vsao Journal Nr. 5 - Oktober 2022
Form - Rechnen, fliegen, gestalten Politik - Gesperrte Betten – Handeln tut not Diabetes - Neue Therapieformen Vitamine/Mineralstoffe - Ernährung bei Diabetes mellitus
Form - Rechnen, fliegen, gestalten
Politik - Gesperrte Betten – Handeln tut not
Diabetes - Neue Therapieformen
Vitamine/Mineralstoffe - Ernährung bei Diabetes mellitus
- Keine Tags gefunden...
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
Perspektiven<br />
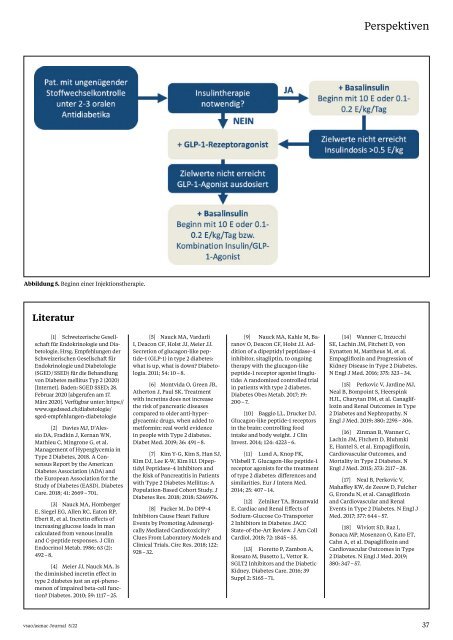
Abbildung 5. Beginn einer Injektionstherapie.<br />
Literatur<br />
[1] Schweizerische Gesellschaft<br />
für Endokrinologie und Diabetologie,<br />
Hrsg. Empfehlungen der<br />
Schweizerischen Gesellschaft für<br />
Endokrinologie und Diabetologie<br />
(SGED / SSED) für die Behandlung<br />
von Diabetes mellitus Typ 2 (2020)<br />
[Internet]. Baden: SGED SSED; 28.<br />
Februar 2020 [abgerufen am 17.<br />
März 2020]. Verfügbar unter: https://<br />
www.sgedssed.ch/diabetologie/<br />
sged-empfehlungen-diabetologie<br />
[2] Davies MJ, D'Alessio<br />
DA, Fradkin J, Kernan WN,<br />
Mathieu C, Mingrone G, et al.<br />
Management of Hyperglycemia in<br />
Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus<br />
Report by the American<br />
Diabetes Association (ADA) and<br />
the European Association for the<br />
Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes<br />
Care. 2018; 41: 2669 – 701.<br />
[3] Nauck MA, Homberger<br />
E, Siegel EG, Allen RC, Eaton RP,<br />
Ebert R, et al. Incretin effects of<br />
increasing glucose loads in man<br />
calculated from venous insulin<br />
and C-peptide responses. J Clin<br />
Endocrinol Metab. 1986; 63 (2):<br />
492 – 8.<br />
[4] Meier JJ, Nauck MA. Is<br />
the diminished incretin effect in<br />
type 2 diabetes just an epi-phenomenon<br />
of impaired beta-cell function?<br />
Diabetes. 2010; 59: 1117 – 25.<br />
[5] Nauck MA, Vardarli<br />
I, Deacon CF, Holst JJ, Meier JJ.<br />
Secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1<br />
(GLP-1) in type 2 diabetes:<br />
what is up, what is down? Diabetologia.<br />
2011; 54: 10 – 8.<br />
[6] Montvida O, Green JB,<br />
Atherton J, Paul SK. Treatment<br />
with incretins does not increase<br />
the risk of pancreatic diseases<br />
compared to older anti-hyperglycaemic<br />
drugs, when added to<br />
metformin: real world evidence<br />
in people with Type 2 diabetes.<br />
Diabet Med. 2019; 36: 491 – 8.<br />
[7] Kim Y-G, Kim S, Han SJ,<br />
Kim DJ, Lee K-W, Kim HJ. Dipeptidyl<br />
Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and<br />
the Risk of Pancreatitis in Patients<br />
with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A<br />
Population-Based Cohort Study. J<br />
Diabetes Res. 2018; 2018: 5246976.<br />
[8] Packer M. Do DPP-4<br />
Inhibitors Cause Heart Failure<br />
Events by Promoting Adrenergically<br />
Mediated Cardiotoxicity?<br />
Clues From Laboratory Models and<br />
Clinical Trials. Circ Res. 2018; 122:<br />
928 – 32.<br />
[9] Nauck MA, Kahle M, Baranov<br />
O, Deacon CF, Holst JJ. Addition<br />
of a dipeptidyl peptidase-4<br />
inhibitor, sitagliptin, to ongoing<br />
therapy with the glucagon-like<br />
peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide:<br />
A randomized controlled trial<br />
in patients with type 2 diabetes.<br />
Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017; 19:<br />
200 – 7.<br />
[10] Baggio LL, Drucker DJ.<br />
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors<br />
in the brain: controlling food<br />
intake and body weight. J Clin<br />
Invest. 2014; 124: 4223 – 6.<br />
[11] Lund A, Knop FK,<br />
Vilsbøll T. Glucagon-like peptide-1<br />
receptor agonists for the treatment<br />
of type 2 diabetes: differences and<br />
similarities. Eur J Intern Med.<br />
2014; 25: 407 – 14.<br />
[12] Zelniker TA, Braunwald<br />
E. Cardiac and Renal Effects of<br />
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter<br />
2 Inhibitors in Diabetes: JACC<br />
State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll<br />
Cardiol. 2018; 72: 1845 – 55.<br />
[13] Fioretto P, Zambon A,<br />
Rossato M, Busetto L, Vettor R.<br />
SGLT2 Inhibitors and the Diabetic<br />
Kidney. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39<br />
Suppl 2: S165 – 71.<br />
[14] Wanner C, Inzucchi<br />
SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von<br />
Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al.<br />
Empagliflozin and Progression of<br />
Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes.<br />
N Engl J Med. 2016; 375: 323 – 34.<br />
[15] Perkovic V, Jardine MJ,<br />
Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink<br />
HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin<br />
and Renal Outcomes in Type<br />
2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N<br />
Engl J Med. 2019; 380: 2295 – 306.<br />
[16] Zinman B, Wanner C,<br />
Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki<br />
E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin,<br />
Cardiovascular Outcomes, and<br />
Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N<br />
Engl J Med. 2015; 373: 2117 – 28.<br />
[17] Neal B, Perkovic V,<br />
Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher<br />
G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin<br />
and Cardiovascular and Renal<br />
Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J<br />
Med. 2017; 377: 644 – 57.<br />
[18] Wiviott SD, Raz I,<br />
Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET,<br />
Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and<br />
Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type<br />
2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;<br />
380: 347 – 57.<br />
<strong>vsao</strong> /asmac <strong>Journal</strong> 5/22 37