Cours sur les méthodes d'évaluation acoustique ... - Fao - Copemed
Cours sur les méthodes d'évaluation acoustique ... - Fao - Copemed
Cours sur les méthodes d'évaluation acoustique ... - Fao - Copemed
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
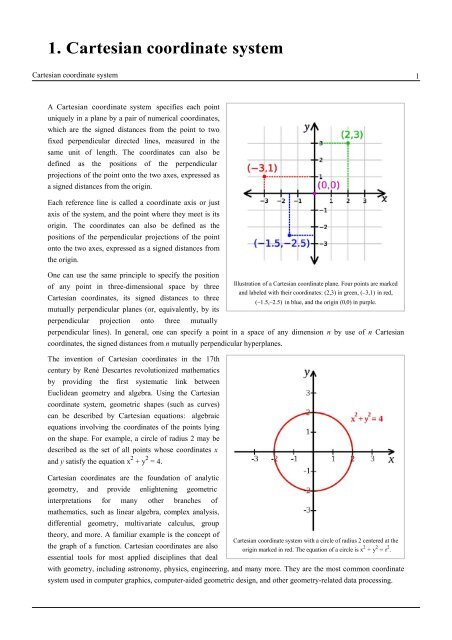
1. Cartesian coordinate systemCartesian coordinate system 1A Cartesian coordinate system specifies each pointuniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates,which are the signed distances from the point to twofixed perpendicular directed lines, mea<strong>sur</strong>ed in thesame unit of length. The coordinates can also bedefined as the positions of the perpendicularprojections of the point onto the two axes, expressed asa signed distances from the origin.Each reference line is called a coordinate axis or justaxis of the system, and the point where they meet is itsorigin. The coordinates can also be defined as thepositions of the perpendicular projections of the pointonto the two axes, expressed as a signed distances fromthe origin.One can use the same principle to specify the positionIllustration of a Cartesian coordinate plane. Four points are markedof any point in three-dimensional space by threeand labeled with their coordinates: (2,3) in green, (−3,1) in red,Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three(−1.5,−2.5) in blue, and the origin (0,0) in purple.mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by itsperpendicular projection onto three mutuallyperpendicular lines). In general, one can specify a point in a space of any dimension n by use of n Cartesiancoordinates, the signed distances from n mutually perpendicular hyperplanes.The invention of Cartesian coordinates in the 17thcentury by René Descartes revolutionized mathematicsby providing the first systematic link betweenEuclidean geometry and algebra. Using the Cartesiancoordinate system, geometric shapes (such as curves)can be described by Cartesian equations: algebraicequations involving the coordinates of the points lyingon the shape. For example, a circle of radius 2 may bedescribed as the set of all points whose coordinates xand y satisfy the equation x 2 + y 2 = 4.Cartesian coordinates are the foundation of analyticgeometry, and provide enlightening geometricinterpretations for many other branches ofmathematics, such as linear algebra, complex analysis,differential geometry, multivariate calculus, grouptheory, and more. A familiar example is the concept ofCartesian coordinate system with a circle of radius 2 centered at thethe graph of a function. Cartesian coordinates are alsoorigin marked in red. The equation of a circle is x 2 + y 2 = r 2 .essential tools for most applied disciplines that dealwith geometry, including astronomy, physics, engineering, and many more. They are the most common coordinatesystem used in computer graphics, computer-aided geometric design, and other geometry-related data processing.