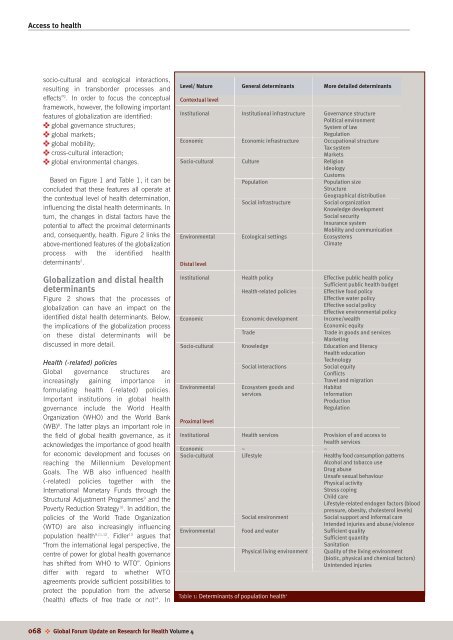
Access <strong>to</strong> <strong>health</strong>socio-cultural <strong>and</strong> ecological interactions,resulting in transborder processes <strong>and</strong>effects” 2 . In order <strong>to</strong> focus <strong>the</strong> conceptualframework, however, <strong>the</strong> following importantfeatures of globalization are identified:✜ global governance structures;✜ global markets;✜ global mobility;✜ cross-cultural interaction;✜ global environmental changes.Based on Figure 1 <strong>and</strong> Table 1, it can beconcluded that <strong>the</strong>se features all operate at<strong>the</strong> contextual level of <strong>health</strong> determination,influencing <strong>the</strong> distal <strong>health</strong> determinants. Inturn, <strong>the</strong> changes in distal fac<strong>to</strong>rs have <strong>the</strong>potential <strong>to</strong> affect <strong>the</strong> proximal determinants<strong>and</strong>, consequently, <strong>health</strong>. Figure 2 links <strong>the</strong>above-mentioned features of <strong>the</strong> globalizationprocess with <strong>the</strong> identified <strong>health</strong>determinants 2 .Globalization <strong>and</strong> distal <strong>health</strong>determinantsFigure 2 shows that <strong>the</strong> processes ofglobalization can have an impact on <strong>the</strong>identified distal <strong>health</strong> determinants. Below,<strong>the</strong> implications of <strong>the</strong> globalization processon <strong>the</strong>se distal determinants will bediscussed in more detail.Health (-related) policiesGlobal governance structures areincreasingly gaining importance informulating <strong>health</strong> (-related) policies.Important institutions in global <strong>health</strong>governance include <strong>the</strong> World HealthOrganization (WHO) <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> World Bank(WB) 8 . The latter plays an important role in<strong>the</strong> field of global <strong>health</strong> governance, as itacknowledges <strong>the</strong> importance of good <strong>health</strong>for economic development <strong>and</strong> focuses on<strong>reach</strong>ing <strong>the</strong> Millennium DevelopmentGoals. The WB also influenced <strong>health</strong>(-related) policies <strong>to</strong>ge<strong>the</strong>r with <strong>the</strong>International Monetary Funds through <strong>the</strong>Structural Adjustment Programmes 9 <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>Poverty Reduction Strategy 10 . In addition, <strong>the</strong>policies of <strong>the</strong> World Trade Organization(WTO) are also increasingly influencingpopulation <strong>health</strong> 9,11,12 . Fidler 13 argues that“from <strong>the</strong> international legal perspective, <strong>the</strong>centre of power for global <strong>health</strong> governancehas shifted from WHO <strong>to</strong> WTO”. Opinionsdiffer with regard <strong>to</strong> whe<strong>the</strong>r WTOagreements provide sufficient possibilities <strong>to</strong>protect <strong>the</strong> population from <strong>the</strong> adverse(<strong>health</strong>) effects of free trade or not 14 . InLevel/ Nature General determinants More detailed determinantsContextual levelInstitutional Institutional infrastructure Governance structurePolitical environmentSystem of lawRegulationEconomic Economic infrastructure Occupational structureTax systemMarketsSocio-cultural Culture ReligionIdeologyCus<strong>to</strong>msPopulationPopulation sizeStructureSocial infrastructureEnvironmental Ecological settings EcosystemsClimateDistal levelGeographical distributionSocial organizationKnowledge developmentSocial securityInsurance systemMobility <strong>and</strong> communicationInstitutional Health policy Effective public <strong>health</strong> policySufficient public <strong>health</strong> budgetHealth-related policiesEffective food policyEffective water policyEffective <strong>social</strong> policyEffective environmental policyEconomic Economic development Income/wealthEconomic equityTradeTrade in goods <strong>and</strong> servicesMarketingSocio-cultural Knowledge Education <strong>and</strong> literacyHealth educationTechnologySocial interactionsSocial equityConflictsTravel <strong>and</strong> migrationEnvironmental Ecosystem goods <strong>and</strong> HabitatservicesProximal levelInformationProductionRegulationInstitutional Health services Provision of <strong>and</strong> access <strong>to</strong><strong>health</strong> servicesEconomic – –Socio-cultural Lifestyle Healthy food consumption patternsAlcohol <strong>and</strong> <strong>to</strong>bacco useDrug abuseUnsafe sexual behaviourPhysical activityStress copingChild careLifestyle-related endogen fac<strong>to</strong>rs (bloodpressure, obesity, cholesterol levels)Social environmentSocial support <strong>and</strong> informal careIntended injuries <strong>and</strong> abuse/violenceEnvironmental Food <strong>and</strong> water Sufficient qualitySufficient quantitySanitationPhysical living environmentTable 1: Determinants of population <strong>health</strong> 2Quality of <strong>the</strong> living environment(biotic, physical <strong>and</strong> chemical fac<strong>to</strong>rs)Unintended injuries068 ✜ Global Forum Update on Research for Health Volume 4
Access <strong>to</strong> <strong>health</strong>2001, WTO ruled that <strong>the</strong> French ban on <strong>the</strong> import of allproducts containing asbes<strong>to</strong>s was legal on <strong>health</strong> grounds,despite protests from Canada 15,16 . However, protecting citizensagainst <strong>health</strong> risks in cases of scientific uncertainty is stilldifficult, as WTO is reluctant <strong>to</strong> accept precautionary traderestrictions 17 .Economic developmentOpinions differ with regard <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> economic benefits ofeconomic globalization. On one side, “optimists” argue thatglobal markets facilitate economic growth <strong>and</strong> economicsecurity, which would benefit <strong>health</strong> (e.g. Frankel 18 , BenDavid 19 , Dollar <strong>and</strong> Kraay 20 <strong>and</strong> Feachem 21 ). On <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>rside, “pessimists” are worried about <strong>the</strong> <strong>health</strong> effects of <strong>the</strong>global market. Baum 22 states that “<strong>the</strong> current forms ofglobalization are making <strong>the</strong> world a safe place for unfetteredmarket liberalism <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> consequent growth ofinequities…posing severe threats <strong>to</strong> people’s <strong>health</strong>”. The2005 Human Development Report 23 argues that one of <strong>the</strong>prevailing “myths” of economic globalization is that openmarkets will result in an era of convergence; tradeliberalization “has done little <strong>to</strong> slow down <strong>the</strong>marginalization of sub-Saharan Africa” <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> current“trading system favours <strong>the</strong> developed world”. In fact,notwithst<strong>and</strong>ing some spectacular growth rates, especially inEast Asia, incomes declined between 1965 <strong>and</strong> 1997 in 16of <strong>the</strong> world poorest countries 24 .TradeDue <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> establishment of global markets <strong>and</strong> a globaltrading system, <strong>the</strong>re has been a continuing increase in worldtrade. According <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> WTO, <strong>to</strong>tal trade multiplied by a fac<strong>to</strong>rof 14 between 1950 <strong>and</strong> 1997 25 . More recently, <strong>the</strong> year2004 saw an impressive growth in trade, which exceededaverage growth recorded over <strong>the</strong> preceding decade 26 . Todayall countries trade internationally <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>y trade significantproportions of <strong>the</strong>ir national income. The array of productsbeing traded is wide-ranging; from primary commodities <strong>to</strong>manufactured goods. Besides goods, services are increasinglybeing traded as well 27 . In addition <strong>to</strong> legal trade transactions,illegal drug trade is also globalizing.Social interactions: migrationDue <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> changes in <strong>the</strong> infrastructures of transportation <strong>and</strong>communication, human migration has increased atunprecedented rates. According <strong>to</strong> Held et al. 27 , <strong>to</strong>urism is oneof <strong>the</strong> most obvious forms of cultural globalization. However,travel for business <strong>and</strong> pleasure constitutes only a fraction of<strong>to</strong>tal human movement. O<strong>the</strong>r examples of people migrating aremissionaries, merchant marines, students, pilgrims, militaries,migrant workers <strong>and</strong> Peace Corps workers 27,28 . Besides <strong>the</strong>seforms of voluntary migration, resettlement by refugees is also animportant issue. The UN Population Division estimates <strong>the</strong>global migrant population in 2005 at between 185 <strong>and</strong> 192million people 29 . However, <strong>the</strong> concerns regarding <strong>the</strong>economic, political, <strong>social</strong> <strong>and</strong> environmental consequences ofmigration are growing 30 <strong>and</strong> many governments are moving<strong>to</strong>wards more restrictive immigration policies.Social interactions: conflictsIn <strong>the</strong> aftermath of <strong>the</strong> terrorist attacks on September 112001, many questioned <strong>the</strong> possible links betweenglobalization <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> risk on conflicts. On <strong>the</strong> one side,globalizations can decrease <strong>the</strong> risk on tensions <strong>and</strong>conflicts, as societies become more dependent on each.O<strong>the</strong>rs argue that <strong>the</strong> resistance <strong>to</strong> globalization has resultedin religious fundamentalism, <strong>and</strong> worldwide tensions <strong>and</strong>in<strong>to</strong>lerance 31 . According <strong>to</strong> Hunting<strong>to</strong>n 32 , <strong>the</strong> increasingcross-cultural interactions will result in a “clash ofcivilizations”. Nassar 33 describes globalization as a processthat leads <strong>to</strong> a “migration of dreams” in which <strong>the</strong> world’spoor are able <strong>to</strong> learn of <strong>the</strong> luxuries of <strong>the</strong> western world;<strong>the</strong> increased degree of relative deprivation results in growingtensions. In addition, Zwi et al. 34 identify several o<strong>the</strong>r fac<strong>to</strong>rsthat are associated with both globalization <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> risk ofconflicts, such as increased global trade in arms <strong>and</strong>inadequate policies.Social interactions: <strong>social</strong> equity <strong>and</strong> <strong>social</strong> networksGlobal communication, global mobility <strong>and</strong> cross-culturalinteraction can also influence cultural norms <strong>and</strong> valuesabout <strong>social</strong> solidarity <strong>and</strong> <strong>social</strong> equity. It is feared that <strong>the</strong>self-interested individualism of <strong>the</strong> marketplace spills overin<strong>to</strong> cultural norms <strong>and</strong> values resulting in increasing <strong>social</strong>exclusion <strong>and</strong> <strong>social</strong> inequity. Exclusion involvesdisintegration from common cultural processes, lack ofparticipation in <strong>social</strong> activities, alienation from decisionmaking<strong>and</strong> civic participation <strong>and</strong> barriers <strong>to</strong> employment<strong>and</strong> material sources 35 . On <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r h<strong>and</strong>, however, <strong>the</strong>geographical scale of <strong>social</strong> networks is increasing due <strong>to</strong>global communications <strong>and</strong> global media. Like-mindedpeople are now able <strong>to</strong> interact at distance through, forexample, <strong>the</strong> Internet. The women’s movement, <strong>the</strong> peacemovement, organized religion <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> environmentalmovement are good examples of transnational networks 27 .The digital divide between poor <strong>and</strong> rich, however, can resultin <strong>social</strong> exclusion from <strong>the</strong> global civil society.KnowledgeThe knowledge capital within a population is increasinglyaffected by global developments in communication <strong>and</strong>mobility. The term “globalization of education” suggestsgetting education in<strong>to</strong> every nook <strong>and</strong> cranny of <strong>the</strong> globe.Millions of people now acquire part of <strong>the</strong>ir knowledge fromtransworld textbooks. Most universities work <strong>to</strong>ge<strong>the</strong>r withacademics from different countries, students have ampleopportunities <strong>to</strong> study abroad <strong>and</strong> “virtual campuses” havebeen developed. In addition, television, film <strong>and</strong> computergraphics have greatly enlarged <strong>the</strong> visual dimensions ofcommunication. Many people <strong>to</strong>day “read” <strong>the</strong> globalizedworld without a book 36 . Overall, it is expected that <strong>the</strong>sedevelopments will also improve <strong>health</strong> training <strong>and</strong> <strong>health</strong>education (e.g. Feachem 21 <strong>and</strong> Lee 37 ).Ecosystem goods <strong>and</strong> servicesGlobal environmental changes are affecting <strong>the</strong> provision ofecosystem goods <strong>and</strong> services <strong>to</strong> mankind. TheGlobal Forum Update on Research for Health Volume 4 ✜ 069












![[re-tender] RFQ for supply of Diesel Generator - Brac](https://img.yumpu.com/44421374/1/186x260/re-tender-rfq-for-supply-of-diesel-generator-brac.jpg?quality=85)
