Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
SINGLE-CYLINDER ENGINES 69<br />
0<br />
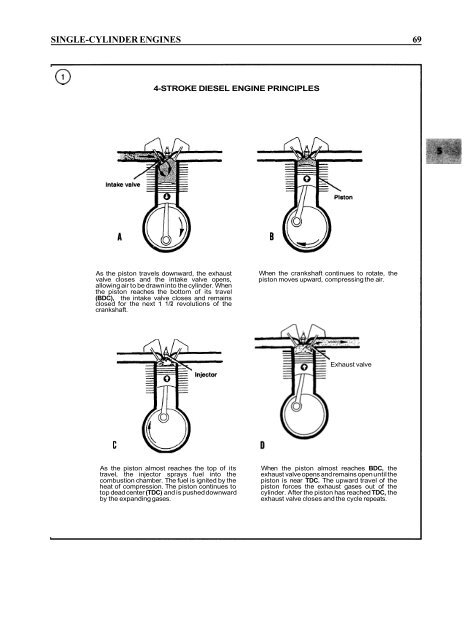
4-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE PRINCIPLES<br />
As the piston travels downward, the exhaust<br />
valve closes and the intake valve opens,<br />
allowing air to be drawn into the cylinder. When<br />
the piston reaches the bottom of its travel<br />
(BDC), the intake valve closes and remains<br />
closed for the next 1 112 revolutions of the<br />
crankshaft.<br />
When the crankshaft continues to rotate, the<br />
piston moves upward, compressing the air.<br />
Exhaust valve<br />
As the piston almost reaches the top of its<br />
travel, the injector sprays fuel into the<br />
combustion chamber. The fuel is ignited by the<br />
heat of compression. The piston continues to<br />
top dead center (TDC) and is pushed downward<br />
by the expanding gases.<br />
When the piston almost reaches BDC, the<br />
exhaust valve opens and remains open until the<br />
piston is near TDC. The upward travel of the<br />
piston forces the exhaust gases out of the<br />
cylinder. After the piston has reached TDC, the<br />
exhaust valve closes and the cycle repeats.