Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Section 3—Antiretroviral Therapy | 3–51<br />
Antiretroviral Medications and Oral Contraceptive Agents<br />
Background<br />
This chapter highlights <strong>the</strong> interactions between<br />
currently available antiretroviral agents and oral<br />
contraceptives.<br />
The oral contraceptives ethinyl estradiol and<br />
norethindrone may interact in <strong>com</strong>plex ways with<br />
protease inhibitors (PIs) and nonnucleoside reverse<br />
transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). The mechanism <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong>se interactions may be multifactorial and includes <strong>the</strong><br />
activity <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se agents on cytochrome P450 enzymes.<br />
Pharmacokinetic studies have shown changes (ei<strong>the</strong>r<br />
increases or decreases) in levels <strong>of</strong> ethinyl estradiol<br />
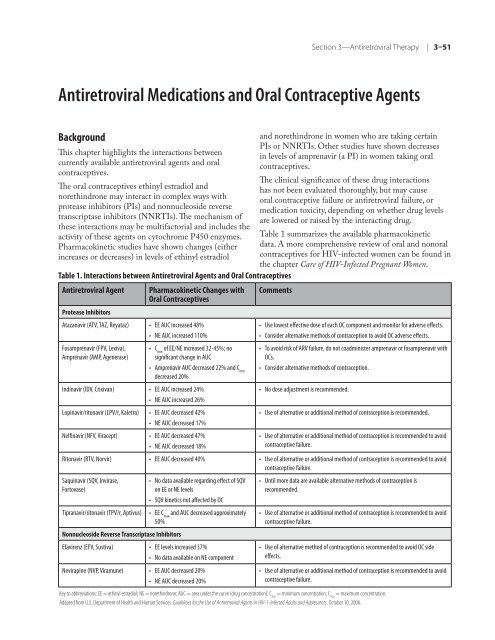
Table 1. Interactions between Antiretroviral Agents and Oral Contraceptives<br />
Antiretroviral Agent Pharmacokinetic Changes with<br />
Oral Contraceptives<br />
Protease Inhibitors<br />
Atazanavir (ATV, TAZ, Reyataz) • EE AUC increased 48%<br />
• NE AUC increased 110%<br />
Fosamprenavir (FPV, Lexiva),<br />
Amprenavir (AMP, Agenerase)<br />
•<br />
•<br />
C min <strong>of</strong> EE/NE increased 32-45%; no<br />
significant change in AUC<br />
Amprenavir AUC decreased 22% and C min<br />
decreased 20%<br />
Indinavir (IDV, Crixivan) • EE AUC increased 24%<br />
• NE AUC increased 26%<br />
Lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r, Kaletra) • EE AUC decreased 42%<br />
• NE AUC decreased 17%<br />
Nelfinavir (NFV, Viracept) • EE AUC decreased 47%<br />
• NE AUC decreased 18%<br />
and norethindrone in women who are taking certain<br />
PIs or NNRTIs. O<strong>the</strong>r studies have shown decreases<br />
in levels <strong>of</strong> amprenavir (a PI) in women taking oral<br />
contraceptives.<br />
The clinical significance <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se drug interactions<br />
has not been evaluated thoroughly, but may cause<br />
oral contraceptive failure or antiretroviral failure, or<br />
medication toxicity, depending on whe<strong>the</strong>r drug levels<br />
are lowered or raised by <strong>the</strong> interacting drug.<br />
Table 1 summarizes <strong>the</strong> available pharmacokinetic<br />
data. A more <strong>com</strong>prehensive review <strong>of</strong> oral and nonoral<br />
contraceptives <strong>for</strong> <strong>HIV</strong>-infected women can be found in<br />
<strong>the</strong> chapter Care <strong>of</strong> <strong>HIV</strong>-<strong>Infected</strong> Pregnant Women.<br />
Comments<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
Use lowest effective dose <strong>of</strong> each OC <strong>com</strong>ponent and monitor <strong>for</strong> adverse effects.<br />
Consider alternative methods <strong>of</strong> contraception to avoid OC adverse effects.<br />
To avoid risk <strong>of</strong> ARV failure, do not coadminister amprenavir or fosamprenavir with<br />
OCs.<br />
Consider alternative methods <strong>of</strong> contraception.<br />
No dose adjustment is re<strong>com</strong>mended.<br />
Use <strong>of</strong> alternative or additional method <strong>of</strong> contraception is re<strong>com</strong>mended.<br />
Use <strong>of</strong> alternative or additional method <strong>of</strong> contraception is re<strong>com</strong>mended to avoid<br />
contraceptive failure.<br />
Ritonavir (RTV, Norvir) • EE AUC decreased 40%<br />
• Use <strong>of</strong> alternative or additional method <strong>of</strong> contraception is re<strong>com</strong>mended to avoid<br />
contraceptive failure.<br />
Saquinavir (SQV, Invirase,<br />
Fortovase)<br />
•<br />
•<br />
No data available regarding effect <strong>of</strong> SQV<br />
on EE or NE levels<br />
SQV kinetics not affected by OC<br />
•<br />
Until more data are available alternative methods <strong>of</strong> contraception is<br />
re<strong>com</strong>mended.<br />
Tipranavir/ritonavir (TPV/r, Aptivus) • EE C and AUC decreased approximately • Use <strong>of</strong> alternative or additional method <strong>of</strong> contraception is re<strong>com</strong>mended to avoid<br />
max<br />
50%<br />
contraceptive failure.<br />
Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors<br />
Efavirenz (EFV, Sustiva) • EE levels increased 37%<br />
• No data available on NE <strong>com</strong>ponent<br />
Nevirapine (NVP, Viramune) • EE AUC decreased 20%<br />
• NE AUC decreased 20%<br />
•<br />
•<br />
Use <strong>of</strong> alternative method <strong>of</strong> contraception is re<strong>com</strong>mended to avoid OC side<br />
effects.<br />
Use <strong>of</strong> alternative or additional method <strong>of</strong> contraception is re<strong>com</strong>mended to avoid<br />
contraceptive failure.<br />
Key to abbreviations: EE = ethinyl estradiol; NE = norethindrone; AUC = area under <strong>the</strong> curve (drug concentration); C min = minimum concentration; C max = maximum concentration.<br />
Adapted from U.S. Department <strong>of</strong> Health and Human Services. Guidelines <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> Use <strong>of</strong> Antiretroviral Agents in <strong>HIV</strong>-1-<strong>Infected</strong> Adults and Adolescents. October 10, 2006.