L09: Termodinámica estadística del gas ideal
L09: Termodinámica estadística del gas ideal
L09: Termodinámica estadística del gas ideal
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>L09</strong>: <strong>Termodinámica</strong> <strong>estadística</strong> <strong>del</strong> <strong>gas</strong> <strong>ideal</strong> Equilibrio químico entre <strong>gas</strong>es <strong>ideal</strong>es<br />
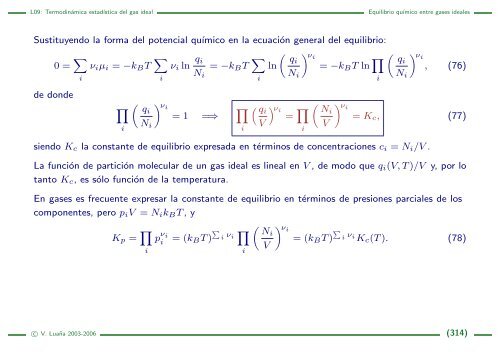
Sustituyendo la forma <strong>del</strong> potencial químico en la ecuación general <strong>del</strong> equilibrio:<br />
0 = <br />
νiµi = −kBT <br />
νi ln qi<br />
= −kBT <br />
<br />
qi<br />
ln<br />
νi = −kBT ln <br />
de donde<br />
i<br />
<br />
i<br />
qi<br />
Ni<br />
i<br />
νi<br />
Ni<br />
= 1 =⇒ <br />
i<br />
i<br />
qi<br />
V<br />
νi<br />
Ni<br />
= <br />
i<br />
Ni<br />
V<br />
νi<br />
i<br />
qi<br />
Ni<br />
νi<br />
, (76)<br />
= Kc, (77)<br />
siendo Kc la constante de equilibrio expresada en términos de concentraciones ci = Ni/V .<br />
La función de partición molecular de un <strong>gas</strong> <strong>ideal</strong> es lineal en V , de modo que qi(V, T )/V y, por lo<br />
tanto Kc, es sólo función de la temperatura.<br />
En <strong>gas</strong>es es frecuente expresar la constante de equilibrio en términos de presiones parciales de los<br />
componentes, pero piV = NikBT , y<br />
Kp = <br />
p νi i = (kBT ) <br />
i ν <br />
νi Ni<br />
i<br />
= (kBT )<br />
V<br />
<br />
i νiKc(T ). (78)<br />
i<br />
i<br />
c○ V. Luaña 2003-2006 (314)