Combining health and social protection measures to reach the ultra ...
Combining health and social protection measures to reach the ultra ...
Combining health and social protection measures to reach the ultra ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
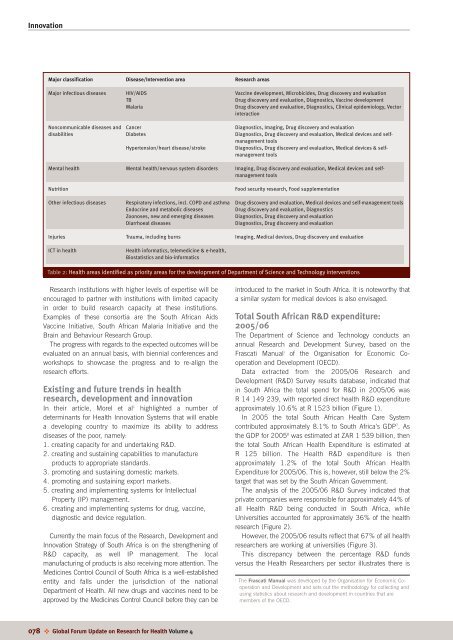
InnovationMajor classificationMajor infectious diseasesNoncommunicable diseases <strong>and</strong>disabilitiesMental <strong>health</strong>NutritionO<strong>the</strong>r infectious diseasesInjuriesICT in <strong>health</strong>Disease/Intervention areaHIV/AIDSTBMalariaCancerDiabetesHypertension/heart disease/strokeMental <strong>health</strong>/nervous system disordersRespira<strong>to</strong>ry infections, incl. COPD <strong>and</strong> asthmaEndocrine <strong>and</strong> metabolic diseasesZoonoses, new <strong>and</strong> emerging diseasesDiarrhoeal diseasesTrauma, including burnsHealth informatics, telemedicine & e-<strong>health</strong>,Biostatistics <strong>and</strong> bio-informaticsResearch areasVaccine development, Microbicides, Drug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluationDrug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluation, Diagnostics, Vaccine developmentDrug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluation, Diagnostics, Clinical epidemiology, Vec<strong>to</strong>rinteractionDiagnostics, Imaging, Drug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluationDiagnostics, Drug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluation, Medical devices <strong>and</strong> selfmanagement<strong>to</strong>olsDiagnostics, Drug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluation, Medical devices & selfmanagement<strong>to</strong>olsImaging, Drug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluation, Medical devices <strong>and</strong> selfmanagement<strong>to</strong>olsFood security research, Food supplementationDrug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluation, Medical devices <strong>and</strong> self-management <strong>to</strong>olsDrug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluation, DiagnosticsDiagnostics, Drug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluationDiagnostics, Drug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluationImaging, Medical devices, Drug discovery <strong>and</strong> evaluationTable 2: Health areas identified as priority areas for <strong>the</strong> development of Department of Science <strong>and</strong> Technology interventionsResearch institutions with higher levels of expertise will beencouraged <strong>to</strong> partner with institutions with limited capacityin order <strong>to</strong> build research capacity at <strong>the</strong>se institutions.Examples of <strong>the</strong>se consortia are <strong>the</strong> South African AidsVaccine Initiative, South African Malaria Initiative <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>Brain <strong>and</strong> Behaviour Research Group.The progress with regards <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> expected outcomes will beevaluated on an annual basis, with biennial conferences <strong>and</strong>workshops <strong>to</strong> showcase <strong>the</strong> progress <strong>and</strong> <strong>to</strong> re-align <strong>the</strong>research efforts.Existing <strong>and</strong> future trends in <strong>health</strong>research, development <strong>and</strong> innovationIn <strong>the</strong>ir article, Morel et al 1 highlighted a number ofdeterminants for Health Innovation Systems that will enablea developing country <strong>to</strong> maximize its ability <strong>to</strong> addressdiseases of <strong>the</strong> poor, namely:1. creating capacity for <strong>and</strong> undertaking R&D.2. creating <strong>and</strong> sustaining capabilities <strong>to</strong> manufactureproducts <strong>to</strong> appropriate st<strong>and</strong>ards.3. promoting <strong>and</strong> sustaining domestic markets.4. promoting <strong>and</strong> sustaining export markets.5. creating <strong>and</strong> implementing systems for IntellectualProperty (IP) management.6. creating <strong>and</strong> implementing systems for drug, vaccine,diagnostic <strong>and</strong> device regulation.Currently <strong>the</strong> main focus of <strong>the</strong> Research, Development <strong>and</strong>Innovation Strategy of South Africa is on <strong>the</strong> streng<strong>the</strong>ning ofR&D capacity, as well IP management. The localmanufacturing of products is also receiving more attention. TheMedicines Control Council of South Africa is a well-establishedentity <strong>and</strong> falls under <strong>the</strong> jurisdiction of <strong>the</strong> nationalDepartment of Health. All new drugs <strong>and</strong> vaccines need <strong>to</strong> beapproved by <strong>the</strong> Medicines Control Council before <strong>the</strong>y can beintroduced <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> market in South Africa. It is noteworthy thata similar system for medical devices is also envisaged.Total South African R&D expenditure:2005/06The Department of Science <strong>and</strong> Technology conducts anannual Research <strong>and</strong> Development Survey, based on <strong>the</strong>Frascati Manual i of <strong>the</strong> Organisation for Economic Cooperation<strong>and</strong> Development (OECD).Data extracted from <strong>the</strong> 2005/06 Research <strong>and</strong>Development (R&D) Survey results database, indicated thatin South Africa <strong>the</strong> <strong>to</strong>tal spend for R&D in 2005/06 wasR 14 149 239, with reported direct <strong>health</strong> R&D expenditureapproximately 10.6% at R 1523 billion (Figure 1).In 2005 <strong>the</strong> <strong>to</strong>tal South African Health Care Systemcontributed approximately 8.1% <strong>to</strong> South Africa’s GDP 7 . As<strong>the</strong> GDP for 2005 8 was estimated at ZAR 1 539 billion, <strong>the</strong>n<strong>the</strong> <strong>to</strong>tal South African Health Expenditure is estimated atR 125 billion. The Health R&D expenditure is <strong>the</strong>napproximately 1.2% of <strong>the</strong> <strong>to</strong>tal South African HealthExpenditure for 2005/06. This is, however, still below <strong>the</strong> 2%target that was set by <strong>the</strong> South African Government.The analysis of <strong>the</strong> 2005/06 R&D Survey indicated thatprivate companies were responsible for approximately 44% ofall Health R&D being conducted in South Africa, whileUniversities accounted for approximately 36% of <strong>the</strong> <strong>health</strong>research (Figure 2).However, <strong>the</strong> 2005/06 results reflect that 67% of all <strong>health</strong>researchers are working at universities (Figure 3).This discrepancy between <strong>the</strong> percentage R&D fundsversus <strong>the</strong> Health Researchers per sec<strong>to</strong>r illustrates <strong>the</strong>re isi.The Frascati Manual was developed by <strong>the</strong> Organisation for Economic Cooperation<strong>and</strong> Development <strong>and</strong> sets out <strong>the</strong> methodology for collecting <strong>and</strong>using statistics about research <strong>and</strong> development in countries that aremembers of <strong>the</strong> OECD.078 ✜ Global Forum Update on Research for Health Volume 4












![[re-tender] RFQ for supply of Diesel Generator - Brac](https://img.yumpu.com/44421374/1/186x260/re-tender-rfq-for-supply-of-diesel-generator-brac.jpg?quality=85)
