Early Cretaceous Freshwater Fish Fauna in Kyushu, Japan
Early Cretaceous Freshwater Fish Fauna in Kyushu, Japan
Early Cretaceous Freshwater Fish Fauna in Kyushu, Japan
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Early</strong> <strong>Cretaceous</strong> <strong>Freshwater</strong> Fisli <strong>Fauna</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Kyushu</strong>, <strong>Japan</strong> 127<br />
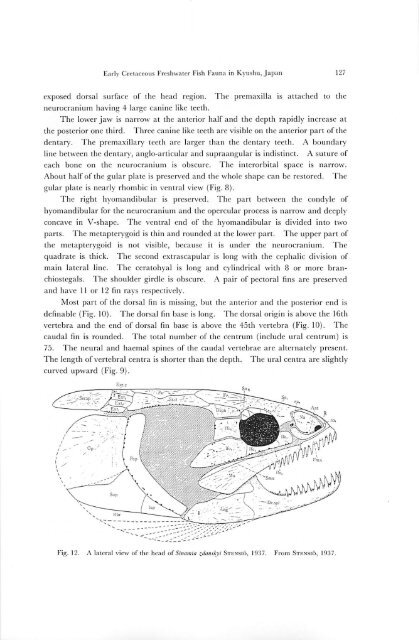
exposed dorsal surface of the head region. The premaxilla is attached to the<br />
neurocranium hav<strong>in</strong>g 4 large can<strong>in</strong>e like teeth.<br />
The lower jaw is narrow at the anterior half and the depth rapidly <strong>in</strong>crease at<br />
the posterior one third. Three can<strong>in</strong>e like teeth are visible on the anterior part of the<br />
dentary. The premaxillary teeth arc larger than the dentary teeth. A boundary<br />
l<strong>in</strong>e between the dentary, anglo-articular and supraangular is <strong>in</strong>dist<strong>in</strong>ct. A suture of<br />
each bone on the neurocranium is obscure. The <strong>in</strong>terorbital space is narrow.<br />
About half of the gular plate is preserved and the whole shape can be restored. The<br />
gular plate is nearly rhombic <strong>in</strong> ventral view (Fig. 8).<br />
The right hyomandibular is preserved. The part between the condyle of<br />
hyomandibular for the neurocranium and the opercular process is narrow and deeply<br />
concave <strong>in</strong> V-shapc. The ventral end of the hyomandibular is divided <strong>in</strong>to two<br />
parts. The metapterygoid is th<strong>in</strong> and rounded at the lower part. The upper part of<br />
the metapterygoid is not visible, because it is under the neurocranium. The<br />
quadrate is thick. The second extrascapular is long with the cephalic division of<br />
ma<strong>in</strong> lateral l<strong>in</strong>e. The ecratohyal is long and cyl<strong>in</strong>drical with 8 or more branchiostegals.<br />
The shoulder girdle is obscure. A pair of pectoral f<strong>in</strong>s are preserved<br />
and have 11 or 12 f<strong>in</strong> rays respectively.<br />
Most part of the dorsal f<strong>in</strong> is miss<strong>in</strong>g, but the anterior and the posterior end is<br />
def<strong>in</strong>able (Fig. 10). The dorsal f<strong>in</strong> base is long. The dorsal orig<strong>in</strong> is above the 16th<br />
vertebra and the end of dorsal f<strong>in</strong> base is above the 45th vertebra (Fig. 10). The<br />
caudal fm is rounded. The total number of the centrum (<strong>in</strong>clude ural centrum) is<br />
75. The neural and haemal sp<strong>in</strong>es of the caudal vertebrae are alternately present.<br />
The length of vertebral centra is shorter than the depth. The ural centra arc slightly<br />
curved upward (Fig. 9).<br />
Fig. 12. A lateral view of the head of S<strong>in</strong>amia zdanskyi Stensio, 1937. From Stensio, 1937.