Proceedings of the International Cyanide Detection Testing Workshop
Proceedings of the International Cyanide Detection Testing Workshop
Proceedings of the International Cyanide Detection Testing Workshop
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
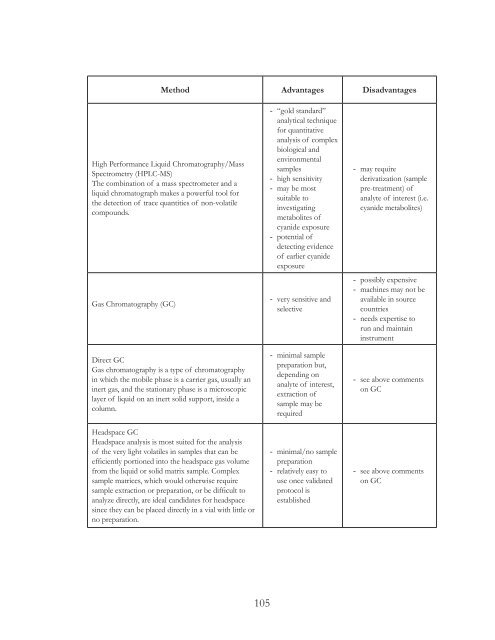
Method Advantages Disadvantages<br />
High Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass<br />
Spectrometry (HPLC-MS)<br />
The combination <strong>of</strong> a mass spectrometer and a<br />
liquid chromatograph makes a powerful tool for<br />
<strong>the</strong> detection <strong>of</strong> trace quantities <strong>of</strong> non-volatile<br />
compounds.<br />
Gas Chromatography (GC)<br />
Direct GC<br />
Gas chromatography is a type <strong>of</strong> chromatography<br />
in which <strong>the</strong> mobile phase is a carrier gas, usually an<br />
inert gas, and <strong>the</strong> stationary phase is a microscopic<br />
layer <strong>of</strong> liquid on an inert solid support, inside a<br />
column.<br />
Headspace GC<br />
Headspace analysis is most suited for <strong>the</strong> analysis<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> very light volatiles in samples that can be<br />
effi ciently portioned into <strong>the</strong> headspace gas volume<br />
from <strong>the</strong> liquid or solid matrix sample. Complex<br />
sample matrices, which would o<strong>the</strong>rwise require<br />
sample extraction or preparation, or be diffi cult to<br />
analyze directly, are ideal candidates for headspace<br />
since <strong>the</strong>y can be placed directly in a vial with little or<br />
no preparation.<br />
105<br />
- “gold standard”<br />
analytical technique<br />
for quantitative<br />
analysis <strong>of</strong> complex<br />
biological and<br />
environmental<br />
samples<br />
- high sensitivity<br />
- may be most<br />
suitable to<br />
investigating<br />
metabolites <strong>of</strong><br />
cyanide exposure<br />
- potential <strong>of</strong><br />
detecting evidence<br />
<strong>of</strong> earlier cyanide<br />
exposure<br />
- very sensitive and<br />
selective<br />
- minimal sample<br />
preparation but,<br />
depending on<br />
analyte <strong>of</strong> interest,<br />
extraction <strong>of</strong><br />
sample may be<br />
required<br />
- minimal/no sample<br />
preparation<br />
- relatively easy to<br />
use once validated<br />
protocol is<br />
established<br />
- may require<br />
derivatization (sample<br />
pre-treatment) <strong>of</strong><br />
analyte <strong>of</strong> interest (i.e.<br />
cyanide metabolites)<br />
- possibly expensive<br />
- machines may not be<br />
available in source<br />
countries<br />
- needs expertise to<br />
run and maintain<br />
instrument<br />
- see above comments<br />
on GC<br />
- see above comments<br />
on GC