ASD/LRFD Manual - American Wood Council
ASD/LRFD Manual - American Wood Council
ASD/LRFD Manual - American Wood Council
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
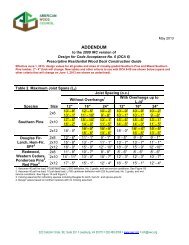
64 M9: WOOD STRUCTURAL PANELS<br />
Compression (F c A)<br />
Compression (Figure M9.2-3) capacities listed in<br />
Table M9.2-2 are based on testing according to the principles<br />
of ASTM D3501 Method B. Compressive properties<br />
are generally influenced by buckling; however, this effect<br />
was eliminated by restraining the edges of the specimens<br />
during testing. Compression capacity is given as F c A. F c is<br />
the reference compression stress of the material, and A is<br />
the area of the cross section. The units of F c A are pounds<br />
per foot of panel width.<br />
Shear Capacities<br />
Figure M9.2-3<br />
Structural Panel with<br />
Axial Compression<br />
Load in the Plane of<br />
the Panel<br />
Planar (Rolling) Shear (F s [Ib/Q])<br />
Shear-in-the-plane of the panel (rolling shear) capacities<br />
listed in Table M9.2-3 are based on testing according<br />
to the principles of ASTM D2718. Shear strength in the<br />
plane of the panel is the capacity to resist horizontal shear<br />
breaking loads when loads are applied or developed on opposite<br />
faces of the panel (Figure M9.2-4), as in flat panel<br />
bending. Planar shear capacity is given as F s [Ib/Q]. F s is<br />
the reference material stress, and Ib/Q is the panel crosssectional<br />
shear constant. The units of F s [Ib/Q] are pounds<br />
per foot of panel width.<br />
Figure M9.2-5 Through-the-Thickness<br />
Shear for <strong>Wood</strong><br />
Structural Panels<br />
Rigidity Through-the-Thickness (G v t v )<br />
Panel rigidities listed in Table M9.2-4 are based on<br />
testing according to the principles of ASTM D2719 Method<br />
C. Panel rigidity is the capacity to resist deformation<br />
under shear through the thickness stress (Figure M9.2-5).<br />
Rigidity is given as G v t v . G v is the reference modulus of<br />
rigidity, and t v is the effective panel thickness for shear.<br />
The units of G v t v are pounds per inch of panel depth (for<br />
vertical applications). Multiplication of G v t v by panel depth<br />
gives GA, used by designers for some applications.<br />
Through-the-Thickness Shear (F v t v )<br />
Through-the-thickness shear capacities listed in Table<br />
M9.2-4 are based on testing according to the principles of<br />
ASTM D2719 Method C. Allowable through the thickness<br />
shear is the capacity to resist horizontal shear breaking<br />
loads when loads are applied or developed on opposite<br />
edges of the panel (Figure M9.2-5), such as in an I-beam.<br />
Where additional support is not provided to prevent<br />
bucking, design capacities in Table M9.2-4 are limited to<br />
sections 2 ft or less in depth. Deeper sections may require<br />
additional reductions. F v is the reference stress of the<br />
material, and t v is the effective panel thickness for shear.<br />
The units of F v t v are pounds per inch of shear resisting<br />
panel length.<br />
Figure M9.2-4<br />
Planar (Rolling) Shear<br />
or Shear-in-the-Plane<br />
for <strong>Wood</strong> Structural<br />
Panels<br />
<strong>American</strong> <strong>Wood</strong> <strong>Council</strong>