PDFlib TET PDF IFilter 4.0 Manual
PDFlib TET PDF IFilter 4.0 Manual
PDFlib TET PDF IFilter 4.0 Manual
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
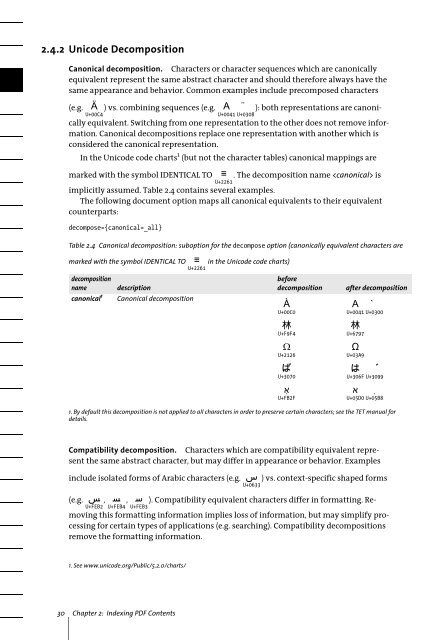
2.4.2 Unicode Decomposition<br />
Canonical decomposition. Characters or character sequences which are canonically<br />
equivalent represent the same abstract character and should therefore always have the<br />
same appearance and behavior. Common examples include precomposed characters<br />
<br />
U+00C4<br />
(e.g. ) vs. combining sequences (e.g. ): both representations are canonically<br />
equivalent. Switching from one representation to the other does not remove information.<br />
Canonical decompositions replace one representation with another which is<br />
considered the canonical representation.<br />
In the Unicode code charts 1 (but not the character tables) canonical mappings are<br />
marked with the symbol IDENTICAL TO<br />
. The decomposition name is<br />
implicitly assumed. Table 2.4 contains several examples.<br />
The following document option maps all canonical equivalents to their equivalent<br />
counterparts:<br />
decompose={canonical=_all}<br />
Table 2.4 Canonical decomposition: suboption for the decompose option (canonically equivalent characters are<br />
<br />
marked with the symbol IDENTICAL TO in the Unicode code charts)<br />
U+00C4 U+2261<br />
decomposition<br />
name description<br />
before<br />
decomposition<br />
canonical 1 Canonical decomposition<br />
<br />
U+00C0<br />
<br />
U+F9F4<br />
<br />
U+2126<br />
<br />
U+3070<br />
<br />
U+FB2F<br />
<br />
U+0041 U+0308<br />
<br />
U+00C4 U+2261<br />
after decomposition<br />
1. By default this decomposition is not applied to all characters in order to preserve certain characters; see the <strong>TET</strong> manual for<br />
details.<br />
<br />
U+0041 U+0300<br />
<br />
U+6797<br />
<br />
U+03A9<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
U+2126 U+306F U+2126 U+306F U+3099<br />
<br />
<br />
U+05D0 U+05B8<br />
Compatibility decomposition. Characters which are compatibility equivalent represent<br />
the same abstract character, but may differ in appearance or behavior. Examples<br />
include isolated forms of Arabic characters (e.g.<br />
<br />
) vs. context-specific shaped forms<br />
U+FEB2<br />
<br />
<br />
U+FEB4 U+FEB3<br />
(e.g. , , ). Compatibility equivalent characters differ in formatting. Removing<br />
this formatting information implies loss of information, but may simplify processing<br />
for certain types of applications (e.g. searching). Compatibility decompositions<br />
remove the formatting information.<br />
<br />
U+0633<br />
1. See www.unicode.org/Public/5.2.0/charts/<br />
30 Chapter 2: Indexing <strong>PDF</strong> Contents