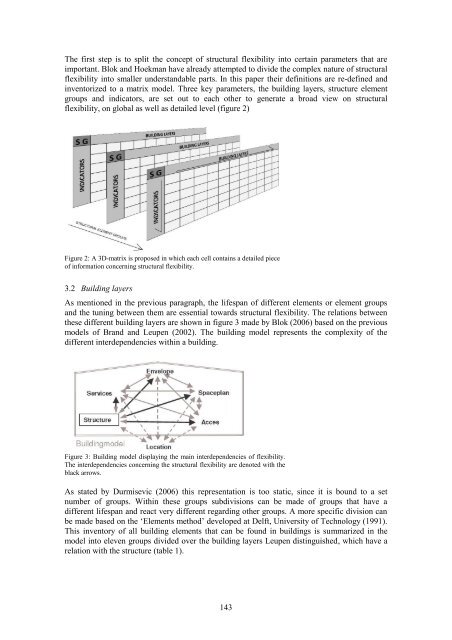
The first step is to split the concept of structural flexibility <strong>in</strong>to certa<strong>in</strong> parameters that are<br />
important. Blok and Hoekman have already attempted to divide the complex nature of structural<br />
flexibility <strong>in</strong>to smaller understandable parts. In this paper their def<strong>in</strong>itions are re-def<strong>in</strong>ed and<br />
<strong>in</strong>ventorized to a matrix model. Three key parameters, the build<strong>in</strong>g layers, structure element<br />
groups and <strong>in</strong>dicators, are set out to each other to generate a broad view on structural<br />
flexibility, on global as well as detailed level (figure 2)<br />
Figure 2: A 3D-matrix is proposed <strong>in</strong> which each cell conta<strong>in</strong>s a detailed piece<br />
of <strong>in</strong>formation concern<strong>in</strong>g structural flexibility.<br />
3.2 Build<strong>in</strong>g layers<br />
As mentioned <strong>in</strong> the previous paragraph, the lifespan of different elements or element groups<br />
and the tun<strong>in</strong>g between them are essential towards structural flexibility. The relations between<br />
these different build<strong>in</strong>g layers are shown <strong>in</strong> figure 3 made by Blok (2006) based on the previous<br />
models of Brand and Leupen (2002). The build<strong>in</strong>g model represents the complexity of the<br />
different <strong>in</strong>terdependencies with<strong>in</strong> a build<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Figure 3: Build<strong>in</strong>g model display<strong>in</strong>g the ma<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>terdependencies of flexibility.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terdependencies concern<strong>in</strong>g the structural flexibility are denoted with the<br />
black arrows.<br />
As stated by Durmisevic (2006) this representation is too static, s<strong>in</strong>ce it is bound to a set<br />
number of groups. With<strong>in</strong> these groups subdivisions can be made of groups that have a<br />
different lifespan and react very different regard<strong>in</strong>g other groups. A more specific division can<br />
be made based on the ‘Elements method’ developed at Delft, University of Technology (1991).<br />
This <strong>in</strong>ventory of all build<strong>in</strong>g elements that can be found <strong>in</strong> build<strong>in</strong>gs is summarized <strong>in</strong> the<br />
model <strong>in</strong>to eleven groups divided over the build<strong>in</strong>g layers Leupen dist<strong>in</strong>guished, which have a<br />
relation with the structure (table 1).<br />
143









![Weibull [Compatibility Mode]](https://img.yumpu.com/48296360/1/190x134/weibull-compatibility-mode.jpg?quality=85)






