Cleaner Technology Transfer to the Polish Textile ... - Miljøstyrelsen
Cleaner Technology Transfer to the Polish Textile ... - Miljøstyrelsen
Cleaner Technology Transfer to the Polish Textile ... - Miljøstyrelsen
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Table 1.<br />
Purity of different cot<strong>to</strong>n lots (Behnke, 1994).<br />
Brazil Brazil<br />
USA USA<br />
Content, mg/kg Greenhouse Assai Paraná Sao Paulo Peru Texas California<br />
Ca 400-500 3147 845 700 810 600<br />
Mg 300-400 1156 555 440 365 540<br />
66<br />
free grown cot<strong>to</strong>n is higher and very fluctuating compared <strong>to</strong> a greenhouse<br />
grown cot<strong>to</strong>n.<br />
The reason can be found in <strong>the</strong> different soils where <strong>the</strong> cot<strong>to</strong>n is grown combined<br />
with <strong>the</strong> use of fertilizers, pesticides and defoliants in <strong>the</strong> modern cot<strong>to</strong>n<br />
production. Large-scale farming and use of harvesters is absolutely necessary<br />
<strong>to</strong> meet a market characterized by insatiability (Behnke, 1994).<br />
Reactive dye-stuffs Reactive dye-stuffs establish, unlike all o<strong>the</strong>r dye-stuffs, a co-valent bond <strong>to</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> textile fibre, and offer great advantages regarding wash fastness of <strong>the</strong><br />
dyed textile. However, <strong>the</strong> reactive dye-stuffs react undesired with <strong>the</strong><br />
hydroxyl ions of <strong>the</strong> water and form a non-reactive hydrolyzate; a resulting<br />
utilization degree of 60-80% is <strong>the</strong>refore common. To reach <strong>the</strong> desired wash<br />
fastness of <strong>the</strong> dyed cot<strong>to</strong>n <strong>the</strong> remaining 20-40% dye-stuff hydrolysate have<br />
<strong>to</strong> be washed out during <strong>the</strong> rinse.<br />
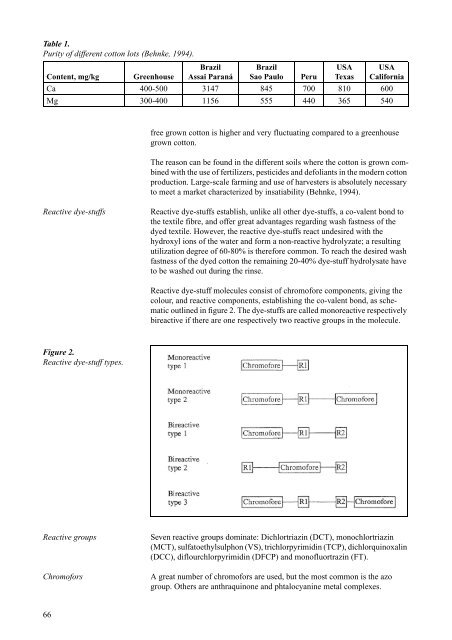
Figure 2.<br />
Reactive dye-stuff types.<br />
Reactive dye-stuff molecules consist of chromofore components, giving <strong>the</strong><br />
colour, and reactive components, establishing <strong>the</strong> co-valent bond, as schematic<br />
outlined in figure 2. The dye-stuffs are called monoreactive respectively<br />
bireactive if <strong>the</strong>re are one respectively two reactive groups in <strong>the</strong> molecule.<br />
Reactive groups Seven reactive groups dominate: Dichlortriazin (DCT), monochlortriazin<br />
(MCT), sulfa<strong>to</strong>ethylsulphon (VS), trichlorpyrimidin (TCP), dichlorquinoxalin<br />
(DCC), diflourchlorpyrimidin (DFCP) and monofluortrazin (FT).<br />
Chromofors A great number of chromofors are used, but <strong>the</strong> most common is <strong>the</strong> azo<br />
group. O<strong>the</strong>rs are anthraquinone and phtalocyanine metal complexes.