- Page 1 and 2:
Clinical Manual for Management of t
- Page 3 and 4:
Table of Contents Clinical Manual f
- Page 5 and 6:
Clinical Manual for Management of t
- Page 7 and 8:
Preface—About this Manual | Clini
- Page 9:
Previous Editions Atlanta Contribut
- Page 12 and 13:
♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ | Clinical Manu
- Page 14 and 15:
1-2 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 16 and 17:
1-4 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 18 and 19:
1-6 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 20 and 21:
1-8 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 23 and 24:
Initial Physical Examination Backgr
- Page 25 and 26:
Genitals/Rectum • Inspect the gen
- Page 27 and 28:
Initial and Interim Laboratory and
- Page 29 and 30:
Section 1—Testing and Assessment
- Page 31:
Patient Education ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ D
- Page 34 and 35:
1-22 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 36 and 37:
1-24 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 38 and 39:
1-26 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 40 and 41:
1-28 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
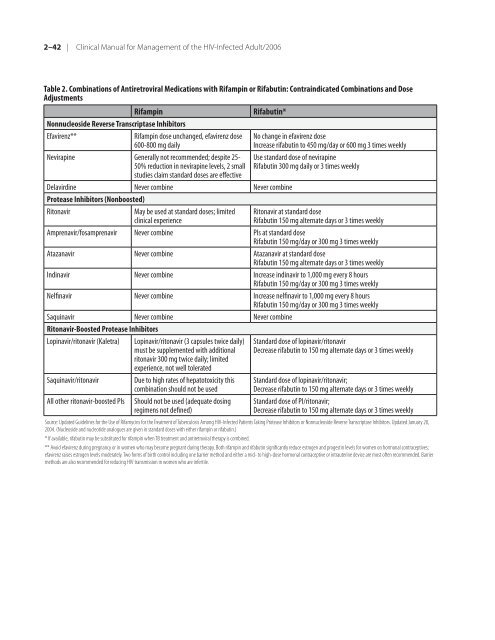
- Page 42 and 43: 1-30 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 44 and 45: 1-32 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 46 and 47: 1-34 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 48 and 49: 1-36 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 51 and 52: Section 2—Health Maintenance and
- Page 53: References ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦
- Page 56 and 57: 2-6 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 58 and 59: 2-8 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 60 and 61: 2-10 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 62 and 63: 2-12 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 64 and 65: 2-14 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 67 and 68: Occupational Postexposure Prophylax
- Page 69 and 70: P: Plan Laboratory Testing Provide
- Page 71 and 72: For hepatitis C, no recommended pro
- Page 73 and 74: Section 2—Health Maintenance and
- Page 75 and 76: as hepatitis C or another sexually
- Page 77 and 78: for treatment is appropriate, and b
- Page 79 and 80: Section 2—Health Maintenance and
- Page 81 and 82: contact with the patient. Patients
- Page 83 and 84: tablet daily of trimethoprim-sulfam
- Page 85 and 86: Opportunistic Infection Prophylaxis
- Page 87 and 88: Discontinuing Primary Prophylaxis P
- Page 89 and 90: Latent Tuberculosis Background Late
- Page 91: INH may cause liver toxicity and it
- Page 96 and 97: 2-46 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 98 and 99: 3-2 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 100 and 101: 3-4 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 102 and 103: 3-6 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 104 and 105: 3-8 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 106 and 107: 3-10 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 108 and 109: 3-12 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 110 and 111: 3-14 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 112 and 113: 3-16 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 114 and 115: 3-18 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 117 and 118: Reducing Maternal-Infant HIV Transm
- Page 119 and 120: Some states require written informe
- Page 121 and 122: contraindicated during pregnancy be
- Page 123 and 124: Section 3—Antiretroviral Therapy
- Page 125 and 126: Nelfinavir (Viracept) Adequate drug
- Page 127 and 128: Section 3—Antiretroviral Therapy
- Page 129 and 130: Section 3—Antiretroviral Therapy
- Page 131 and 132: Patient Education ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦
- Page 133: ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦
- Page 136 and 137: 3-40 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 138 and 139: 3-42 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 140 and 141: 3-44 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 142 and 143:
3-46 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 144 and 145:
3-48 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 146 and 147:
3-50 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 148 and 149:
3-52 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 150 and 151:
4-2 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 152 and 153:
4-4 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 154 and 155:
4-6 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 156 and 157:
4-8 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 158 and 159:
4-10 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 160 and 161:
4-12 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 162 and 163:
4-14 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 165 and 166:
Section 4—Complications of Antire
- Page 167 and 168:
♦ ♦ ♦ Toronto General Hospita
- Page 169 and 170:
Adverse Reactions to HIV Medication
- Page 171 and 172:
♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ Vital signs: No
- Page 173 and 174:
egimen, symptoms of fatigue could i
- Page 175 and 176:
Recreational Drugs and Antiretrovir
- Page 177 and 178:
Section 4—Complications of Antire
- Page 179 and 180:
LSD, Mescaline, Psilocin, and Methy
- Page 181 and 182:
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome Back
- Page 183 and 184:
A: Assessment In the appropriate cl
- Page 185 and 186:
♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ Navas E, Martin
- Page 187 and 188:
5-2 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 189 and 190:
5-4 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 191 and 192:
5-6 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 193 and 194:
5-8 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 195 and 196:
5-10 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 197 and 198:
5-12 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 199 and 200:
5-14 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 202 and 203:
Eye Problems Background The immunos
- Page 204:
of
- Page 207 and 208:
5-22 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 210 and 211:
Fever Background Although fever may
- Page 212 and 213:
Headache Background Headache may ha
- Page 214 and 215:
Lymphadenopathy Background Lymphade
- Page 216:
Treatment Treatment will depend on
- Page 219 and 220:
5-34 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 222 and 223:
Neurologic Symptoms Background The
- Page 224 and 225:
♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦
- Page 226 and 227:
Pulmonary Symptoms Background Short
- Page 228:
Treatment Once the diagnosis is mad
- Page 231 and 232:
5-46 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 233 and 234:
5-48 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 235 and 236:
6-2 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 238 and 239:
Candidiasis, Oral and Esophageal Ba
- Page 240:
Maintenance therapy Use caution whe
- Page 243 and 244:
6-10 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 246 and 247:
Cervical Dysplasia Background Cervi
- Page 248:
Patient Education ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ P
- Page 251 and 252:
6-18 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 254 and 255:
Cryptosporidiosis Background Crypto
- Page 256:
Patient Education ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦
- Page 259 and 260:
6-26 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 261 and 262:
6-28 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 263 and 264:
6-30 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 266 and 267:
Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Background
- Page 268 and 269:
Treatment of Gonorrhea Treatment op
- Page 270 and 271:
Hepatitis B Infection Background He
- Page 272 and 273:
♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ Some patients t
- Page 274 and 275:
Hepatitis C Infection Background He
- Page 276 and 277:
pregnancy. Ribavirin is teratogenic
- Page 278 and 279:
Herpes Simplex, Mucocutaneous Backg
- Page 280:
References ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ Cent
- Page 283 and 284:
6-50 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 285 and 286:
6-52 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 288 and 289:
Kaposi Sarcoma Background Kaposi sa
- Page 290 and 291:
Treatment Treatment of KS is not co
- Page 292 and 293:
Molluscum Contagiosum Background Mo
- Page 294 and 295:
Mycobacterium avium Complex Backgro
- Page 296 and 297:
Table 1. Interactions between Rifab
- Page 298 and 299:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Treatme
- Page 300 and 301:
P: Plan Diagnostic Evaluation Durin
- Page 302 and 303:
Table 1. Regimens for Treatment of
- Page 304 and 305:
Rifabutin may be substituted for ri
- Page 306:
Patient Education ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦
- Page 309 and 310:
6-76 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 311 and 312:
6-78 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 314 and 315:
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Background Non
- Page 316:
Patient Education ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ S
- Page 319 and 320:
6-86 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 321 and 322:
6-88 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 323 and 324:
6-90 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 325 and 326:
6-92 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 327 and 328:
6-94 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 329 and 330:
6-96 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 331 and 332:
6-98 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 333 and 334:
6-100| Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 335 and 336:
6-102| Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 338 and 339:
Toxoplasmosis Background Toxoplasma
- Page 340 and 341:
♦ Atovaquone 1,500 mg orally twic
- Page 342 and 343:
Linear Gingival Erythema Background
- Page 344 and 345:
Background Necrotizing ulcerating p
- Page 346 and 347:
Oral Health Background Examination
- Page 348 and 349:
Maxillary Tori; Mandibular Tori S:
- Page 350 and 351:
Periodontal Disease Background The
- Page 352 and 353:
Oral Hairy Leukoplakia Background O
- Page 354 and 355:
Oral Ulceration Background Oral ulc
- Page 356 and 357:
Oral Warts Background Oral warts ar
- Page 358 and 359:
7-2 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 360 and 361:
7-4 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 362 and 363:
7-6 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 364 and 365:
7-8 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 366 and 367:
7-10 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 369 and 370:
Anxiety Disorders Background Anxiet
- Page 371:
Patient Education ♦ ♦ Behaviora
- Page 374 and 375:
8-6 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 376 and 377:
8-8 | Clinical Manual for Managemen
- Page 378 and 379:
8-10 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 381 and 382:
Insomnia Background Insomnia is a c
- Page 383 and 384:
Suicidal Ideation Background Transi
- Page 385 and 386:
Section 8—Neuropsychiatric Disord
- Page 387 and 388:
P: Plan ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ Check t
- Page 389 and 390:
Correctional Settings Background Ca
- Page 391 and 392:
Adherence Adherence is one of the m
- Page 393:
Karnofsky Performance Scale Backgro
- Page 396 and 397:
10-4 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 398 and 399:
10-6 | Clinical Manual for Manageme
- Page 400:
10-8 | Clinical Manual for Manageme