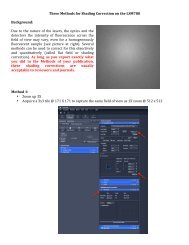
Tecnai on-line help manual -- Alignments - UT Southwestern
Tecnai on-line help manual -- Alignments - UT Southwestern
Tecnai on-line help manual -- Alignments - UT Southwestern
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<str<strong>on</strong>g>Tecnai</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong>-<strong>line</strong> <strong>help</strong> <strong>Alignments</strong> 11<str<strong>on</strong>g>Tecnai</str<strong>on</strong>g> 12 Software versi<strong>on</strong> 23.2 LensesThe lenses in electr<strong>on</strong> microscopes are electromagnetic lenses (the <strong>on</strong>ly excepti<strong>on</strong> being the gun lens inthe FEG instruments, which is an electrostatic lens). These lenses all c<strong>on</strong>sist of a coil, through which anelectrical current flows, and a magnetic circuit, which is a piece of magnetic alloy with a specific shape.The current flowing through the coil generates a magnetic field in the magnetic circuit. Where the circuitis interrupted (the gap), the magnetic field goes out into the vacuum and creates the lens field that isused for focusing the electr<strong>on</strong> beam. How the lens works is determined by the shape of the pole piece(the part of the magnetic circuit where the bore and gap are). Water flows through pipes to remove theheat generated by the electr<strong>on</strong> current in the lens coil.Changing the current through the lens coil changes the magnetic field and thus the strength of the lens.Although electromagnetic lenses and electr<strong>on</strong>s behave quite differently from light lenses and light, thegeneral principles of light optics can be applied and the electromagnetic lenses can be described forc<strong>on</strong>venience like the lenses of light optics.The TEM usually c<strong>on</strong>tains two c<strong>on</strong>denser lenses:• The first c<strong>on</strong>denser lens, or C1, determines the demagnificati<strong>on</strong> (size reducti<strong>on</strong>) of the electr<strong>on</strong>source <strong>on</strong>to the specimen and thus the spot size. Its c<strong>on</strong>trol is found under the spot size c<strong>on</strong>trol,which has 11 steps.• The sec<strong>on</strong>d c<strong>on</strong>denser lens, or C2, determines how str<strong>on</strong>gly the beam is focused <strong>on</strong>to the specimen.As a c<strong>on</strong>sequence it varies the intensity of the beam <strong>on</strong> the viewing screen. The C2 lens is c<strong>on</strong>trolledthrough the Intensity knob. Inside or close to the sec<strong>on</strong>d c<strong>on</strong>denser lens there is an aperture (thesec<strong>on</strong>d-c<strong>on</strong>denser or C2 aperture), which is used as the beam-defining aperture (it limits the amountof the beam c<strong>on</strong>vergence for a fully focused beam).The magnificati<strong>on</strong> system of the microscope c<strong>on</strong>sists of a set of five lenses: the objective, diffracti<strong>on</strong>,intermediate, projector 1 and projector 2 lenses. Except in low-magnificati<strong>on</strong> (LM) mode, the objectivelens is always the str<strong>on</strong>gest lens in the microscope, magnifying between about 20 and 50x, depending<strong>on</strong> the type of objective lens.The individual lenses of the magnificati<strong>on</strong> (or projector) system are not c<strong>on</strong>trolled directly by theoperator, but instead the microscope c<strong>on</strong>tains a number of magnificati<strong>on</strong>s for image and diffracti<strong>on</strong>mode, each with its own settings of the magnifying lenses. The <strong>on</strong>ly lenses that are c<strong>on</strong>trolled directly bythe operator are the objective lens (for focusing the image) and the diffracti<strong>on</strong> lens (for focusing thediffracti<strong>on</strong> pattern).In LM mode the objective lens is switched (nearly) off in order to achieve the smallest magnificati<strong>on</strong>s.With the objective lens off, the diffracti<strong>on</strong> lens is used for focusing the image. The electr<strong>on</strong>-opticalc<strong>on</strong>figurati<strong>on</strong> in LM is reversed with respect to the high-magnificati<strong>on</strong> range: the functi<strong>on</strong>s of the