Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
Some patients treated with ART may experience<br />
worsening <strong>of</strong> HBV symptoms and laboratory<br />
markers in <strong>the</strong> weeks after ART initiation, because<br />
<strong>of</strong> immune reconstitution. Hepatic de<strong>com</strong>pensation<br />
due to immune reconstitution must be distinguished<br />
from o<strong>the</strong>r causes, such as medication toxicity,<br />
or o<strong>the</strong>r infection. Liver function tests should be<br />
monitored closely in patients starting ART.<br />
Some antiretroviral medications are hepatotoxic and<br />
should be avoided or used cautiously. These include<br />
nevirapine, tipranavir, and high-dose ritonavir.<br />
Numerous o<strong>the</strong>r medications (eg, fluconazole and<br />
isoniazid) are known to be hepatotoxic and can pose<br />
problems <strong>for</strong> people with impaired liver function.<br />
For patients with treatment failure, consult an HBV<br />
specialist.<br />
Caution: Discontinuation <strong>of</strong> HBV medications in<br />
patients with <strong>HIV</strong>/HBV coinfection may cause<br />
a flare <strong>of</strong> liver disease. If this occurs, consider<br />
reinstating HBV <strong>the</strong>rapy as soon as possible. Be<br />
very cautious when discontinuing HBV-active<br />
medications from an <strong>HIV</strong> ART regimen. In this<br />
scenario, consider continuing or substituting <strong>the</strong><br />
HBV-active medications to avoid rebound liver<br />
inflammation and de<strong>com</strong>pensation. For example, if<br />
it is decided to discontinue <strong>HIV</strong> treatment <strong>for</strong> an<br />
<strong>HIV</strong>/HBV-coinfected patient taking lamivudine<br />
+ ten<strong>of</strong>ovir + lopinavir/ritonavir, consider starting<br />
adefovir or entecavir to maintain activity against<br />
HPV.<br />
O<strong>the</strong>r care issues<br />
Acute hepatitis A virus (HAV) or HCV in persons<br />
with chronic HBV infection can cause de<strong>com</strong>pensated<br />
liver disease. All patients with HBV infection should<br />
be tested <strong>for</strong> immunity to HAV and HCV. Patients<br />
who are not immune to HAV should be vaccinated<br />
and patients who are not immune to HCV should be<br />
counseled about how to avoid <strong>the</strong> acquisition <strong>of</strong> HCV.<br />
All HBV-infected individuals should be taught how<br />
to reduce <strong>the</strong> risk <strong>of</strong> HBV transmission to o<strong>the</strong>rs. As<br />
appropriate, patients should be counseled to adopt<br />
“safer sex” approaches, avoid blood exposures (eg, from<br />
sharing razors or tattoo equipment), and practice safe<br />
drug injection techniques. Persons with HBV infection<br />
should be counseled to avoid exposure to hepatotoxins,<br />
including alcohol and hepatotoxic medications<br />
(eg, acetaminophen in large doses, fluconazole, and<br />
isoniazid).<br />
Section 6—Disease-Specific Treatment | 6–39<br />
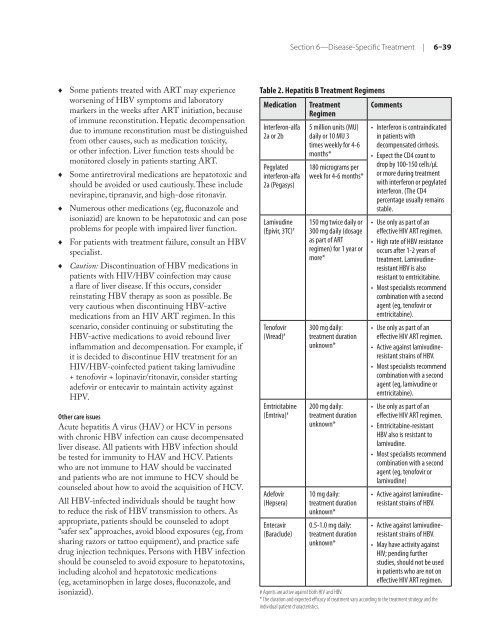
Table 2. Hepatitis B Treatment Regimens<br />
Medication Treatment<br />
Regimen<br />
Interferon-alfa<br />
2a or 2b<br />
Pegylated<br />
interferon-alfa<br />
2a (Pegasys)<br />
Lamivudine<br />
(Epivir, 3TC) #<br />
Ten<strong>of</strong>ovir<br />
(Viread) #<br />
Emtricitabine<br />
(Emtriva) #<br />
Adefovir<br />
(Hepsera)<br />
Entecavir<br />
(Baraclude)<br />
5 million units (MU)<br />
daily or 10 MU 3<br />
times weekly <strong>for</strong> 4-6<br />
months*<br />
180 micrograms per<br />
week <strong>for</strong> 4-6 months*<br />
150 mg twice daily or<br />
300 mg daily (dosage<br />
as part <strong>of</strong> ART<br />
regimen) <strong>for</strong> 1 year or<br />
more*<br />
300 mg daily:<br />
treatment duration<br />
unknown*<br />
200 mg daily:<br />
treatment duration<br />
unknown*<br />
10 mg daily:<br />
treatment duration<br />
unknown*<br />
0.5-1.0 mg daily:<br />
treatment duration<br />
unknown*<br />
Comments<br />
• Interferon is contraindicated<br />
in patients with<br />
de<strong>com</strong>pensated cirrhosis.<br />
• Expect <strong>the</strong> CD4 count to<br />
drop by 100-150 cells/µL<br />
or more during treatment<br />
with interferon or pegylated<br />
interferon. (The CD4<br />
percentage usually remains<br />
stable.<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
Use only as part <strong>of</strong> an<br />
effective <strong>HIV</strong> ART regimen.<br />
High rate <strong>of</strong> HBV resistance<br />
occurs after 1-2 years <strong>of</strong><br />
treatment. Lamivudineresistant<br />
HBV is also<br />
resistant to emtricitabine.<br />
Most specialists re<strong>com</strong>mend<br />
<strong>com</strong>bination with a second<br />
agent (eg, ten<strong>of</strong>ovir or<br />
emtricitabine).<br />
Use only as part <strong>of</strong> an<br />
effective <strong>HIV</strong> ART regimen.<br />
Active against lamivudineresistant<br />
strains <strong>of</strong> HBV.<br />
Most specialists re<strong>com</strong>mend<br />
<strong>com</strong>bination with a second<br />
agent (eg, lamivudine or<br />
emtricitabine).<br />
Use only as part <strong>of</strong> an<br />
effective <strong>HIV</strong> ART regimen.<br />
Emtricitabine-resistant<br />
HBV also is resistant to<br />
lamivudine.<br />
Most specialists re<strong>com</strong>mend<br />
<strong>com</strong>bination with a second<br />
agent (eg, ten<strong>of</strong>ovir or<br />
lamivudine)<br />
• Active against lamivudineresistant<br />
strains <strong>of</strong> HBV.<br />
• Active against lamivudineresistant<br />
strains <strong>of</strong> HBV.<br />
• May have activity against<br />
<strong>HIV</strong>; pending fur<strong>the</strong>r<br />
studies, should not be used<br />
in patients who are not on<br />
effective <strong>HIV</strong> ART regimen.<br />
# Agents are active against both <strong>HIV</strong> and HBV.<br />
* The duration and expected efficacy <strong>of</strong> treatment vary according to <strong>the</strong> treatment strategy and <strong>the</strong><br />
individual patient characteristics.