Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
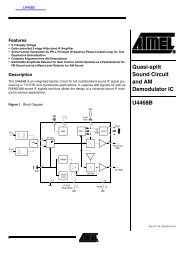
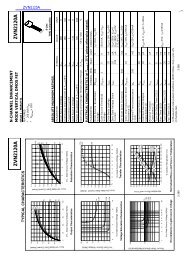
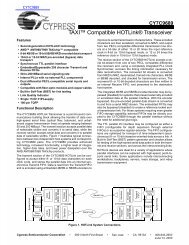
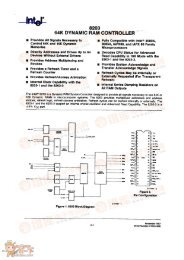
Numonyx <strong>Wireless</strong> <strong>Flash</strong> <strong>Memory</strong> (<strong>W30</strong>)<br />
Table 13: AC Write Characteristics (Sheet 2 of 2)<br />
# Sym Parameter 1,2<br />
W14 t WHGL (t EHGL ) Write Recovery before Read - 0 - 0 - ns<br />
W16 t WHQV WE# High to Valid Data<br />
November 2007 Datasheet<br />
Order Number: 290702-13 39<br />
3,6,1<br />
0<br />
t AVQV<br />
+ 40<br />
-<br />
t AVQV<br />
+ 50<br />
- ns<br />
W18 tWHAV WE# High to Address Valid<br />
3,9,1<br />
0<br />
0 - 0 - ns<br />
W19 tWHCV WE# High to CLK Valid 3,10 20 - 20 - ns<br />
W20<br />
Notes:<br />
tWHVH WE# High to ADV# High 3,10 20 - 20 - ns<br />
1. Write timing characteristics during erase suspend are the same as during write-only operations.<br />
2. A write operation can be terminated with either CE# or WE#.<br />
3. Sampled, not 100% tested.<br />
4.<br />
5.<br />
6.<br />
Write pulse width low (tWLWH or tELEH ) is defined from CE# or WE# low (whichever occurs last) to CE# or WE# high<br />
(whichever occurs first). Hence, tWLWH = tELEH = tWLEH = tELWH .<br />
Write pulse width high (tWHWL or tEHEL) is defined from CE# or WE# high (whichever is first) to CE# or WE# low<br />
(whichever is last). Hence, tWHWL = tEHEL = tWHEL = tEHWL .<br />
System designers must take this into account, and can insert a software No-Op instruction to delay the first read after<br />
issuing a command.<br />
7. For commands other than resume commands.<br />
8.<br />
9.<br />
VPP must be held at VPPL or VPPH until block erase or program success is determined.<br />
Applicable during asynchronous reads following a write.<br />
10. tWHCH/L OR tWHVH must be met when transitioning from a write cycle to a synchronous burst read. tWHCH/L and tWHVH both refer to the address latching event (either the rising/falling clock edge or the rising ADV# edge, whichever occurs<br />
first).<br />
Notes<br />
32-Mbit<br />
64-Mbit<br />
128-Mbit<br />
-70 -85 / -90<br />
Min Max Min Max<br />
Unit