- Page 1 and 2:
Aditi Lahiri, Judith Meinschaefer,
- Page 3 and 4:
Contents Acquaviva, Paolo (Dublin/K
- Page 5 and 6:
Inflectional morphology as lexeme f
- Page 7 and 8:
Why nouns? Why plural? Inflectional
- Page 9 and 10:
Inflectional morphology as lexeme f
- Page 11 and 12:
Inflectional morphology as lexeme f
- Page 13 and 14:
Metaphony in two Southern Italian d
- Page 15 and 16:
3 12
- Page 17 and 18:
Metaphony (in general) Raising and/
- Page 19 and 20:
Issue Is metaphony phonological? P
- Page 21 and 22:
Characteristics of the chosen diale
- Page 23 and 24:
Previous research Phonologcial asp
- Page 25 and 26:
Piedimonte Matese (Campania) 13 22
- Page 27 and 28:
verbs total Lexical category nouns
- Page 29 and 30:
Examples Piedimonte Matese: Nouns &
- Page 31 and 32:
Gender Number Gender/ Number Morpho
- Page 33 and 34:
Phonological Model Lahiri & Reetz (
- Page 35 and 36:
Inventory of vowels (Piedimonte M.)
- Page 37 and 38:
1SG 2SG 3SG 1PL 2PL 3PL Overview of
- Page 39 and 40:
Hypotheses for the absence of metap
- Page 41 and 42:
1SG 2SG 3SG 1PL 2PL 3PL Piedimonte
- Page 43 and 44:
Morphological analysis for metaphon
- Page 45 and 46:
Exceptions Asymmetric specification
- Page 47 and 48:
Exceptions All exceptions that are
- Page 49 and 50:
Paradigmatic distribution of stems
- Page 51 and 52:
Evidence from derivation (word-form
- Page 53 and 54:
M-Type 2 Not the lexicalized metap
- Page 55 and 56:
Cutrofiano (Salento - Puglia) 43 52
- Page 57 and 58:
System of stressed vowels and metap
- Page 59 and 60:
Examples (Garrapa, 2004; Gaglia, in
- Page 61 and 62:
Evidence from derivation (word-form
- Page 63 and 64:
Conclusions Different conditions f
- Page 65 and 66:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 67 and 68:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 69 and 70:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 71 and 72:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 73 and 74:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 75 and 76:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 77 and 78:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 79 and 80:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 81 and 82:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 83 and 84:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 85 and 86:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 87 and 88:
L. Garrapa: Italian Vowel Deletion
- Page 89 and 90:
(4) C’est la combientième inonda
- Page 91 and 92:
(15) a [[deux —] NP [ou [trois
- Page 93 and 94:
Mismatches between morphological an
- Page 95 and 96:
Martin Maiden, University of Oxford
- Page 97 and 98:
3.1.5. The distribution of -tu beco
- Page 99 and 100:
i. They are distinctively identifia
- Page 101 and 102:
1 st . conj. 3 rd conj. Infinitive
- Page 103 and 104:
References Aronoff, Mark. 1994. Mor
- Page 105 and 106:
Nominal infinitives (and deverbal n
- Page 107 and 108:
For the sake of simplicity, I start
- Page 109 and 110:
Other verb classes • Unaccusative
- Page 111 and 112:
• Atelic transitive verbs (37) lo
- Page 113 and 114:
• The sharp decrease of frequency
- Page 115 and 116:
• Infinitives preceded by a deter
- Page 117 and 118:
4.2.2 Lexical category change in sy
- Page 119 and 120:
5 Conclusion Is this of any relevan
- Page 121 and 122:
Fabio Montermini CLLE - ERSS CNRS &
- Page 123 and 124:
amí[t]i ‘friends’ gré[t]i ‘
- Page 125 and 126:
stress on the penult, if there is o
- Page 127 and 128:
(13) limóne ‘lemon’ farína
- Page 129 and 130:
In all the cases of (18) the obliga
- Page 131 and 132:
P 71 50 47 30 16 13 9 9 8
- Page 133 and 134:
The features which are under evalua
- Page 135 and 136:
Lignon S., Plénat M. (to appear),
- Page 137 and 138:
form that preserves the most distin
- Page 139 and 140:
Press. Bybee, J. and Slobin, D. (19
- Page 141 and 142:
F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 143 and 144:
F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 145 and 146:
F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 147 and 148:
F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 149 and 150:
F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 151 and 152: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 153 and 154: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 155 and 156: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 157 and 158: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 159 and 160: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 161 and 162: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 163 and 164: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 165 and 166: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 167 and 168: Interim conclusion: F. Plank (frans
- Page 169 and 170: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 171 and 172: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 173 and 174: Same conclusion: F. Plank (frans.pl
- Page 175 and 176: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 177 and 178: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 179 and 180: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 181 and 182: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 183 and 184: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 185 and 186: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 187 and 188: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 189 and 190: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 191 and 192: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 193 and 194: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
- Page 195 and 196: F. Plank (frans.plank@uni-konstanz.
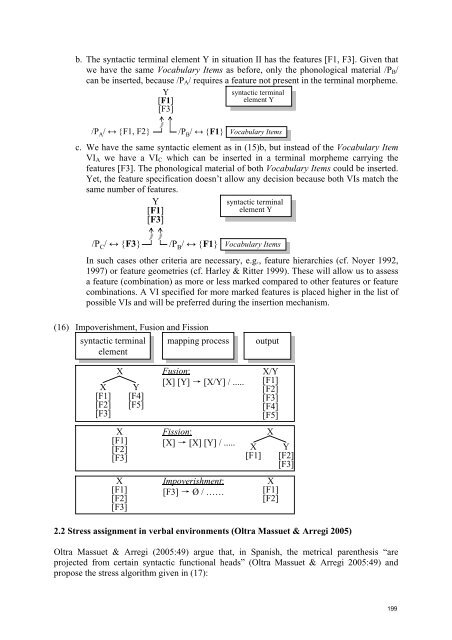
- Page 197 and 198: On the context-sensitivity of Spani
- Page 199 and 200: (5) The grammar model (Pomino 2005)
- Page 201: (11) a. At MS [morphological struct
- Page 205 and 206: (24) a. cant-a-mos [1pl], [S EQUALS
- Page 207 and 208: (34) Inward Sensitivity √/kant/ [
- Page 209 and 210: d. Strong preterite forms (P4) 1sg
- Page 211 and 212: (53) b. anduvimos Syntax √/and/ v
- Page 213 and 214: (59) c. dijo Syntax √/de-/+α Mor
- Page 215 and 216: Christoph Schwarze & Christine Kasc
- Page 217 and 218: The second and the third category w
- Page 219 and 220: Evidence for the recognition of the
- Page 221: with which they normally do not occ
- Page 224 and 225: a. ["jO…gurt] yogurt b. ["bjanko]
- Page 226 and 227: • Lexical /i/ appeared as [i] in