Protocols for Secure Communication in Wireless Sensor Networks
Protocols for Secure Communication in Wireless Sensor Networks
Protocols for Secure Communication in Wireless Sensor Networks
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 6<br />
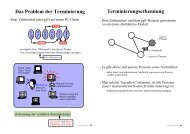
Integrity-Preserv<strong>in</strong>g <strong>Communication</strong>s<br />
6.1 Authentication and Integrity Protection<br />
Authentication is an important tool <strong>for</strong> ensur<strong>in</strong>g the identity and <strong>in</strong>tegrity of<br />
objects that are outside of one’s own control. In particular, we consider the<br />
protection of the <strong>in</strong>tegrity of messages that are transmitted with<strong>in</strong> a WSN. We<br />
show how message <strong>in</strong>tegrity relates to the communication patterns with<strong>in</strong> a<br />
WSN and the assumed threat model.<br />
6.1.1 Def<strong>in</strong>itions<br />
Be<strong>in</strong>g authentic <strong>for</strong> an entity means “be<strong>in</strong>g actually and exactly what is<br />
claimed”, especially “worthy of acceptance [. . . ] as con<strong>for</strong>m<strong>in</strong>g to or based on<br />
fact” and “true to one’s own personality, spirit, or character” accord<strong>in</strong>g to [125].<br />
The last part of this def<strong>in</strong>ition suggests that authenticity is strongly l<strong>in</strong>ked to<br />
certa<strong>in</strong> characteristics (“personality, spirit, or character”) of an entity, which<br />
could be subsumed under the notion of identity. We will not go <strong>in</strong>to the philosophical<br />
details of this notion. For our purpose it is sufficient to assume that<br />
there are features based on which the identity of an object can be established.<br />
The process, which accomplishes this, is called authentication.<br />
In the context of computer and network security, there are three ma<strong>in</strong> k<strong>in</strong>ds<br />
of objects to authenticate: entities (users, pr<strong>in</strong>cipals, nodes), keys, and data<br />
(messages). For the latter, an important property is <strong>in</strong>tegrity. The follow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
def<strong>in</strong>itions are taken from the Handbook of Applied Cryptography [122]:<br />
Def<strong>in</strong>ition 6.1. Entity authentication is the process whereby one party is assured<br />
(through acquisition of corroborative evidence) of the identity of a second<br />
party <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> a protocol, and that the second has actually participated<br />
(i.e., is active at, or immediately prior to, the time the evidence is acquired).