Programmable Controllers: Theory and Implementation
Programmable Controllers: Theory and Implementation
Programmable Controllers: Theory and Implementation
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
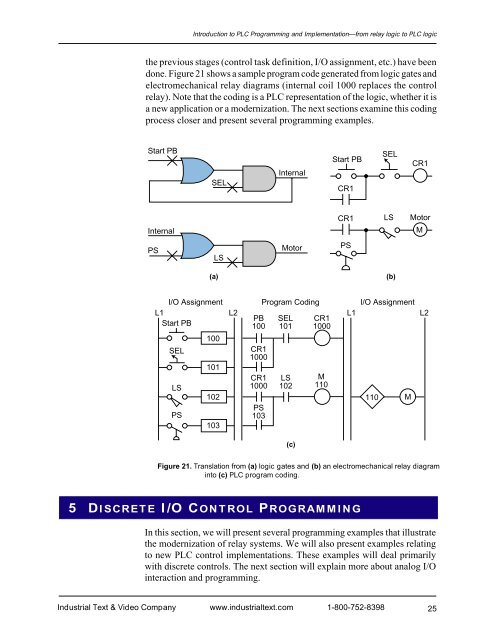
Introduction to PLC Programming <strong>and</strong> <strong>Implementation</strong>—from relay logic to PLC logicthe previous stages (control task definition, I/O assignment, etc.) have beendone. Figure 21 shows a sample program code generated from logic gates <strong>and</strong>electromechanical relay diagrams (internal coil 1000 replaces the controlrelay). Note that the coding is a PLC representation of the logic, whether it isa new application or a modernization. The next sections examine this codingprocess closer <strong>and</strong> present several programming examples.Start PBSELInternalStart PBCR1SELCR1InternalCR1LSMotorMPSLSMotorPS(a)(b)I/O Assignment Program Coding I/O AssignmentL1 L2L1 L2PB SEL CR1Start PB100 101 1000100SELCR11000101CR1 LS MLS1000 102 110102110 MPSPS103103(c)Figure 21. Translation from (a) logic gates <strong>and</strong> (b) an electromechanical relay diagraminto (c) PLC program coding.5 DISCRETE I/O CONTROL PROGRAMMINGIn this section, we will present several programming examples that illustratethe modernization of relay systems. We will also present examples relatingto new PLC control implementations. These examples will deal primarilywith discrete controls. The next section will explain more about analog I/Ointeraction <strong>and</strong> programming.Industrial Text & Video Company www.industrialtext.com 1-800-752-839825