You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
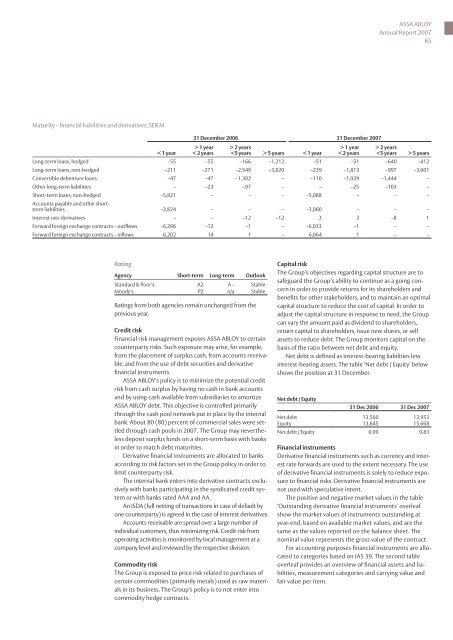
Maturity – financial liabilities and derivatives, SEK M<br />
Rating<br />
< 1 year<br />
Agency Short-term Long-term Outlook<br />
Standard & Poor’s A2 A – Stable<br />
Moody’s P2 n/a Stable<br />
Ratings from both agencies remain unchanged from the<br />
previous year.<br />
Credit risk<br />
Financial risk management exposes ASSA ABLOY to certain<br />
counterparty risks. Such exposure may arise, for example,<br />
from the placement of surplus cash, from accounts receivable,<br />
and from the use of debt securities and derivative<br />
financial instruments.<br />
ASSA ABLOY’s policy is to minimize the potential credit<br />
risk from cash surplus by having no cash in bank accounts<br />
and by using cash available from subsidiaries to amortize<br />
ASSA ABLOY debt. This objective is controlled primarily<br />
through the cash pool network put in place by the internal<br />
bank. About 80 (80) percent of commercial sales were settled<br />
through cash pools in 2007. The Group may nevertheless<br />
deposit surplus funds on a short-term basis with banks<br />
in order to match debt maturities.<br />
Derivative financial instruments are allocated to banks<br />
according to risk factors set in the Group policy in order to<br />
limit counterparty risk.<br />
The internal bank enters into derivative contracts exclusively<br />
with banks participating in the syndicated credit system<br />
or with banks rated AAA and AA.<br />
An ISDA (full netting of transactions in case of default by<br />
one counterparty) is agreed in the case of interest derivatives.<br />
Accounts receivable are spread over a large number of<br />
individual customers, thus minimizing risk. Credit risk from<br />
operating activities is monitored by local management at a<br />
company level and reviewed by the respective division.<br />
Commodity risk<br />
The Group is exposed to price risk related to purchases of<br />
certain commodities (primarily metals) used as raw materials<br />
in its business. The Group’s policy is to not enter into<br />
commodity hedge contracts.<br />
31 December 2006 31 December 2007<br />
> 1 year<br />
< 2 years<br />
> 2 years<br />
5 years < 1 year<br />
ASSA ABLOY<br />
Annual Report 2007<br />
65<br />
Capital risk<br />
The Group’s objectives regarding capital structure are to<br />
safeguard the Group’s ability to continue as a going concern<br />
in order to provide returns for its shareholders and<br />
benefits for other stakeholders, and to maintain an optimal<br />
capital structure to reduce the cost of capital. In order to<br />
adjust the capital structure in response to need, the Group<br />
can vary the amount paid as dividend to shareholders,<br />
return capital to shareholders, issue new shares, or sell<br />
assets to reduce debt. The Group monitors capital on the<br />
basis of the ratio between net debt and equity.<br />
Net debt is defined as interest-bearing liabilities less<br />
interest-bearing assets. The table ‘Net debt / Equity’ below<br />
shows the position at 31 December.<br />
Net debt / Equity<br />
> 1 year<br />
< 2 years<br />
> 2 years<br />
5 years<br />
Long-term loans, hedged –55 –55 –166 –1,212 –51 –51 –640 –412<br />
Long-term loans, non-hedged –211 –271 –2,549 –3,820 –239 –1,813 –997 –3,601<br />
Convertible debenture loans –47 –47 – 1,302 – –110 –1,029 –1,444 –<br />
Other long-term liabilities – –23 –97 – – –25 –103 –<br />
Short-term loans, non-hedged –5,821 – – – –5,088 – – –<br />
Accounts payable and other shortterm<br />
liabilities –2,824 – – – –3,060 – – –<br />
Interest rate derivatives – – –12 –12 3 3 –8 1<br />
Forward foreign exchange contracts – outflows –6,206 –12 –1 – –6,033 –1 – –<br />
Forward foreign exchange contracts – inflows 6,202 14 1 – 6,064 1 – –<br />
31 Dec 2006 31 Dec 2007<br />
Net debt 13,560 12,953<br />
Equity 13,645 15,668<br />
Net debt / Equity 0.99 0.83<br />
Financial instruments<br />
Derivative financial instruments such as currency and interest<br />
rate forwards are used to the extent necessary. The use<br />
of derivative financial instruments is solely to reduce exposure<br />
to financial risks. Derivative financial instruments are<br />
not used with speculative intent.<br />
The positive and negative market values in the table<br />
‘Outstanding derivative financial instruments’ overleaf<br />
show the market values of instruments outstanding at<br />
year-end, based on available market values, and are the<br />
same as the values reported on the balance sheet. The<br />
nominal value represents the gross value of the contract.<br />
For accounting purposes financial instruments are allocated<br />
to categories based on IAS 39. The second table<br />
overleaf provides an overview of financial assets and liabilities,<br />
measurement categories and carrying value and<br />
fair value per item.