Seed Health Management for Better Productivity - Govind Ballabh ...
Seed Health Management for Better Productivity - Govind Ballabh ...
Seed Health Management for Better Productivity - Govind Ballabh ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
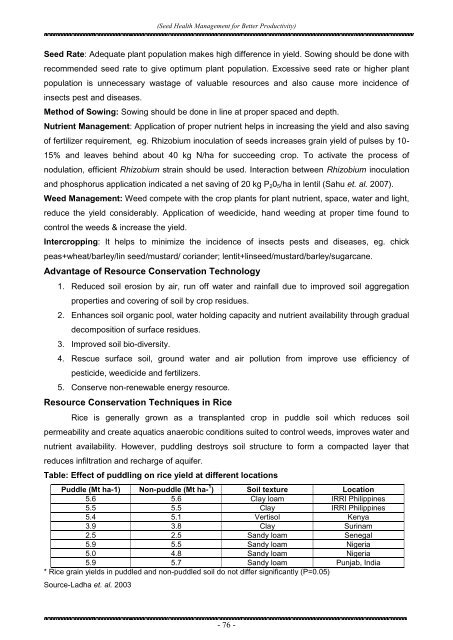
(<strong>Seed</strong> <strong>Health</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Better</strong> <strong>Productivity</strong>)<strong>Seed</strong> Rate: Adequate plant population makes high difference in yield. Sowing should be done withrecommended seed rate to give optimum plant population. Excessive seed rate or higher plantpopulation is unnecessary wastage of valuable resources and also cause more incidence ofinsects pest and diseases.Method of Sowing: Sowing should be done in line at proper spaced and depth.Nutrient <strong>Management</strong>: Application of proper nutrient helps in increasing the yield and also savingof fertilizer requirement, eg. Rhizobium inoculation of seeds increases grain yield of pulses by 10-15% and leaves behind about 40 kg N/ha <strong>for</strong> succeeding crop. To activate the process ofnodulation, efficient Rhizobium strain should be used. Interaction between Rhizobium inoculationand phosphorus application indicated a net saving of 20 kg P 2 0 5 /ha in lentil (Sahu et. al. 2007).Weed <strong>Management</strong>: Weed compete with the crop plants <strong>for</strong> plant nutrient, space, water and light,reduce the yield considerably. Application of weedicide, hand weeding at proper time found tocontrol the weeds & increase the yield.Intercropping: It helps to minimize the incidence of insects pests and diseases, eg. chickpeas+wheat/barley/lin seed/mustard/ coriander; lentit+linseed/mustard/barley/sugarcane.Advantage of Resource Conservation Technology1. Reduced soil erosion by air, run off water and rainfall due to improved soil aggregationproperties and covering of soil by crop residues.2. Enhances soil organic pool, water holding capacity and nutrient availability through gradualdecomposition of surface residues.3. Improved soil bio-diversity.4. Rescue surface soil, ground water and air pollution from improve use efficiency ofpesticide, weedicide and fertilizers.5. Conserve non-renewable energy resource.Resource Conservation Techniques in RiceRice is generally grown as a transplanted crop in puddle soil which reduces soilpermeability and create aquatics anaerobic conditions suited to control weeds, improves water andnutrient availability. However, puddling destroys soil structure to <strong>for</strong>m a compacted layer thatreduces infiltration and recharge of aquifer.Table: Effect of puddling on rice yield at different locationsPuddle (Mt ha-1) Non-puddle (Mt ha- 1 ) Soil texture Location5.6 5.6 Clay loam IRRI Philippines5.5 5.5 Clay IRRI Philippines5.4 5.1 Vertisol Kenya3.9 3.8 Clay Surinam2.5 2.5 Sandy loam Senegal5.9 5.5 Sandy loam Nigeria5.0 4.8 Sandy loam Nigeria5.9 5.7 Sandy loam Punjab, India* Rice grain yields in puddled and non-puddled soil do not differ significantly (P=0.05)Source-Ladha et. al. 2003- 76 -