GTP 2.0 - Prime Minister's Office of Malaysia
GTP 2.0 - Prime Minister's Office of Malaysia
GTP 2.0 - Prime Minister's Office of Malaysia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
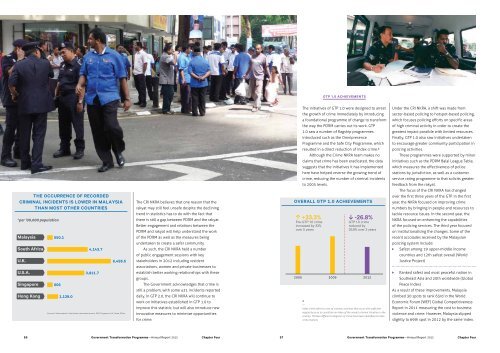
THE OCCURRENCE OF RECORDED<br />
CRIMINAL INCIDENTS IS LOWER IN MALAYSIA<br />
THAN MOST OTHER COUNTRIES<br />
*per '00,000 population<br />
<strong>Malaysia</strong><br />
South Africa<br />
U.K.<br />
U.S.A.<br />
Singapore<br />
Hong Kong<br />
550.1<br />
606<br />
1,139.0<br />
4,143.7<br />
3,811.7<br />
6,498.5<br />
Sources: Nationmaster: http://www.nationmaster.com; DOS Singapore; UK Home Oice<br />
The CRI NKRA believes that one reason that the<br />
rakyat may still feel unsafe despite the declining<br />
trend in statistics has to do with the fact that<br />
there is still a gap between PDRM and the rakyat.<br />
Better engagement and relations between the<br />
PDRM and rakyat will help understand the work<br />
<strong>of</strong> the PDRM as well as the measures being<br />
undertaken to create a safer community.<br />
As such, the CRI NKRA held a number<br />
<strong>of</strong> public engagement sessions with key<br />
stakeholders in 2012 including resident<br />
associations, women and private businesses to<br />
establish better working relationships with these<br />
groups.<br />
The Government acknowledges that crime is<br />
still a problem, with some 421 incidents reported<br />
daily. In <strong>GTP</strong> <strong>2.0</strong>, the CRI NKRA will continue to<br />
work on initiatives established in <strong>GTP</strong> 1.0 to<br />
improve this statistic, but will also introduce new<br />
innovative measures to minimize opportunities<br />
for crime.<br />
GtP 1.0 aChIEvEmENts<br />
The initiatives <strong>of</strong> <strong>GTP</strong> 1.0 were designed to arrest<br />
the growth <strong>of</strong> crime immediately by introducing<br />
a foundational programme <strong>of</strong> change to transform<br />
the way the PDRM carries out its work. <strong>GTP</strong><br />
1.0 saw a number <strong>of</strong> flagship programmes<br />
introduced such as the Omnipresence<br />
Programme and the Safe City Programme, which<br />
resulted in a direct reduction <strong>of</strong> index crime. 1<br />
Although the Crime NKRA team makes no<br />
claims that crime has been eradicated, the data<br />
suggests that the initiatives it has implemented<br />
here have helped reverse the growing trend <strong>of</strong><br />
crime, reducing the number <strong>of</strong> criminal incidents<br />
to 2005 levels.<br />
OVERALL <strong>GTP</strong> 1.0 ACHIEVEMENTS<br />
+33.3%<br />
Pre-<strong>GTP</strong> 1.0 crime<br />
increased by 33%<br />
over 5 years<br />
2005<br />
2009<br />
-26.8%<br />
<strong>GTP</strong> 1.0 crime<br />
reduced by<br />
26.8% over 3 years<br />
2012<br />
1<br />
—<br />
Index crime refers to a set <strong>of</strong> criminal activities that occur with sufficient<br />
regularity so as to constitute an index <strong>of</strong> the overall criminal situation in the<br />
country. Thirteen different categories <strong>of</strong> crime have been identified as index<br />
crime markers.<br />
Under the CRI NKRA, a shift was made from<br />
sector-based policing to hotspot-based policing,<br />
which focuses policing efforts on specific areas<br />
<strong>of</strong> high criminal activity in order to create the<br />
greatest impact possible with limited resources.<br />
Finally, <strong>GTP</strong> 1.0 also saw initiatives undertaken<br />
to encourage greater community participation in<br />
policing activities.<br />
These programmes were supported by minor<br />
initiatives such as the PDRM Balai League Table,<br />
which measures the effectiveness <strong>of</strong> police<br />
stations by jurisdiction, as well as a customer<br />
service rating programme to that solicits greater<br />
feedback from the rakyat.<br />
The focus <strong>of</strong> the CRI NKRA has changed<br />
over the first three years <strong>of</strong> the <strong>GTP</strong>. In the first<br />
year, the NKRA focused on improving crime<br />
numbers by bringing in people and resources to<br />
tackle resource issues. In the second year, the<br />
NKRA focused on enhancing the capabilities<br />
<strong>of</strong> the policing services. The third year focused<br />
on institutionalising the changes. Some <strong>of</strong> the<br />
recent accolades received by the <strong>Malaysia</strong>n<br />
policing system include:<br />
Safest among 19 upper-middle income<br />
countries and 12th safest overall (World<br />
Justice Project)<br />
Ranked safest and most peaceful nation in<br />
Southeast Asia and 20th worldwide (Global<br />
Peace Index)<br />
As a result <strong>of</strong> these improvements, <strong>Malaysia</strong><br />
climbed 30 spots to rank 63rd in the World<br />
Economic Forum (WEF) Global Competitiveness<br />
Report in 2011 measuring the cost to business<br />
violence and crime. However, <strong>Malaysia</strong> slipped<br />
slightly to 69th spot in 2012 by the same index.<br />
56 Government transformation Programme—Annual Report 2012 Chapter Four 57<br />
Government transformation Programme—Annual Report 2012 Chapter Four