- Page 1 and 2:
CHAPTER #: NAME OF CHAPTERIEvaluati
- Page 3 and 4:
IIITable of ContentsVVI010717252835
- Page 5 and 6:
VForewordDespite the investments ma
- Page 7 and 8: VIILyn Kathlene®°Megan Kemple®°
- Page 9 and 10: 101IntroductionImage created by att
- Page 11 and 12: CHAPTER 01: INTRODUCTION3approaches
- Page 13: CHAPTER 01: INTRODUCTION5Policy-Lev
- Page 16 and 17: 8CHAPTER 02: BACKGROUNDThe Evolutio
- Page 18 and 19: 10CHAPTER 02: BACKGROUNDFigure 1Edu
- Page 20 and 21: 12CHAPTER 02: BACKGROUNDFigure 2Fig
- Page 22 and 23: 14CHAPTER 02: BACKGROUNDFigure 4: T
- Page 25 and 26: CHAPTER 03: FRAMEWORK DEVELOPMENT P
- Page 27 and 28: CHAPTER 03: FRAMEWORK DEVELOPMENT P
- Page 29 and 30: CHAPTER 03: FRAMEWORK DEVELOPMENT P
- Page 31 and 32: CHAPTER 03: FRAMEWORK DEVELOPMENT P
- Page 34 and 35: 26 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 36 and 37: 28 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 38 and 39: 30 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 40 and 41: 32 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 42 and 43: 34 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 44 and 45: 36 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 46 and 47: 38 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 48 and 49: 40 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
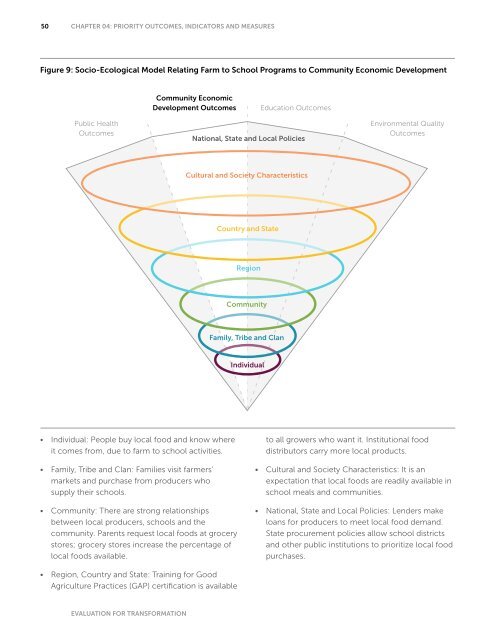
- Page 50 and 51: 42 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 54 and 55: 46 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 57: CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, INDI
- Page 61: CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, INDI
- Page 65 and 66: CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, INDI
- Page 68 and 69: 60 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 70 and 71: 62 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 72 and 73: 64 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 74 and 75: 66 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 76 and 77: 68 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 78 and 79: 70 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 80 and 81: 72 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 82 and 83: 74 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 84 and 85: 76 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 86 and 87: 78 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 88 and 89: 80 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 90 and 91: 82 CHAPTER 04: PRIORITY OUTCOMES, I
- Page 93 and 94: CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 95 and 96: CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 97 and 98: CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 99 and 100: CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 101 and 102: CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 103 and 104: CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 105 and 106: CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 107 and 108: CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 109 and 110:
CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 111 and 112:
CHAPTER 05: CONCLUSION AND NEXT STE
- Page 113 and 114:
105ReferencesChapter 11. Joshi, A.,
- Page 115 and 116:
10746. Langellotto, G.A., Gupta, A.
- Page 117 and 118:
10918. Schneider, L., Chriqui, J.,
- Page 119 and 120:
11112. Mary, P.D.S., Karen, M., Kap
- Page 121 and 122:
11360. Zarling, P. When farm-to-sch
- Page 123 and 124:
115103. Story, M., Neumark-Sztainer
- Page 125 and 126:
11736. Eisner, R., Foster, S., Hans
- Page 127 and 128:
11910. Fusco, D. Creating relevant
- Page 129 and 130:
12158. Vermont Law School, Center f
- Page 131 and 132:
12352. Physicians for Social Respon
- Page 133 and 134:
12506Appendices
- Page 135 and 136:
APPENDICES127Appendix 1Evaluation R
- Page 137 and 138:
APPENDICES129• Evaluation Plannin
- Page 139 and 140:
APPENDICES131Appendix 2Farm to Scho
- Page 141 and 142:
APPENDICES133procurement and a guid
- Page 143 and 144:
APPENDICES135Farm to School Core El
- Page 145 and 146:
APPENDICES137Appendix 3 References1
- Page 147 and 148:
APPENDICES139Appendix 5Sample Evalu
- Page 149 and 150:
APPENDICES141• Healthy Eating, Ac
- Page 151 and 152:
APPENDICES143Appendix 6Ideas for Fu
- Page 153:
APPENDICES145• Amount of acres se