Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
6–70 | <strong>Clinical</strong> <strong>Manual</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>HIV</strong>-<strong>Infected</strong> Adult/2006<br />
drugs should be avoided during pregnancy. <strong>HIV</strong>-infected<br />
women in <strong>the</strong> United States are instructed not to<br />
breast-feed, so <strong>the</strong>re are usually no issues regarding TB<br />
treatment <strong>of</strong> <strong>HIV</strong>-infected women during breast-feeding.<br />
Treatment <strong>of</strong> pediatric patients<br />
Children are <strong>of</strong>ten treated with a 7-month continuation<br />
phase <strong>for</strong> a total treatment time <strong>of</strong> 9 months, although<br />
<strong>the</strong>re are no data on this issue. Some experts avoid<br />
ethambutol in young children who cannot be tested <strong>for</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> adverse event <strong>of</strong> color blindness; o<strong>the</strong>rs consider <strong>the</strong><br />
risk so small with current ethambutol dosages that <strong>the</strong><br />
drug can be included safely. Treatment <strong>of</strong> children <strong>for</strong><br />
TB should be done in consultation with an expert.<br />
Coordinating with Antiretroviral Therapy<br />
ART and TB treatment must be coordinated <strong>for</strong><br />
both to be successful. Rifampin is a potent inducer <strong>of</strong><br />
cytochrome p450 enzymes and has clinically important<br />
interactions with many medications, including certain<br />
antiretrovirals and oral contraceptives. Rifampin<br />
reduces <strong>the</strong> blood concentrations <strong>of</strong> nonnucleoside<br />
reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) and protease<br />
inhibitors (PIs), but does not affect nucleoside/<br />
nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) or<br />
<strong>the</strong> entry inhibitor enfuvirtide. Some NNRTIs and PIs<br />
cannot be used with rifampin while o<strong>the</strong>r require dose<br />
adjustment when coadministered (Table 3). Triplenucleoside<br />
regimens can be administered safely during<br />
rifampin treatment but are less potent than o<strong>the</strong>r firstline<br />
antiretroviral (ARV) <strong>com</strong>binations. The safest ARV<br />
<strong>com</strong>bination to use with rifampin is a 2-drug nucleoside<br />
backbone with efavirenz. Some clinicians increase <strong>the</strong><br />
efavirenz dosage to 800 mg/day because efavirenz blood<br />
concentrations may be reduced 25% by con<strong>com</strong>itant<br />
rifampin. Note that efavirenz is teratogenic; women<br />
who take efavirenz should avoid pregnancy by using<br />
birth control methods that use are not affected by<br />
rifampin (preferably condoms plus injectable progestins<br />
or condoms plus an intrauterine device).<br />
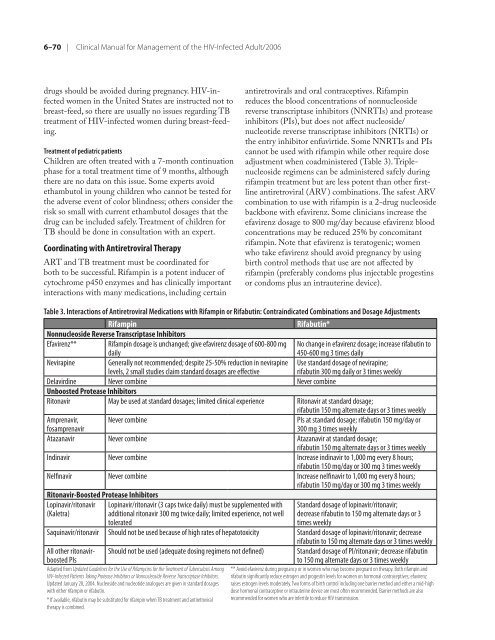
Table 3. Interactions <strong>of</strong> Antiretroviral Medications with Rifampin or Rifabutin: Contraindicated Combinations and Dosage Adjustments<br />
Rifampin<br />
Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors<br />
Rifabutin*<br />
Efavirenz** Rifampin dosage is unchanged; give efavirenz dosage <strong>of</strong> 600-800 mg No change in efavirenz dosage; increase rifabutin to<br />
daily<br />
450-600 mg 3 times daily<br />
Nevirapine Generally not re<strong>com</strong>mended; despite 25-50% reduction in nevirapine Use standard dosage <strong>of</strong> nevirapine;<br />
levels, 2 small studies claim standard dosages are effective<br />
rifabutin 300 mg daily or 3 times weekly<br />
Delavirdine Never <strong>com</strong>bine Never <strong>com</strong>bine<br />
Unboosted Protease Inhibitors<br />
Ritonavir May be used at standard dosages; limited clinical experience Ritonavir at standard dosage;<br />
rifabutin 150 mg alternate days or 3 times weekly<br />
Amprenavir,<br />
Never <strong>com</strong>bine PIs at standard dosage; rifabutin 150 mg/day or<br />
fosamprenavir<br />
300 mg 3 times weekly<br />
Atazanavir Never <strong>com</strong>bine Atazanavir at standard dosage;<br />
rifabutin 150 mg alternate days or 3 times weekly<br />
Indinavir Never <strong>com</strong>bine Increase indinavir to 1,000 mg every 8 hours;<br />
rifabutin 150 mg/day or 300 mg 3 times weekly<br />
Nelfinavir Never <strong>com</strong>bine Increase nelfinavir to 1,000 mg every 8 hours;<br />
rifabutin 150 mg/day or 300 mg 3 times weekly<br />
Ritonavir-Boosted Protease Inhibitors<br />
Lopinavir/ritonavir Lopinavir/ritonavir (3 caps twice daily) must be supplemented with Standard dosage <strong>of</strong> lopinavir/ritonavir;<br />
(Kaletra)<br />
additional ritonavir 300 mg twice daily; limited experience, not well decrease rifabutin to 150 mg alternate days or 3<br />
tolerated<br />
times weekly<br />
Saquinavir/ritonavir Should not be used because <strong>of</strong> high rates <strong>of</strong> hepatotoxicity Standard dosage <strong>of</strong> lopinavir/ritonavir; decrease<br />
rifabutin to 150 mg alternate days or 3 times weekly<br />
All o<strong>the</strong>r ritonavir- Should not be used (adequate dosing regimens not defined) Standard dosage <strong>of</strong> PI/ritonavir; decrease rifabutin<br />
boosted PIs<br />
to 150 mg alternate days or 3 times weekly<br />
Adapted from Updated Guidelines <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> Use <strong>of</strong> Rifamycins <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> Treatment <strong>of</strong> Tuberculosis Among<br />
<strong>HIV</strong>-<strong>Infected</strong> Patients Taking Protease Inhibitors or Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors.<br />
Updated January 20, 2004. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogues are given in standard dosages<br />
with ei<strong>the</strong>r rifampin or rifabutin.<br />
* If available, rifabutin may be substituted <strong>for</strong> rifampin when TB treatment and antiretroviral<br />
<strong>the</strong>rapy is <strong>com</strong>bined.<br />
** Avoid efavirenz during pregnancy or in women who may be<strong>com</strong>e pregnant on <strong>the</strong>rapy. Both rifampin and<br />
rifabutin significantly reduce estrogen and progestin levels <strong>for</strong> women on hormonal contraceptives; efavirenz<br />
raises estrogen levels moderately. Two <strong>for</strong>ms <strong>of</strong> birth control including one barrier method and ei<strong>the</strong>r a mid-high<br />
dose hormonal contraceptive or intrauterine device are most <strong>of</strong>ten re<strong>com</strong>mended. Barrier methods are also<br />
re<strong>com</strong>mended <strong>for</strong> women who are infertile to reduce <strong>HIV</strong> transmission.