BIOENERGY FOR EUROPE: WHICH ONES FIT BEST?
BIOENERGY FOR EUROPE: WHICH ONES FIT BEST?
BIOENERGY FOR EUROPE: WHICH ONES FIT BEST?
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
7.1 Country specific life cycle comparisons 145<br />
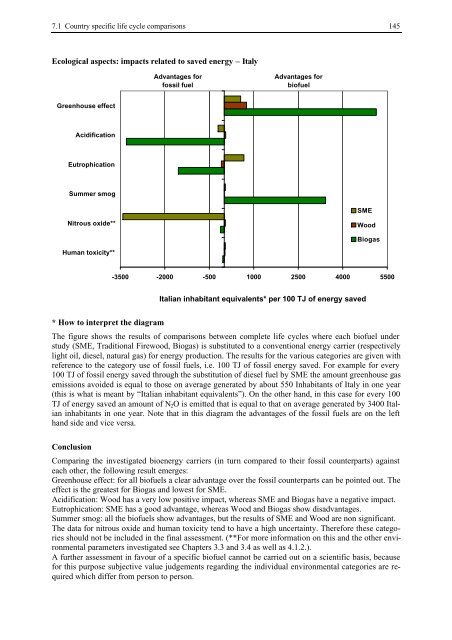
Ecological aspects: impacts related to saved energy – Italy<br />
Greenhouse effect<br />
Acidification<br />
Eutrophication<br />
Summer smog<br />
Nitrous oxide**<br />
Human toxicity**<br />
* How to interpret the diagram<br />
Advantages for<br />
fossil fuel<br />
Advantages for<br />
biofuel<br />
SME<br />
Wood<br />
Biogas<br />
-3500 -2000 -500 1000 2500 4000 5500<br />
Italian inhabitant equivalents* per 100 TJ of energy saved<br />
The figure shows the results of comparisons between complete life cycles where each biofuel under<br />
study (SME, Traditional Firewood, Biogas) is substituted to a conventional energy carrier (respectively<br />
light oil, diesel, natural gas) for energy production. The results for the various categories are given with<br />
reference to the category use of fossil fuels, i.e. 100 TJ of fossil energy saved. For example for every<br />
100 TJ of fossil energy saved through the substitution of diesel fuel by SME the amount greenhouse gas<br />
emissions avoided is equal to those on average generated by about 550 Inhabitants of Italy in one year<br />
(this is what is meant by “Italian inhabitant equivalents”). On the other hand, in this case for every 100<br />
TJ of energy saved an amount of N2O is emitted that is equal to that on average generated by 3400 Italian<br />
inhabitants in one year. Note that in this diagram the advantages of the fossil fuels are on the left<br />
hand side and vice versa.<br />
Conclusion<br />
Comparing the investigated bioenergy carriers (in turn compared to their fossil counterparts) against<br />
each other, the following result emerges:<br />
Greenhouse effect: for all biofuels a clear advantage over the fossil counterparts can be pointed out. The<br />
effect is the greatest for Biogas and lowest for SME.<br />
Acidification: Wood has a very low positive impact, whereas SME and Biogas have a negative impact.<br />
Eutrophication: SME has a good advantage, whereas Wood and Biogas show disadvantages.<br />
Summer smog: all the biofuels show advantages, but the results of SME and Wood are non significant.<br />
The data for nitrous oxide and human toxicity tend to have a high uncertainty. Therefore these categories<br />
should not be included in the final assessment. (**For more information on this and the other environmental<br />
parameters investigated see Chapters 3.3 and 3.4 as well as 4.1.2.).<br />
A further assessment in favour of a specific biofuel cannot be carried out on a scientific basis, because<br />
for this purpose subjective value judgements regarding the individual environmental categories are required<br />
which differ from person to person.