- Page 2 and 3:
Coordinating Committee for Geoscien
- Page 4 and 5:
Thematic Session on New Energy Reso
- Page 6 and 7:
CONTENTS Page OPENING REMARKS……
- Page 8 and 9:
OPENING REMARKS by Chen Shik Pei Di
- Page 10 and 11:
WELCOME ADDRESS by Tai-Sup Lee Pres
- Page 12 and 13:
WELCOME ADDRESS by Keun-Pil Park Di
- Page 14 and 15:
CONGRATULATORY ADDRESS by David Pri
- Page 16 and 17:
PART I GAS HYDRATE: EXPLORATION, RE
- Page 18 and 19:
Partial differential equations for
- Page 20 and 21:
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In the follo
- Page 22 and 23:
REFERENCES Berner R. A. (1980) Earl
- Page 24 and 25:
features of the seabed than those o
- Page 26 and 27:
secure the stability of the solutio
- Page 28 and 29:
trends depending on the following f
- Page 30 and 31:
Organic carbon in sediments is of i
- Page 32 and 33:
Sedimentological and Geochemical As
- Page 34 and 35:
Figure 3. Sedimentation rate of the
- Page 36 and 37:
Marine Gas Hydrate off W. Canada an
- Page 38 and 39:
Several methods for computing the Q
- Page 40 and 41:
0.035 0.03 Amplitude 0.025 0.02 0.0
- Page 42 and 43:
60 50 Amplitude 40 30 20 10 0 0 50
- Page 44 and 45:
REFERENCES Dallimore, S.R. and T.S.
- Page 46 and 47:
Frequency % 20 16 12 8 HAMA #5, MV=
- Page 48 and 49:
Figure 3. Experimental procedures f
- Page 50 and 51:
Figure 7 shows two cases of the com
- Page 52 and 53:
Seismic Characteristics of Gas Hydr
- Page 54 and 55:
Purpose The purpose of this paper i
- Page 56 and 57:
The dissociation zone created by th
- Page 58 and 59:
hydrate that forms near the wellbor
- Page 60 and 61:
dissociation, composite thermal con
- Page 62 and 63:
Figure 9. The Advanced Light Source
- Page 64 and 65:
Experimental Studies and Developmen
- Page 66 and 67:
Natural gas hydrate exploitation an
- Page 68 and 69:
Natural gas Free gas layer Figure 5
- Page 70 and 71:
Figure 7. One-dimensional developme
- Page 72 and 73:
Temper at ur e 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -4
- Page 74 and 75:
From the above discussion, the heat
- Page 76 and 77:
INTRODUCTION Clathrate hydrates are
- Page 78 and 79:
MATHEMATICAL MODEL The mathematical
- Page 80 and 81:
Where the hydrate-aqueous radius of
- Page 82 and 83:
REFERENCES Brooks, R.H., and A.T. C
- Page 84 and 85:
86 New Energy Resources in the CCOP
- Page 86 and 87:
In this paper, an overview of the M
- Page 88 and 89:
The brief tasks in the Phase I are:
- Page 90 and 91:
In "Development of the dissociation
- Page 92 and 93:
Figure 5. Preparation equipment. AN
- Page 94 and 95:
Other recent research subjects in t
- Page 96 and 97:
same crystalline structure directly
- Page 98 and 99:
Another important aspect of the pre
- Page 100 and 101:
a + CO 2 CH 4 C 2 H 6 b CH 4 in sII
- Page 102 and 103: REFERENCES Collett, T.S. and Kuuskr
- Page 104 and 105: Figure 1. Physiographic and crust m
- Page 106 and 107: Figure 3. Seismic profile showing s
- Page 108 and 109: Figure 7. Distribution of echo char
- Page 110 and 111: Figure 10. Seismic profile and its
- Page 112 and 113: In the early stage of back-arc open
- Page 114 and 115: PART II COALBED METHANE (CBM)
- Page 116 and 117: Supply and demand infrastructure of
- Page 118 and 119: Amisan, Jogyeri, Baegunsa, and Seon
- Page 120 and 121: PROPERTIES OF ANTHRACITE The coals
- Page 122 and 123: Table 4. Average chemical compositi
- Page 124 and 125: CONCLUSIONS 1. Most of the coals em
- Page 126 and 127: INTRODUCTION Coal (total reserves 2
- Page 128 and 129: ีีีีีีีีี ั ิ
- Page 130 and 131: RESULTS By Government: The outcomes
- Page 132 and 133: The gas composition (12 samples ana
- Page 134 and 135: Table 4. Coal Depth Interval Hole N
- Page 136 and 137: The results of studies made on 11 c
- Page 138 and 139: CONCLUSION CBM is still hoped to be
- Page 140 and 141: The Government of Indonesia through
- Page 142 and 143: The Berau basin is a major coal pro
- Page 144 and 145: PP: CBM - 1 Rambutan (GOI Sponsor)
- Page 146 and 147: Overview of Project for CO 2 Seques
- Page 148 and 149: The organic geochemistry research g
- Page 150 and 151: 3.5 25 3.0 20 Ar(%) C O 2(%) 2.5 2
- Page 154 and 155: Figure 1. Index map of Akabira Coal
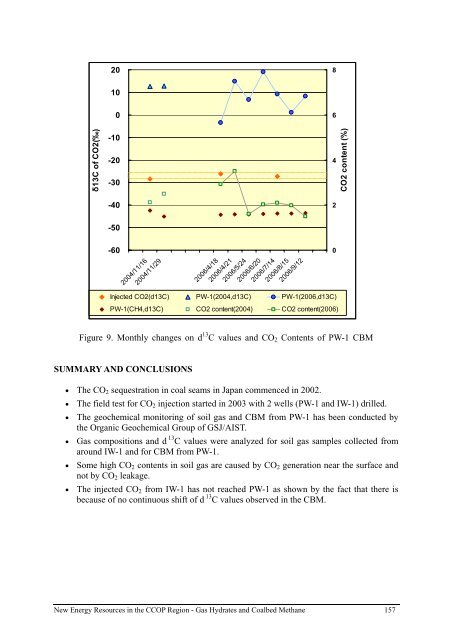
- Page 156: ORIGIN OF AKABIRA CBM In Akabira mi