Sustainable Construction A Life Cycle Approach in Engineering
Sustainable Construction A Life Cycle Approach in Engineering
Sustainable Construction A Life Cycle Approach in Engineering
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Although a number of papers can be found <strong>in</strong> the literature related to the analysis of connections<br />
with dowels, not many researches were concerned with the behaviour of jo<strong>in</strong>ts with timber<br />
pegs. With specific regard to connections with timber pegs, simplified orthotropic elastoplastic<br />
bil<strong>in</strong>ear material model have been used by some authors, as <strong>in</strong> Miller 2004. In this case,<br />
the plasticity model is based on the von Mises yield criterion, with an associated flow rule and<br />
with isotropic harden<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
The aim of this numerical model<strong>in</strong>g is to <strong>in</strong>vestigate the possibility to use Hash<strong>in</strong> criterion as<br />
material constitutive law <strong>in</strong> the model<strong>in</strong>g of connections with timber pegs by f<strong>in</strong>ite elements.<br />
This type of failure criterion presents several advantages. It is available <strong>in</strong> commercial codes<br />
and <strong>in</strong>cludes the possibility to set different strength values <strong>in</strong> tension and compression along<br />
longitud<strong>in</strong>al and radial directions, with different values of fracture energy.<br />
In particular, the aim of numerical <strong>in</strong>vestigation is to extend the results of experimental activities<br />
by a parametric analysis devoted to characterize the behaviour of connections with particular<br />
regard to the peg and to the <strong>in</strong>teraction area with the plates.<br />
The connection considered was tested by Ceraldi et al. 2008 and was assembled us<strong>in</strong>g different<br />
materials. In particular, ash was used for pegs and fir for plates. The different materials were<br />
selected with the aim of evaluat<strong>in</strong>g the effects of various material densities on the type of collapse<br />
mechanism of the pegs.<br />
The numerical model of the connection was calibrated on the basis of experimental tests on<br />
wood materials <strong>in</strong> compression, bend<strong>in</strong>g and cutt<strong>in</strong>g shear. Afterwards, the predicted behaviour<br />
of the double shear jo<strong>in</strong>t has been validated aga<strong>in</strong>st experimental results <strong>in</strong> terms of loaddisplacement<br />
curves and failure modes.<br />
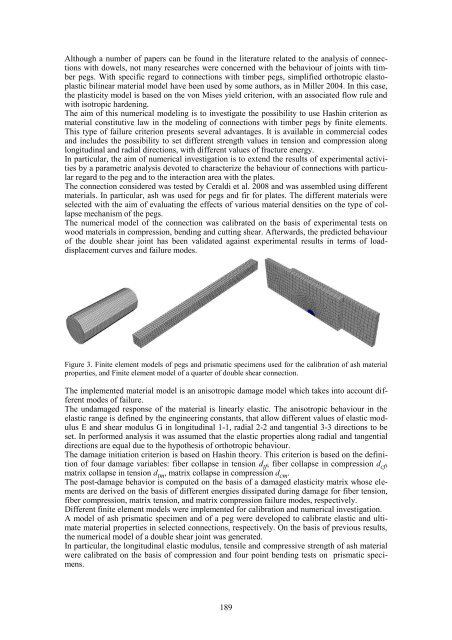
Figure 3. F<strong>in</strong>ite element models of pegs and prismatic specimens used for the calibration of ash material<br />
properties, and F<strong>in</strong>ite element model of a quarter of double shear connection.<br />
The implemented material model is an anisotropic damage model which takes <strong>in</strong>to account different<br />
modes of failure.<br />
The undamaged response of the material is l<strong>in</strong>early elastic. The anisotropic behaviour <strong>in</strong> the<br />
elastic range is def<strong>in</strong>ed by the eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g constants, that allow different values of elastic modulus<br />
E and shear modulus G <strong>in</strong> longitud<strong>in</strong>al 1-1, radial 2-2 and tangential 3-3 directions to be<br />
set. In performed analysis it was assumed that the elastic properties along radial and tangential<br />
directions are equal due to the hypothesis of orthotropic behaviour.<br />
The damage <strong>in</strong>itiation criterion is based on Hash<strong>in</strong> theory. This criterion is based on the def<strong>in</strong>ition<br />
of four damage variables: fiber collapse <strong>in</strong> tension d tf , fiber collapse <strong>in</strong> compression d cf ,<br />
matrix collapse <strong>in</strong> tension d tm , matrix collapse <strong>in</strong> compression d cm .<br />
The post-damage behavior is computed on the basis of a damaged elasticity matrix whose elements<br />
are derived on the basis of different energies dissipated dur<strong>in</strong>g damage for fiber tension,<br />
fiber compression, matrix tension, and matrix compression failure modes, respectively.<br />
Different f<strong>in</strong>ite element models were implemented for calibration and numerical <strong>in</strong>vestigation.<br />
A model of ash prismatic specimen and of a peg were developed to calibrate elastic and ultimate<br />
material properties <strong>in</strong> selected connections, respectively. On the basis of previous results,<br />
the numerical model of a double shear jo<strong>in</strong>t was generated.<br />
In particular, the longitud<strong>in</strong>al elastic modulus, tensile and compressive strength of ash material<br />
were calibrated on the basis of compression and four po<strong>in</strong>t bend<strong>in</strong>g tests on prismatic specimens.<br />
189









![Weibull [Compatibility Mode]](https://img.yumpu.com/48296360/1/190x134/weibull-compatibility-mode.jpg?quality=85)






