Folia Geographica 10. sÄjums - Latvijas UniversitÄte
Folia Geographica 10. sÄjums - Latvijas UniversitÄte
Folia Geographica 10. sÄjums - Latvijas UniversitÄte
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
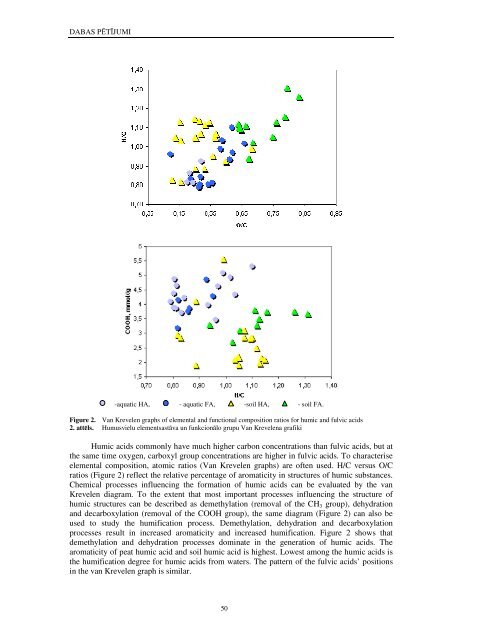
DABAS PĒTĪJUMI-aquatic HA, - aquatic FA, -soil HA, - soil FA.Figure 2. Van Krevelen graphs of elemental and functional composition ratios for humic and fulvic acids2. attēls. Humusvielu elementsastāva un funkcionālo grupu Van Krevelena grafikiHumic acids commonly have much higher carbon concentrations than fulvic acids, but atthe same time oxygen, carboxyl group concentrations are higher in fulvic acids. To characteriseelemental composition, atomic ratios (Van Krevelen graphs) are often used. H/C versus O/Cratios (Figure 2) reflect the relative percentage of aromaticity in structures of humic substances.Chemical processes influencing the formation of humic acids can be evaluated by the vanKrevelen diagram. To the extent that most important processes influencing the structure ofhumic structures can be described as demethylation (removal of the CH 3 group), dehydrationand decarboxylation (removal of the COOH group), the same diagram (Figure 2) can also beused to study the humification process. Demethylation, dehydration and decarboxylationprocesses result in increased aromaticity and increased humification. Figure 2 shows thatdemethylation and dehydration processes dominate in the generation of humic acids. Thearomaticity of peat humic acid and soil humic acid is highest. Lowest among the humic acids isthe humification degree for humic acids from waters. The pattern of the fulvic acids’ positionsin the van Krevelen graph is similar.50