Tecnai on-line help manual -- Alignments - UT Southwestern
Tecnai on-line help manual -- Alignments - UT Southwestern
Tecnai on-line help manual -- Alignments - UT Southwestern
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
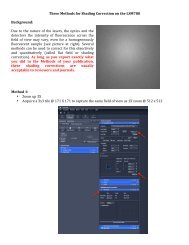
<str<strong>on</strong>g>Tecnai</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong>-<strong>line</strong> <strong>help</strong> <strong>Alignments</strong> 37<str<strong>on</strong>g>Tecnai</str<strong>on</strong>g> 12 Software versi<strong>on</strong> 27 Beam LM Procedure7.1 Preparati<strong>on</strong> Beam LM alignmentPurpose: Set up microscope for aligning the upper part of the column (illuminati<strong>on</strong> system) in LM.Importance: ESSENTIAL to make sure that the alignment is d<strong>on</strong>e for the correct c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s: centeredC2 aperture, eucentric height and specimen in focus.Method:C2 aperture centering:• Focus spot and center it <strong>on</strong> the screen• Turn INTENSITY overfocus (clockwise)• Center aperture until illuminated area is symmetrical around the screen centerEucentric height: with the CompuStage switch <strong>on</strong> the Alpha wobbler and minimize image movement bychanging the Z height.7.2 Pivot point beam shift LMPurpose: Align beam shift pivot point = make sure that the beam does not tilt when it is shifted.Importance: ESSENTIAL for keeping the beam parallel to the optical axis when shifting.Method: Shifting a beam parallel to itself means that it must always go through the fr<strong>on</strong>t-focal point (=shift pivot point) of the diffracti<strong>on</strong> lens (the 'objective' lens in LM). This plane is c<strong>on</strong>jugate to the backfocal(LAD diffracti<strong>on</strong>) plane and the alignment of the pivot point can thus be seen in LAD diffracti<strong>on</strong>. Theshift 'wobble' d<strong>on</strong>e by the microscope should give no beam tilt, so the two central spots in the diffracti<strong>on</strong>pattern should overlap.ProcedureThe alignment procedure c<strong>on</strong>sists of four steps:• Two preparati<strong>on</strong> steps for setting up the image and diffracti<strong>on</strong> pattern, respectively.• Two steps in which the X and Y pivot points are aligned.Notes:• The shift 'wobble' may have <strong>on</strong>e beam positi<strong>on</strong> blocked by the specimen. If no sec<strong>on</strong>d beam isvisible when turning MF-X, then (re)move the specimen.• Diffracti<strong>on</strong> focus: in LAD the objective lens (which is here the focusing lens) is switched to fixedsetting. To focus the diffracti<strong>on</strong> pattern to a spot pattern the Intensity should be used, not the Focus.Only if the pattern cannot be focused with the Intensity should the Focus knob (objective lens) beused. In the latter case, turn the Intensity completely overfocus (clockwise), then focus the LADpattern with the Focus knob.7.3 Pivot point beam tilt LMPurpose: Align beam tilt pivot point = make sure that the beam does not shift when it is tilted.Importance: ESSENTIAL for keeping the beam centered during rotati<strong>on</strong>-center alignment and focusingusing the wobbler.Method: A tilting beam must remain centered <strong>on</strong> the specimen (so the tilt pivot point coincides with thespecimen). The tilt wobble d<strong>on</strong>e by the microscope should give no beam shift, so <strong>on</strong>ly <strong>on</strong>e spot shouldbe visible in the image.