- Page 1 and 2: ������� � ���
- Page 3 and 4: 1. Overview − Introduction ......
- Page 5 and 6: 8. WRF Software − Introduction ..
- Page 7 and 8: Table of Contents Chapter 1: Overvi
- Page 9 and 10: OVERVIEW • Map projections for 1)
- Page 11 and 12: Table of Contents Chapter 2: Softwa
- Page 13 and 14: SOFTWARE INSTALLATION Note 1: If on
- Page 15 and 16: Building the WRF Code SOFTWARE INST
- Page 17 and 18: Building the WRF-Var Code SOFTWARE
- Page 19 and 20: Chapter 3: WRF Preprocessing System
- Page 21 and 22: WPS information specified by the us
- Page 23 and 24: Required Libraries The only library
- Page 25 and 26: ls drwxr-xr-x 2 4096 arch -rwxr-xr-
- Page 27 and 28: should be written to may be indicat
- Page 29 and 30: WPS When configuring a rotated lati
- Page 31 and 32: WPS geog_data_path variable. Also,
- Page 33 and 34: WPS supplied with Vtable files for
- Page 35 and 36: &share wrf_core = 'ARW', max_dom =
- Page 37 and 38: &share wrf_core = 'ARW', max_dom =
- Page 39: that the MODIS-based categories sho
- Page 43 and 44: WPS If no field is found in more th
- Page 45 and 46: WPS Output from the ungrib program
- Page 47 and 48: 5 19121.152344 0.093761623 6 19371.
- Page 49 and 50: WPS ! 0 = cylindrical equidistant !
- Page 51 and 52: The meanings of the level fields ar
- Page 53 and 54: not possible to write a geogrid bin
- Page 55 and 56: Description of the Namelist Variabl
- Page 57 and 58: 3. I_PARENT_START : A list of MAX_D
- Page 59 and 60: 21. POLE_LON : For the latitude-lon
- Page 61 and 62: 2. PRIORITY : An integer specifying
- Page 63 and 64: Default value is null (i.e., no dom
- Page 65 and 66: 17. TILE_Y : An integer specifying
- Page 67 and 68: 5. FROM_INPUT : A character string
- Page 69 and 70: 21. FLAG_IN_OUTPUT : A character st
- Page 71 and 72: 6. wt_average_16pt : Weighted sixte
- Page 73 and 74: Table 2: IGBP-Modified MODIS 20-cat
- Page 75 and 76: float MAPFAC_MY(Time, south_north,
- Page 77 and 78: :corner_lons = -93.64893f, -92.3966
- Page 79 and 80: :SOUTH-NORTH_PATCH_END_UNSTAG = 60
- Page 81 and 82: Table of Contents Chapter 4: WRF In
- Page 83 and 84: INITIALIZATION programs should be r
- Page 85 and 86: INITIALIZATION o Symmetric north an
- Page 87 and 88: INITIALIZATION • Link the WPS fil
- Page 89 and 90: Table of Contents Chapter 5: WRF Mo
- Page 91 and 92:
MODEL Hint: If using netCDF-4, make
- Page 93 and 94:
Enter appropriate options that are
- Page 95 and 96:
. Real-data case For a real-data ca
- Page 97 and 98:
MODEL eta_levels: model eta levels
- Page 99 and 100:
estart file named wrfrst_d_ will be
- Page 101 and 102:
Real Data Cases MODEL For real-data
- Page 103 and 104:
MODEL The purpose of this step is t
- Page 105 and 106:
f. Moving-Nested Run MODEL Two type
- Page 107 and 108:
MODEL Spectral Nudging is a new upp
- Page 109 and 110:
MODEL data and update these fields.
- Page 111 and 112:
MODEL If the model did not run to c
- Page 113 and 114:
2.1 Longwave Radiation (ra_lw_physi
- Page 115 and 116:
MODEL km_opt = 2 or 3, see below. A
- Page 117 and 118:
MODEL b. Vertical velocity damping
- Page 119 and 120:
MODEL The value of relax_zone may b
- Page 121 and 122:
MODEL cycling F whether this run is
- Page 123 and 124:
MODEL max_dom 1 number of domains -
- Page 125 and 126:
MODEL when SKINTEMP is not present.
- Page 127 and 128:
MODEL 0 no action taken, no adjustm
- Page 129 and 130:
MODEL 3 NCEP GFS scheme (NMM only),
- Page 131 and 132:
MODEL 5-layer slab scheme, set to l
- Page 133 and 134:
MODEL if_zfac_ph (max_dom) 0 0= nud
- Page 135 and 136:
MODEL obs_prt_freq (max_dom)10 freq
- Page 137 and 138:
MODEL recommended, except for highl
- Page 139 and 140:
&grib2 MODEL background_proc_id 255
- Page 141 and 142:
MODEL &tc controls for tc_em.exe on
- Page 143 and 144:
float Q2(Time, south_north, west_ea
- Page 145 and 146:
E:units = "s-1" ; float SINALPHA(Ti
- Page 147 and 148:
map_proj = 1: Lambert Conformal Lis
- Page 149 and 150:
Table of Contents Chapter 6: WRF-Va
- Page 151 and 152:
WRF-VAR WARNING: It is impossible t
- Page 153 and 154:
14. Darwin (MACOS) g95 with gcc (dm
- Page 155 and 156:
gzip -cd WRFNL3.1_PATCH.tar.gz | ta
- Page 157 and 158:
WRF-VAR Before running obsproc.exe,
- Page 159 and 160:
WRF-VAR There is an alternative way
- Page 161 and 162:
Observations Background Error Stati
- Page 163 and 164:
WRF-VAR / &wrfvar16 / &wrfvar17 / &
- Page 165 and 166:
Total number of obs. = 26726 Final
- Page 167 and 168:
ln -fs ad/ad_d01_2008-02-05_12:00:0
- Page 169 and 170:
WRF-VAR > ln -sf WRFDA/var/run/VARB
- Page 171 and 172:
WRF-VAR RTMINIT_NSENSOR = 12 # 5 AM
- Page 173 and 174:
WRF-VAR tions are present to keep t
- Page 175 and 176:
6: U.S. Standard Atmosphere WRF-VAR
- Page 177 and 178:
WRF-VAR clwp: cloud liquid water pa
- Page 179 and 180:
WRF-VAR and/or low boundary conditi
- Page 181 and 182:
WRF-VAR Note: Larger analysis incre
- Page 183 and 184:
WRF-VAR The variance of each variab
- Page 185 and 186:
Additional WRF-Var Exercises: (a) S
- Page 187 and 188:
You may like to compare various dia
- Page 189 and 190:
WRF-VAR thin_mesh_conv 20. for ob_f
- Page 191 and 192:
WRF-VAR &wrfvar7 cv_options 5 3: NC
- Page 193 and 194:
WRF-VAR warnings_are_fatal false cl
- Page 195 and 196:
WRF-VAR use_antcorr false (max_inst
- Page 197 and 198:
'v' = Y-direction component of wind
- Page 199 and 200:
WRF-VAR obs_gpspw_read.diag print_r
- Page 201 and 202:
write_satem If keep satem obs in ob
- Page 203 and 204:
Table of Contents Chapter 7: Object
- Page 205 and 206:
OBSGRID • Provide surface fields
- Page 207 and 208:
Banana Scheme OBSGRID In analyses o
- Page 209 and 210:
Objective Analysis on Model Nests O
- Page 211 and 212:
Check your output OBSGRID Examine t
- Page 213 and 214:
OBSGRID • All reports for each se
- Page 215 and 216:
Each report in the wrf_obs/little_r
- Page 217 and 218:
OBSGRID The end data record is simp
- Page 219 and 220:
OBSGRID remove_data_above_qc_flag 2
- Page 221 and 222:
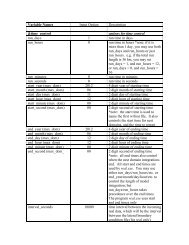
Namelist Variable Value Description
- Page 223 and 224:
Namelist record8 OBSGRID The data i
- Page 225 and 226:
Chapter 8: WRF Software Table of Co
- Page 227 and 228:
SOFTWARE variable like MPICH_F90 to
- Page 229 and 230:
SOFTWARE time configuration options
- Page 231 and 232:
SOFTWARE While the model state and
- Page 233 and 234:
SOFTWARE u_gc. It is a three dimens
- Page 235 and 236:
Registry Rconfig: SOFTWARE The Regi
- Page 237 and 238:
SOFTWARE The parallel communication
- Page 239 and 240:
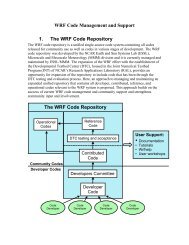
WRF source modules and subroutines
- Page 241 and 242:
Table of Contents • Introduction
- Page 243 and 244:
POST-PROCESSING It runs on many dif
- Page 245 and 246:
; load functions and procedures loa
- Page 247 and 248:
3. Create an NCL plotting script. 4
- Page 249 and 250:
POST-PROCESSING Resources unique to
- Page 251 and 252:
POST-PROCESSING If you want to add
- Page 253 and 254:
wrf_user_ll_to_ij (nc_file, lons, l
- Page 255 and 256:
NCL built-in Functions POST-PROCESS
- Page 257 and 258:
POST-PROCESSING Add the markers NCL
- Page 259 and 260:
RIP4 POST-PROCESSING RIP (which sta
- Page 261 and 262:
POST-PROCESSING Will use NETCDF in
- Page 263 and 264:
The RIP user input file POST-PROCES
- Page 265 and 266:
Plot Specification Table POST-PROCE
- Page 267 and 268:
e.g. idt rip_sample.cgm POST-PROCES
- Page 269 and 270:
POST-PROCESSING • gribinfo.txt &
- Page 271 and 272:
POST-PROCESSING plot ‘all’ Whic
- Page 273 and 274:
POST-PROCESSING User will be prompt
- Page 275 and 276:
WPP POST-PROCESSING The NCEP WRF Po
- Page 277 and 278:
./configure You will be given a lis
- Page 279 and 280:
POST-PROCESSING pressure fields on
- Page 281 and 282:
POST-PROCESSING • When using the
- Page 283 and 284:
POST-PROCESSING 7. Create namelist
- Page 285 and 286:
2. Add the location of the GrADS ex
- Page 287 and 288:
POST-PROCESSING Column integrated c
- Page 289 and 290:
POST-PROCESSING Direct soil evapora
- Page 291 and 292:
POST-PROCESSING • Animation Contr
- Page 293 and 294:
POST-PROCESSING For example, if the
- Page 295 and 296:
5. Read the VAPOR Documentation POS
- Page 297 and 298:
Table of Contents • Introduction
- Page 299 and 300:
UTILITIES AND TOOLS -ts Generate ti
- Page 301 and 302:
iowrf UTILITIES AND TOOLS This util
- Page 303 and 304:
fields List of fields to process. d
- Page 305 and 306:
&tc insert_bogus_storm = .true. rem
- Page 307 and 308:
./v_interp wrfinput_d01 wrfinput_d0
- Page 309 and 310:
Design WRF model domains WPS/util/p
- Page 311 and 312:
GRIB data UTILITIES AND TOOLS ncrca