Cleaner Technology Transfer to the Polish Textile ... - Miljøstyrelsen
Cleaner Technology Transfer to the Polish Textile ... - Miljøstyrelsen
Cleaner Technology Transfer to the Polish Textile ... - Miljøstyrelsen
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
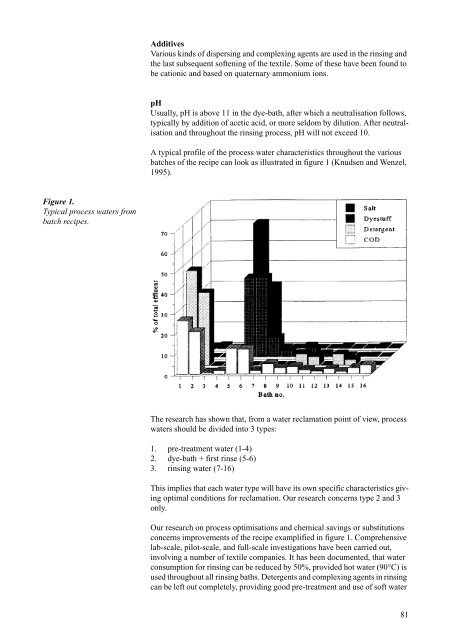
Figure 1.<br />
Typical process waters from<br />
batch recipes.<br />
Additives<br />
Various kinds of dispersing and complexing agents are used in <strong>the</strong> rinsing and<br />
<strong>the</strong> last subsequent softening of <strong>the</strong> textile. Some of <strong>the</strong>se have been found <strong>to</strong><br />
be cationic and based on quaternary ammonium ions.<br />
pH<br />
Usually, pH is above 11 in <strong>the</strong> dye-bath, after which a neutralisation follows,<br />
typically by addition of acetic acid, or more seldom by dilution. After neutralisation<br />
and throughout <strong>the</strong> rinsing process, pH will not exceed 10.<br />
A typical profile of <strong>the</strong> process water characteristics throughout <strong>the</strong> various<br />
batches of <strong>the</strong> recipe can look as illustrated in figure 1 (Knudsen and Wenzel,<br />
1995).<br />
The research has shown that, from a water reclamation point of view, process<br />
waters should be divided in<strong>to</strong> 3 types:<br />
1. pre-treatment water (1-4)<br />
2. dye-bath + first rinse (5-6)<br />
3. rinsing water (7-16)<br />
This implies that each water type will have its own specific characteristics giving<br />
optimal conditions for reclamation. Our research concerns type 2 and 3<br />
only.<br />
Our research on process optimisations and chemical savings or substitutions<br />
concerns improvements of <strong>the</strong> recipe examplified in figure 1. Comprehensive<br />
lab-scale, pilot-scale, and full-scale investigations have been carried out,<br />
involving a number of textile companies. It has been documented, that water<br />
consumption for rinsing can be reduced by 50%, provided hot water (90°C) is<br />
used throughout all rinsing baths. Detergents and complexing agents in rinsing<br />
can be left out completely, providing good pre-treatment and use of soft water<br />
81