Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Clinical Manual for Management of the HIV-Infected ... - myCME.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1–32 | <strong>Clinical</strong> <strong>Manual</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>HIV</strong>-<strong>Infected</strong> Adult/2006<br />
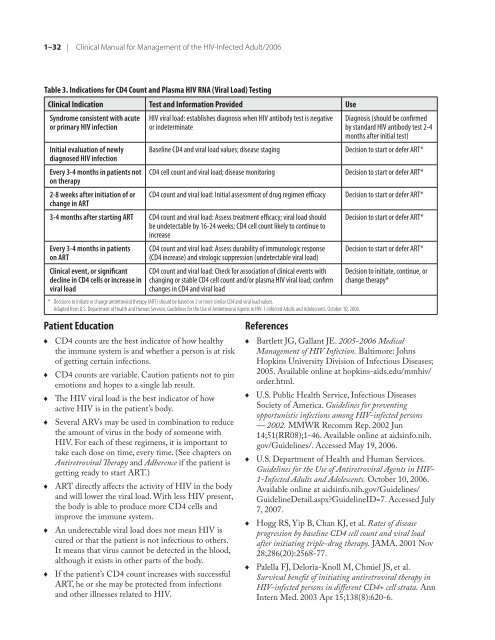
Table 3. Indications <strong>for</strong> CD4 Count and Plasma <strong>HIV</strong> RNA (Viral Load) Testing<br />
Patient Education<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
<strong>Clinical</strong> Indication Test and In<strong>for</strong>mation Provided Use<br />
Syndrome consistent with acute<br />
or primary <strong>HIV</strong> infection<br />
Initial evaluation <strong>of</strong> newly<br />
diagnosed <strong>HIV</strong> infection<br />
Every 3-4 months in patients not<br />
on <strong>the</strong>rapy<br />
2-8 weeks after initiation <strong>of</strong> or<br />
change in ART<br />
CD4 counts are <strong>the</strong> best indicator <strong>of</strong> how healthy<br />
<strong>the</strong> immune system is and whe<strong>the</strong>r a person is at risk<br />
<strong>of</strong> getting certain infections.<br />
CD4 counts are variable. Caution patients not to pin<br />
emotions and hopes to a single lab result.<br />
The <strong>HIV</strong> viral load is <strong>the</strong> best indicator <strong>of</strong> how<br />
active <strong>HIV</strong> is in <strong>the</strong> patient’s body.<br />
Several ARVs may be used in <strong>com</strong>bination to reduce<br />
<strong>the</strong> amount <strong>of</strong> virus in <strong>the</strong> body <strong>of</strong> someone with<br />
<strong>HIV</strong>. For each <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se regimens, it is important to<br />
take each dose on time, every time. (See chapters on<br />
Antiretroviral Therapy and Adherence if <strong>the</strong> patient is<br />
getting ready to start ART.)<br />
ART directly affects <strong>the</strong> activity <strong>of</strong> <strong>HIV</strong> in <strong>the</strong> body<br />
and will lower <strong>the</strong> viral load. With less <strong>HIV</strong> present,<br />
<strong>the</strong> body is able to produce more CD4 cells and<br />
improve <strong>the</strong> immune system.<br />
An undetectable viral load does not mean <strong>HIV</strong> is<br />
cured or that <strong>the</strong> patient is not infectious to o<strong>the</strong>rs.<br />
It means that virus cannot be detected in <strong>the</strong> blood,<br />
although it exists in o<strong>the</strong>r parts <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> body.<br />
If <strong>the</strong> patient’s CD4 count increases with successful<br />
ART, he or she may be protected from infections<br />
and o<strong>the</strong>r illnesses related to <strong>HIV</strong>.<br />
<strong>HIV</strong> viral load: establishes diagnosis when <strong>HIV</strong> antibody test is negative<br />
or indeterminate<br />
References<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
♦<br />
Diagnosis (should be confirmed<br />
by standard <strong>HIV</strong> antibody test 2-4<br />
months after initial test)<br />
Baseline CD4 and viral load values; disease staging Decision to start or defer ART*<br />
CD4 cell count and viral load; disease monitoring Decision to start or defer ART*<br />
CD4 count and viral load: Initial assessment <strong>of</strong> drug regimen efficacy Decision to start or defer ART*<br />
3-4 months after starting ART CD4 count and viral load: Assess treatment efficacy; viral load should<br />
be undetectable by 16-24 weeks; CD4 cell count likely to continue to<br />
increase<br />
Every 3-4 months in patients<br />
on ART<br />
<strong>Clinical</strong> event, or significant<br />
decline in CD4 cells or increase in<br />
viral load<br />
CD4 count and viral load: Assess durability <strong>of</strong> immunologic response<br />
(CD4 increase) and virologic suppression (undetectable viral load)<br />
CD4 count and viral load: Check <strong>for</strong> association <strong>of</strong> clinical events with<br />
changing or stable CD4 cell count and/or plasma <strong>HIV</strong> viral load; confirm<br />
changes in CD4 and viral load<br />
* Decisions to initiate or change antiretroviral <strong>the</strong>rapy (ART) should be based on 2 or more similar CD4 and viral load values.<br />
Adapted from U.S. Department <strong>of</strong> Health and Human Services. Guidelines <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> Use <strong>of</strong> Antiretroviral Agents in <strong>HIV</strong>-1-<strong>Infected</strong> Adults and Adolescents. October 10, 2006.<br />
Decision to start or defer ART*<br />
Decision to start or defer ART*<br />
Decision to initiate, continue, or<br />
change <strong>the</strong>rapy*<br />
Bartlett JG, Gallant JE. 2005-2006 Medical<br />
<strong>Management</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>HIV</strong> Infection. Baltimore: Johns<br />
Hopkins University Division <strong>of</strong> Infectious Diseases;<br />
2005. Available online at hopkins-aids.edu/mmhiv/<br />
order.html.<br />
U.S. Public Health Service, Infectious Diseases<br />
Society <strong>of</strong> America. Guidelines <strong>for</strong> preventing<br />
opportunistic infections among <strong>HIV</strong>-infected persons<br />
— 2002. MMWR Re<strong>com</strong>m Rep. 2002 Jun<br />
14;51(RR08);1-46. Available online at aidsinfo.nih.<br />
gov/Guidelines/. Accessed May 19, 2006.<br />
U.S. Department <strong>of</strong> Health and Human Services.<br />
Guidelines <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> Use <strong>of</strong> Antiretroviral Agents in <strong>HIV</strong>-<br />
1-<strong>Infected</strong> Adults and Adolescents. October 10, 2006.<br />
Available online at aidsinfo.nih.gov/Guidelines/<br />
GuidelineDetail.aspx?GuidelineID=7. Accessed July<br />
7, 2007.<br />
Hogg RS, Yip B, Chan KJ, et al. Rates <strong>of</strong> disease<br />
progression by baseline CD4 cell count and viral load<br />
after initiating triple-drug <strong>the</strong>rapy. JAMA. 2001 Nov<br />
28;286(20):2568-77.<br />
Palella FJ, Deloria-Knoll M, Chmiel JS, et al.<br />
Survival benefit <strong>of</strong> initiating antiretroviral <strong>the</strong>rapy in<br />
<strong>HIV</strong>-infected persons in different CD4+ cell strata. Ann<br />
Intern Med. 2003 Apr 15;138(8):620-6.