Novel Design of an Integrated Pulp Mill Biorefinery for the ...
Novel Design of an Integrated Pulp Mill Biorefinery for the ...
Novel Design of an Integrated Pulp Mill Biorefinery for the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2.2 Black Liquor Gasification to Syngas<br />
Gasification <strong>of</strong> biomass is a partial oxidation reaction that converts solid biomass into<br />
product gas or syn<strong>the</strong>sis gas (also called syngas)[32]. Primary syngas components are hydrogen<br />
(H2), <strong>an</strong>d carbon monoxide (CO), with smaller amounts <strong>of</strong> carbon dioxide (CO2), meth<strong>an</strong>e<br />
(CH4), higher hydrocarbons (C2+), <strong>an</strong>d nitrogen (N2). Reactions occur between temperatures <strong>of</strong><br />
500-1400 °C <strong>an</strong>d pressures from atmospheric to 33 bar[32].<br />
The gasification oxid<strong>an</strong>t c<strong>an</strong> be air, steam, oxygen, or a mixture <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se gases[32]. Airbased<br />
gasification produces a product gas with a heating value between 4 <strong>an</strong>d 6 MJ/m 3 that<br />
contains high amounts <strong>of</strong> nitrogen, which is inert, while oxygen-based gasification produces a<br />
high quality product gas (heating value from 10 to 20 MJ/m 3 ) with relatively high amounts <strong>of</strong><br />
hydrogen <strong>an</strong>d carbon monoxide[32]. Typical components in syngas with various gasifying agents<br />
are shown in Table 2 below.<br />
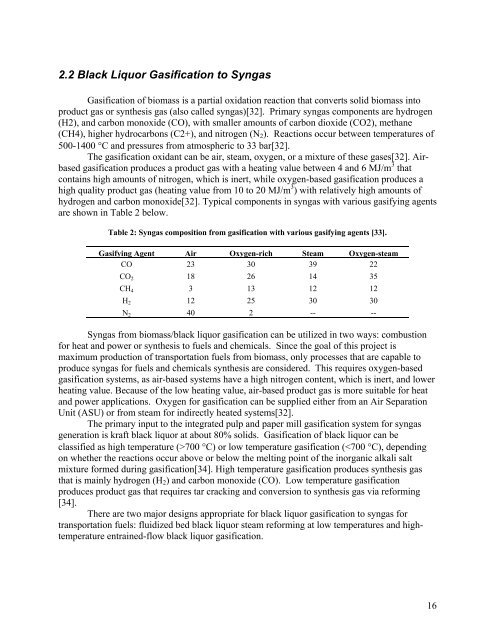
Table 2: Syngas composition from gasification with various gasifying agents [33].<br />
Gasifying Agent Air Oxygen-rich Steam Oxygen-steam<br />
CO 23 30 39 22<br />
CO2 18 26 14 35<br />
CH4 3 13 12 12<br />
H2 12 25 30 30<br />
N2 40 2 -- --<br />
Syngas from biomass/black liquor gasification c<strong>an</strong> be utilized in two ways: combustion<br />
<strong>for</strong> heat <strong>an</strong>d power or syn<strong>the</strong>sis to fuels <strong>an</strong>d chemicals. Since <strong>the</strong> goal <strong>of</strong> this project is<br />
maximum production <strong>of</strong> tr<strong>an</strong>sportation fuels from biomass, only processes that are capable to<br />
produce syngas <strong>for</strong> fuels <strong>an</strong>d chemicals syn<strong>the</strong>sis are considered. This requires oxygen-based<br />
gasification systems, as air-based systems have a high nitrogen content, which is inert, <strong>an</strong>d lower<br />
heating value. Because <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> low heating value, air-based product gas is more suitable <strong>for</strong> heat<br />
<strong>an</strong>d power applications. Oxygen <strong>for</strong> gasification c<strong>an</strong> be supplied ei<strong>the</strong>r from <strong>an</strong> Air Separation<br />
Unit (ASU) or from steam <strong>for</strong> indirectly heated systems[32].<br />
The primary input to <strong>the</strong> integrated pulp <strong>an</strong>d paper mill gasification system <strong>for</strong> syngas<br />
generation is kraft black liquor at about 80% solids. Gasification <strong>of</strong> black liquor c<strong>an</strong> be<br />
classified as high temperature (>700 °C) or low temperature gasification (