Early Cretaceous Freshwater Fish Fauna in Kyushu, Japan
Early Cretaceous Freshwater Fish Fauna in Kyushu, Japan
Early Cretaceous Freshwater Fish Fauna in Kyushu, Japan
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Early</strong> <strong>Cretaceous</strong> <strong>Freshwater</strong> <strong>Fish</strong> <strong>Fauna</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Kyushu</strong>,<strong>Japan</strong> 159<br />
Description of the holotype.<br />
The body is moderate. The body depth is conta<strong>in</strong>ed 3.5 times <strong>in</strong> the standard<br />
length. The head length is conta<strong>in</strong>ed 3.8 times <strong>in</strong> the standard length. The snout<br />
is rounded. The outl<strong>in</strong>e of the head dorsal marg<strong>in</strong> is slightly convex. The outl<strong>in</strong>e<br />
from the occipital region to the dorsal orig<strong>in</strong> is almost straight (Fig. 36). The<br />
restored outl<strong>in</strong>e of the abdomen is almost straight and runs little under the lower end<br />
of each rib (Fig. 37). The median f<strong>in</strong>s are relatively posterior <strong>in</strong> position.<br />
The dorsal orig<strong>in</strong> is beh<strong>in</strong>d the anal orig<strong>in</strong> and vertical with the fifth anal f<strong>in</strong><br />
pterygiophore (about anterior one third of the anal base). The first dorsal f<strong>in</strong><br />
pterygiophore is above the first and second caudal vertebrae. The dorsal f<strong>in</strong> base is<br />
conta<strong>in</strong>ed 2.1 times <strong>in</strong> the anal f<strong>in</strong> base. The pectoral f<strong>in</strong> is moderate and reaches<br />
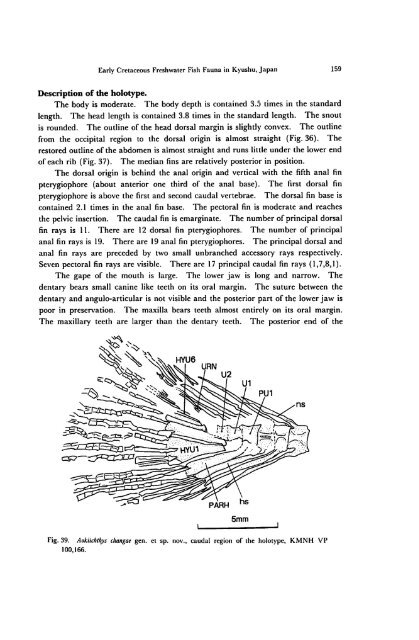
the pelvic <strong>in</strong>sertion. The caudal f<strong>in</strong> is emarg<strong>in</strong>ate. The number of pr<strong>in</strong>cipal dorsal<br />
f<strong>in</strong> rays is 11. There are 12 dorsal f<strong>in</strong> pterygiophores. The number of pr<strong>in</strong>cipal<br />
anal f<strong>in</strong> rays is 19. There are 19 anal f<strong>in</strong> pterygiophores. The pr<strong>in</strong>cipal dorsal and<br />
anal f<strong>in</strong> rays are preceded by two small unbranched accessory rays respectively.<br />
Seven pectoral f<strong>in</strong> rays are visible. There are 17 pr<strong>in</strong>cipal caudal f<strong>in</strong> rays (1,7,8,1).<br />
The gape of the mouth is large. The lower jaw is long and narrow. The<br />
dentary bears small can<strong>in</strong>e like teeth on its oral marg<strong>in</strong>. The suture between the<br />
dentary and angulo-articular is not visible and the posterior part of the lower jaw is<br />
poor <strong>in</strong> preservation. The maxilla bears teeth almost entirely on its oral marg<strong>in</strong>.<br />
The maxillary teeth are larger than the dentary teeth. The posterior end of the<br />
:3^<br />
GS3<br />
PARH<br />
5mm<br />
Fig. 39.<br />
100,166.<br />
Aokiichthys changae gen. et sp. nov., caudal region of the holotype, KMNH VP