BIOENERGY FOR EUROPE: WHICH ONES FIT BEST?
BIOENERGY FOR EUROPE: WHICH ONES FIT BEST?
BIOENERGY FOR EUROPE: WHICH ONES FIT BEST?
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2.3 Life cycles of solid biofuels 17<br />
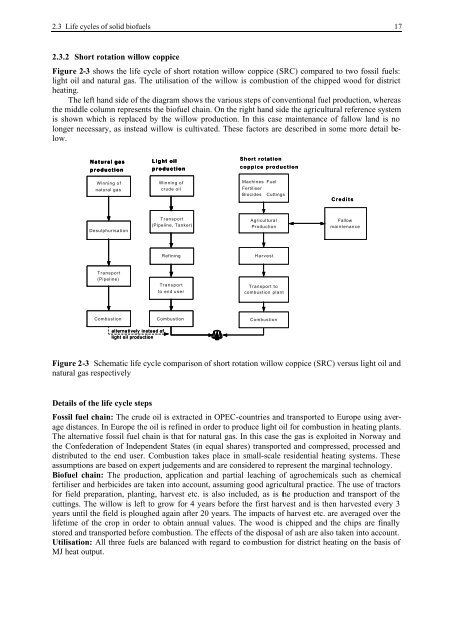
2.3.2 Short rotation willow coppice<br />
Figure 2-3 shows the life cycle of short rotation willow coppice (SRC) compared to two fossil fuels:<br />
light oil and natural gas. The utilisation of the willow is combustion of the chipped wood for district<br />
heating.<br />
The left hand side of the diagram shows the various steps of conventional fuel production, whereas<br />
the middle column represents the biofuel chain. On the right hand side the agricultural reference system<br />
is shown which is replaced by the willow production. In this case maintenance of fallow land is no<br />
longer necessary, as instead willow is cultivated. These factors are described in some more detail below.<br />
Natural gas<br />
production<br />
Winning of<br />
natural gas<br />
Desulphurisation<br />
Transport<br />
(Pipeline)<br />
Combustion<br />
Light oil<br />
alternatively instead of<br />
light oil production<br />
production<br />
Winning of<br />
crude oil<br />
Transport<br />
(Pipeline, Tanker)<br />
Refining<br />
Transport<br />
to end user<br />
Combustion<br />
Short rotation<br />
coppice production<br />
Machines Fuel<br />
Fertiliser<br />
Biocides Cuttings<br />
Agricultural<br />
Production<br />
Harvest<br />
Transport to<br />
combustion plant<br />
Combustion<br />
Credits<br />
Fallow<br />
maintenance<br />
Figure 2-3 Schematic life cycle comparison of short rotation willow coppice (SRC) versus light oil and<br />
natural gas respectively<br />
Details of the life cycle steps<br />
Fossil fuel chain: The crude oil is extracted in OPEC-countries and transported to Europe using average<br />
distances. In Europe the oil is refined in order to produce light oil for combustion in heating plants.<br />
The alternative fossil fuel chain is that for natural gas. In this case the gas is exploited in Norway and<br />
the Confederation of Independent States (in equal shares) transported and compressed, processed and<br />
distributed to the end user. Combustion takes place in small-scale residential heating systems. These<br />
assumptions are based on expert judgements and are considered to represent the marginal technology.<br />
Biofuel chain: The production, application and partial leaching of agrochemicals such as chemical<br />
fertiliser and herbicides are taken into account, assuming good agricultural practice. The use of tractors<br />
for field preparation, planting, harvest etc. is also included, as is the production and transport of the<br />
cuttings. The willow is left to grow for 4 years before the first harvest and is then harvested every 3<br />
years until the field is ploughed again after 20 years. The impacts of harvest etc. are averaged over the<br />
lifetime of the crop in order to obtain annual values. The wood is chipped and the chips are finally<br />
stored and transported before combustion. The effects of the disposal of ash are also taken into account.<br />
Utilisation: All three fuels are balanced with regard to combustion for district heating on the basis of<br />
MJ heat output.