You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
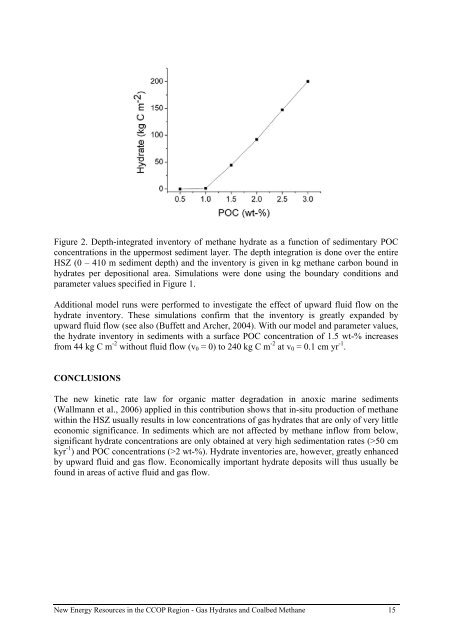
Figure 2. Depth-integrated inventory of methane <strong>hydrate</strong> as a function of sedimentary POC<br />
concentrations in the uppermost sediment layer. The depth integration is done over the entire<br />
HSZ (0 – 410 m sediment depth) and the inventory is given in kg methane carbon bound in<br />
<strong>hydrate</strong>s per depositional area. Simulations were done using the boundary conditions and<br />
parameter values specified in Figure 1.<br />
Additional model runs were performed to investigate the effect of upward fluid flow on the<br />
<strong>hydrate</strong> inventory. These simulations confirm that the inventory is greatly expanded by<br />
upward fluid flow (see also (Buffett and Archer, 2004). With our model and parameter values,<br />
the <strong>hydrate</strong> inventory in sediments with a surface POC concentration of 1.5 wt-% increases<br />
from 44 kg C m -2 without fluid flow (v 0 = 0) to 240 kg C m -2 at v 0 = 0.1 cm yr -1 .<br />
CONCLUSIONS<br />
The new kinetic rate law for organic matter degradation in anoxic marine sediments<br />
(Wallmann et al., 2006) applied in this contribution shows that in-situ production of methane<br />
within the HSZ usually results in low concentrations of <strong>gas</strong> <strong>hydrate</strong>s that are only of very little<br />
economic significance. In sediments which are not affected by methane inflow from below,<br />
significant <strong>hydrate</strong> concentrations are only obtained at very high sedimentation rates (>50 cm<br />
kyr -1 ) and POC concentrations (>2 wt-%). Hydrate inventories are, however, greatly enhanced<br />
by upward fluid and <strong>gas</strong> flow. Economically important <strong>hydrate</strong> deposits will thus usually be<br />
found in areas of active fluid and <strong>gas</strong> flow.<br />
New Energy Resources in the <strong>CCOP</strong> Region - Gas Hydrates and Coalbed Methane 15