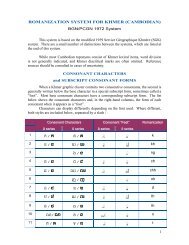
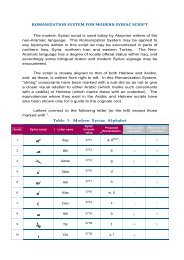
1 - NGA
1 - NGA
1 - NGA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
stetronomlc deta-DMgnatfon of epoch by<br />
year, month, day, and dacfmal fraction. For<br />
ezsmpfe, the astronomic dale of Dacerrtrer 21,<br />
1978, 18h UTC (univeraaf time morcfhalsd) is<br />
1978 Dacarrtrar 21.75 UTC. The astronomic<br />
date k also used In Omrrecfbn wilh the other<br />
lime systems. me system commences every<br />
cafendar year at Oh on Decatir 31 of the<br />
previous year. This epoch is denoted by .faruary<br />
0.0.<br />
astronomic day—A mean mlar dey beginning<br />
at mean noon, 12 hours feter than the beginning<br />
of the cIvII day of the earns date, Aafmnomers<br />
now genaralty use the civil day.<br />
astronomic equator—The fine on the surface<br />
of the Earth wfmse astmnomk fatituda at everv<br />
point is O“. Due 10 the dafbcfion of the plumb’<br />
iine, the aafronomk equator is not a pla”ne curve.<br />
However, the verficafa a! all points on k are<br />
parallel to one and the same plane, the pfane of<br />
the celestial equator; that is, the zenith at every<br />
point on tha eetmnomk equator lies in the<br />
caleatial er$zalor. When lhe astronomic equalor<br />
is corrected for station error, ii becomes the<br />
geodetic equator. Also called terrestrial<br />
aquator. See aiso geodafic aquator.<br />
astronomic latltud+The angie between the<br />
plumb fine and the plane of celestiai equalor.<br />
Also defined as fha angla be fwean tfra piane of<br />
the horizon and the axis of rotation of the Earth.<br />
Astronomic kitnude appfies only to posltfons on<br />
the Earth and is reckoned from the astronomic<br />
equator (0°) notlh and south through 90°.<br />
Aafmnomic Ietffude is the Iatffude whkh results<br />
directly fmm obaervatbns of celestial fmdles,<br />
urcorrecfed for deliecfion of the vertical.<br />
astronomic lavellng—See aatrogeodetlc<br />
ieveling.<br />
eatronomlc iongltude-The angle between<br />
the ptene of the celastlal meridfin end the plane<br />
of an iniiial merfdiin, arbffrarffy chosen.<br />
Astronomk bngffude la the longitude which<br />
resuffs directly from obsewations on ceiesfial<br />
toches, unmrrected for deflacfbn of the vertical.<br />
aatronomlc merldlan plane-A plane that<br />
cdmains the verrfml of the obsewer and is<br />
~a#rl to the inalanrsnaas rotation 6x19 of the<br />
aatronomlc meridian—A great circle 01 the<br />
MIL-HDBK-850<br />
calestial sphere Imersacfing the ncmh and muth<br />
ceiestial poles. me local astronomk marldian is<br />
[hat meridian whtih intersects the zenffh of fhe<br />
poinl.<br />
astronomic parallef-A fine on the surface ot<br />
the Earth which hes the same eshncmdc<br />
Ialiiude at every point. Because the deffactiin of<br />
the veflid is not fhe SSmS at all pofms on tha<br />
Earth, an astronomic peraflsl IS an irregular fine.<br />
not Iyhrg in a single ptane. See afso<br />
aetronomlc equator.<br />
setronomlc poaltion-1. A pdim on the Earlh<br />
whoaa coordhrates have been determined as a<br />
reeuff of observations of caleslial bodies. The<br />
expression is ueualfy used In connacibn with<br />
positions on iand determined wffh greet erxasracy<br />
for survey purposes. 2. A point on fhe Earth,<br />
defined in terms of astronomic Iatituda and<br />
fongllude.<br />
astronomic refraction error-See<br />
astronomic refraction.<br />
astronomic reflection-Tha apparent<br />
displacement of an object that resuffs hem fight<br />
rays from a source outside Ihe atmosphere being<br />
bent in paasing through the atmesphare. This<br />
rasults in all objects appearfrq 10 be higher<br />
above the horizon than they actuaffy are. The<br />
magnitude of Ihk dbplacemem is greater whan<br />
the object Is near the horizon and decreases to a<br />
minimum assumed to be zero when the object is<br />
al the zeniffr. Afao calied aatronomfc<br />
refraction error; calestial refraction. See<br />
afso atmosptserlc ref racllon; rafractlon.<br />
astronomic station—A point on the Earth<br />
whose position has been determined by<br />
observations on cefestial bodies.<br />
aafronom fc ●urva ylng—The caleafiaf<br />
determination of latitude and bn@sde.<br />
Separations ara cefculaled by mmputirrg<br />
distances corresponding to measured angular<br />
displacements afong the reference spheroid.<br />
astronomic theodolita—See altazlmutft<br />
Inatrumant.<br />
aatronomlc tidal constltuant-See<br />
constituent.<br />
astronomic tfme-sofar time In a day<br />
(astronomic day) that begins at noon. Aafronomic<br />
Ime may be eilher apparem solar Ifme or mean<br />
;olar time. Since 192S, civil tires is generalfy<br />
2‘o